Hypertonic Solutions for Better Pulmonary Function Testing
Hypertonic Solutions in PFT: Background and Objectives
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) has been a cornerstone of respiratory medicine for decades, providing crucial insights into lung health and function. However, traditional PFT methods have limitations in sensitivity and specificity, particularly for early-stage lung diseases. The exploration of hypertonic solutions in PFT represents a significant advancement in this field, aiming to enhance the accuracy and diagnostic capabilities of these tests.
The concept of using hypertonic solutions in PFT emerged from the understanding that airway surface liquid (ASL) plays a vital role in maintaining proper lung function. Hypertonic solutions, typically containing high concentrations of salt or other osmotically active substances, can alter the osmotic gradient across the airway epithelium, potentially revealing subtle abnormalities in lung function that might be missed by conventional testing methods.
The primary objective of research into hypertonic solutions for PFT is to develop more sensitive and specific diagnostic tools for a range of respiratory conditions. This includes early detection of diseases such as cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma. By inducing temporary changes in airway physiology, these solutions may unmask underlying abnormalities in mucociliary clearance, airway reactivity, and small airway function.
Historically, the use of hypertonic saline in respiratory medicine dates back to the mid-20th century, with initial applications in sputum induction and airway clearance therapies. The adaptation of this concept to PFT represents a natural evolution, driven by the need for more precise diagnostic methods in an era of personalized medicine and early intervention strategies.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by advancements in both the composition of hypertonic solutions and the methods used to deliver and measure their effects. From simple nebulized saline solutions to more complex formulations incorporating osmolytes and surfactants, researchers have continually refined the approach to maximize diagnostic yield while minimizing patient discomfort and risk.
Current research goals in this area include optimizing the concentration and composition of hypertonic solutions for different patient populations and specific respiratory conditions. There is also a focus on developing standardized protocols for administration and interpretation of results, ensuring reproducibility and clinical relevance across different healthcare settings.
Furthermore, the integration of hypertonic solution-based PFT with other emerging technologies, such as advanced imaging techniques and biomarker analysis, holds promise for creating comprehensive diagnostic platforms. These integrated approaches aim to provide a more holistic view of lung health, potentially revolutionizing how respiratory diseases are diagnosed and monitored.
As the field progresses, researchers are also exploring the potential therapeutic applications of hypertonic solutions beyond their diagnostic use in PFT. This dual-purpose approach could lead to novel treatment modalities that not only diagnose but also intervene in the early stages of respiratory diseases, potentially altering disease trajectories and improving long-term outcomes for patients.
Market Analysis for Advanced PFT Methods
The market for advanced pulmonary function testing (PFT) methods, particularly those involving hypertonic solutions, is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing prevalence of respiratory diseases and the need for more accurate diagnostic tools. The global PFT market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 4.5% from 2021 to 2028, with the hypertonic solution segment showing particularly strong potential.
Hypertonic solutions in PFT offer several advantages over traditional methods, including improved sensitivity in detecting early-stage lung diseases and enhanced ability to differentiate between various respiratory conditions. This has led to a growing demand from healthcare providers seeking to improve diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. Hospitals and specialized respiratory clinics are the primary adopters of these advanced PFT methods, with a notable increase in adoption rates among smaller healthcare facilities as well.
The market for hypertonic solution-based PFT is characterized by regional variations. North America currently holds the largest market share, attributed to its well-established healthcare infrastructure and high awareness of advanced diagnostic techniques. Europe follows closely, with countries like Germany and the UK leading in adoption rates. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising respiratory disease burden in countries such as China and India.
Key factors driving market growth include the aging population, increasing air pollution levels, and the rising incidence of chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of respiratory health, further boosting demand for advanced PFT methods. The market is also benefiting from ongoing technological advancements, such as the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in PFT analysis, which are enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of these tests.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces certain challenges. These include the high cost of advanced PFT equipment and the need for specialized training to conduct and interpret these tests. Reimbursement issues in some regions also pose a barrier to widespread adoption. However, these challenges are gradually being addressed through initiatives aimed at reducing costs and improving accessibility.
Looking ahead, the market for hypertonic solution-based PFT is poised for continued growth. Emerging trends include the development of portable and home-based PFT devices, which could significantly expand the market reach. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining hypertonic solution tests with other diagnostic methods to create more comprehensive respiratory assessment protocols. As research in this field progresses, we can expect to see new applications and refinements of hypertonic solution-based PFT, further driving market expansion and improving respiratory care worldwide.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Solution-based PFT
Hypertonic solution-based pulmonary function testing (PFT) has emerged as a promising technique for assessing respiratory health. However, several challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the standardization of hypertonic solutions used in PFT. The concentration and composition of these solutions can significantly impact test results, making it difficult to compare data across different clinical settings or research studies.
Another challenge lies in the potential for bronchial hyperresponsiveness in some patients when exposed to hypertonic solutions. This can lead to discomfort, coughing, or even bronchospasm, which may affect the accuracy of the test results or limit its applicability to certain patient populations. Developing methods to mitigate these adverse reactions while maintaining the diagnostic value of the test remains a significant hurdle.
The reproducibility and reliability of hypertonic solution-based PFT also present ongoing challenges. Factors such as the method of solution delivery, inhalation technique, and timing of measurements can introduce variability in test results. Establishing standardized protocols and quality control measures is crucial for ensuring consistent and comparable outcomes across different testing environments.
Furthermore, the interpretation of results from hypertonic solution-based PFT requires careful consideration. The relationship between changes in lung function parameters and the underlying physiological mechanisms is not always straightforward. Developing robust algorithms and reference values for different patient populations and disease states is essential for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of respiratory conditions.
The cost and complexity of implementing hypertonic solution-based PFT in clinical practice also pose challenges. Specialized equipment, trained personnel, and additional time requirements may limit its adoption, particularly in resource-constrained settings. Simplifying the testing procedure and developing more cost-effective solutions could help overcome these barriers.
Lastly, the long-term effects of repeated exposure to hypertonic solutions during PFT are not yet fully understood. While the procedure is generally considered safe, concerns about potential airway irritation or other cumulative effects need to be addressed through longitudinal studies and careful monitoring of patients undergoing regular testing.
Addressing these challenges will be crucial for advancing hypertonic solution-based PFT and realizing its full potential as a valuable tool in respiratory medicine. Collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, and industry partners will be essential in overcoming these obstacles and improving the overall effectiveness and accessibility of this promising diagnostic technique.
Existing Hypertonic Solution Formulations for PFT
01 Hypertonic saline solutions for improving pulmonary function
Hypertonic saline solutions are used to improve pulmonary function in patients with respiratory conditions. These solutions can help clear mucus, reduce inflammation, and improve lung function. The higher salt concentration draws water into the airways, thinning mucus and making it easier to expel.- Hypertonic saline solutions for improving pulmonary function: Hypertonic saline solutions are used to improve pulmonary function in patients with respiratory conditions. These solutions can help clear mucus, reduce inflammation, and improve lung function. The higher salt concentration in hypertonic solutions draws water into the airways, thinning mucus and making it easier to expel.
- Nebulization of hypertonic solutions for respiratory therapy: Nebulization is a common method for delivering hypertonic solutions to the lungs. This technique allows for the efficient distribution of the solution throughout the respiratory system, maximizing its therapeutic effects. Specialized nebulizers may be used to optimize the delivery of hypertonic solutions for various pulmonary conditions.
- Combination therapies using hypertonic solutions: Hypertonic solutions are often used in combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance their effectiveness in treating pulmonary disorders. These combinations may include bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs, or antibiotics, which work synergistically with the hypertonic solution to improve overall lung function and patient outcomes.
- Monitoring and assessment of pulmonary function with hypertonic solutions: Various methods and devices are used to monitor and assess pulmonary function in patients treated with hypertonic solutions. These may include spirometry, lung clearance index measurements, or imaging techniques to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and guide therapy adjustments.
- Formulation and delivery optimization of hypertonic solutions: Research focuses on optimizing the formulation and delivery of hypertonic solutions to maximize their beneficial effects on pulmonary function. This includes studying different concentrations, additives, and delivery methods to improve efficacy and patient comfort while minimizing potential side effects.
02 Nebulization of hypertonic solutions for respiratory therapy
Nebulization is a common method for delivering hypertonic solutions to the lungs. This technique allows for the efficient distribution of the solution throughout the respiratory system, enhancing its therapeutic effects. Specialized nebulizers may be used to optimize the delivery of hypertonic solutions for various pulmonary conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination therapies using hypertonic solutions
Hypertonic solutions are often used in combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance pulmonary function. These combinations may include bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs, or mucolytics. The synergistic effects of these combinations can lead to improved outcomes in treating various respiratory disorders.Expand Specific Solutions04 Diagnostic applications of hypertonic solutions in pulmonary function testing
Hypertonic solutions are utilized in diagnostic procedures to assess pulmonary function. These solutions can be used to induce bronchial hyperresponsiveness or to measure airway reactivity. Such tests help in the diagnosis and monitoring of conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel formulations of hypertonic solutions for enhanced pulmonary effects
Research is ongoing to develop new formulations of hypertonic solutions with improved efficacy and tolerability for pulmonary applications. These may include modified salt compositions, pH-adjusted solutions, or the addition of other osmotic agents to enhance the therapeutic effects on lung function while minimizing side effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Respiratory Diagnostics Industry
The research on hypertonic solutions for better pulmonary function testing is in a developing stage, with a growing market driven by increasing respiratory disorders. The technology's maturity varies among key players. Companies like Koninklijke Philips NV and Siemens Healthineers AG are leveraging their established medical device expertise to advance this field. Emerging players such as Windtree Therapeutics, Inc. and Bellerophon Therapeutics, Inc. are focusing on innovative solutions. Academic institutions like Tohoku University and The Johns Hopkins University are contributing significant research. Pharmaceutical giants including Novartis AG and AstraZeneca AB are exploring potential drug-device combinations, indicating a multifaceted approach to improving pulmonary function testing techniques.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Windtree Therapeutics, Inc.
Innovative Approaches in Hypertonic Solution Design
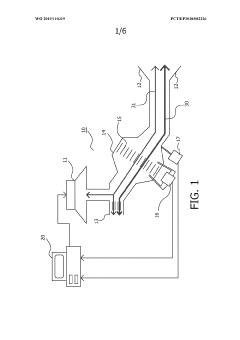
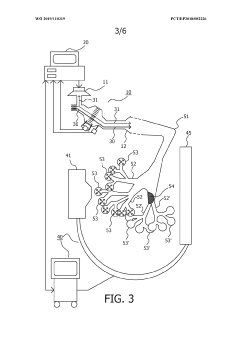
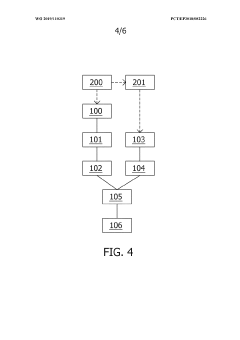
- Administration of a synthetic pulmonary surfactant, such as one comprising phospholipids and an SP-B polypeptide, combined with an osmotically active agent like sodium chloride, to reduce mucus adhesivity and enhance fluidity, thereby improving mucus clearance and airway patency.
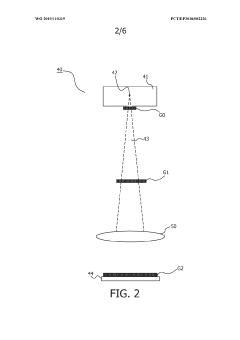
- A device combining Forced Oscillatory Technique (FOT) with dark field x-ray imaging (DAX) to generate respiratory mechanics data and high-resolution images of the alveoli, allowing for precise localization of lung issues by modulating oscillatory and image acquisition frequencies to match alveolic states, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Hypertonic PFT
The safety and efficacy of hypertonic solutions in pulmonary function testing (PFT) are critical considerations that require careful evaluation. Hypertonic solutions, typically containing high concentrations of saline or other osmotic agents, have shown promise in improving the diagnostic accuracy of PFTs, particularly in conditions such as cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. However, their use necessitates a thorough assessment of potential risks and benefits.
Safety considerations for hypertonic PFT primarily focus on the potential for airway irritation and bronchoconstriction. The inhalation of hypertonic solutions may cause temporary discomfort, coughing, or wheezing in some patients. To mitigate these risks, protocols often include pre-treatment with bronchodilators and careful monitoring during the procedure. Additionally, the concentration and administration method of the hypertonic solution must be carefully calibrated to balance efficacy with patient tolerability.
Efficacy assessments of hypertonic PFT have demonstrated several advantages over traditional methods. The increased osmolarity of the inhaled solution can stimulate mucus production and enhance airway clearance, potentially revealing underlying respiratory issues that may be missed with isotonic solutions. Studies have shown improved sensitivity in detecting early-stage lung disease and more accurate quantification of lung function parameters.
Long-term safety data on repeated exposure to hypertonic solutions during PFTs are still being gathered. While short-term use appears to be well-tolerated in most patients, the cumulative effects of frequent testing with hypertonic agents require further investigation. Researchers are exploring the optimal frequency of hypertonic PFTs and any potential impact on airway remodeling or inflammation over time.
The efficacy of hypertonic PFT may vary depending on the specific respiratory condition being evaluated. For instance, in cystic fibrosis patients, hypertonic saline has shown particular promise in improving mucociliary clearance and lung function measurements. However, its effectiveness in other respiratory disorders may be less pronounced, necessitating condition-specific protocols and interpretation guidelines.
Standardization of hypertonic PFT procedures is an ongoing challenge in the field. Variations in solution concentrations, inhalation times, and measurement techniques can affect test results and comparability across different clinical settings. Efforts are underway to establish consensus guidelines for hypertonic PFT administration to ensure consistent and reliable outcomes.
As research in this area progresses, the integration of hypertonic PFT into routine clinical practice requires careful consideration of patient selection criteria, staff training, and quality control measures. The potential benefits of enhanced diagnostic accuracy must be weighed against the additional time, resources, and patient preparation required for these specialized tests.
Patient Comfort and Compliance in Hypertonic PFT
Patient comfort and compliance are crucial factors in the success of pulmonary function testing (PFT) using hypertonic solutions. The use of hypertonic saline or other osmotic agents can induce coughing and bronchospasm, which may lead to discomfort and potentially affect the accuracy of test results. To address these challenges, researchers and clinicians have been exploring various strategies to enhance patient experience and adherence to hypertonic PFT protocols.
One approach involves optimizing the concentration and delivery method of hypertonic solutions. Studies have shown that gradually increasing the concentration of saline from isotonic to hypertonic levels can help patients acclimate to the solution, reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions. Additionally, the use of nebulizers with specific particle sizes and flow rates has been investigated to improve the deposition of hypertonic solutions in the airways while minimizing irritation.
Pre-medication protocols have also been developed to mitigate potential side effects. The administration of bronchodilators, such as short-acting beta-agonists, prior to hypertonic PFT has been found to reduce the incidence of bronchospasm and improve patient tolerance. Some centers have incorporated antihistamines or leukotriene receptor antagonists into their pre-test regimens, particularly for patients with a history of reactive airways.
Patient education and preparation play a significant role in improving comfort and compliance. Comprehensive pre-test counseling, including detailed explanations of the procedure, expected sensations, and coping strategies, has been shown to reduce anxiety and improve test completion rates. Visual aids, demonstration videos, and practice sessions with saline nebulization have been employed to familiarize patients with the testing process and equipment.
Environmental factors within the testing facility have also been considered. Temperature and humidity control in the testing room can help minimize respiratory irritation. Some centers have implemented relaxation techniques, such as guided breathing exercises or music therapy, to create a more calming atmosphere during the procedure.
Technological advancements have contributed to improving the patient experience. The development of more efficient nebulizer systems with shorter administration times has reduced the overall duration of the test, potentially decreasing patient fatigue and discomfort. Real-time monitoring of lung function parameters during hypertonic solution administration allows for personalized adjustments to the protocol, ensuring optimal challenge while minimizing unnecessary discomfort.
Ongoing research is focused on identifying biomarkers or predictive factors that can help tailor hypertonic PFT protocols to individual patients. This personalized approach aims to optimize the balance between diagnostic efficacy and patient comfort, potentially leading to improved compliance and more reliable test results across diverse patient populations.