Hypertonic Formulations: A Guide for Pharmaceutical Innovation
Hypertonic Formulations Background and Objectives
Hypertonic formulations have emerged as a significant area of interest in pharmaceutical innovation, offering unique advantages in drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy. These formulations, characterized by their higher solute concentration compared to physiological fluids, have a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. Initially utilized in parenteral nutrition and rehydration therapies, hypertonic formulations have since evolved to encompass a wide range of applications in modern medicine.
The development of hypertonic formulations has been driven by the need for more effective drug delivery systems, particularly for challenging therapeutic targets. Over the years, researchers have explored various approaches to harness the potential of hypertonicity in pharmaceutical preparations. This has led to significant advancements in areas such as ocular drug delivery, wound healing, and the treatment of edema-related conditions.
One of the key objectives in the field of hypertonic formulations is to enhance drug bioavailability and tissue penetration. By creating an osmotic gradient, these formulations can facilitate the movement of active pharmaceutical ingredients across biological barriers, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes. This mechanism has shown particular promise in topical and transdermal drug delivery systems, where traditional formulations often struggle to achieve adequate penetration.
Another important goal is to develop hypertonic formulations that can provide sustained drug release profiles. This aspect is crucial for reducing dosing frequency and improving patient compliance, especially in the management of chronic conditions. Researchers are exploring various excipients and technologies to create hypertonic matrices that can control the release of active ingredients over extended periods.
The pharmaceutical industry is also focusing on expanding the application of hypertonic formulations to new therapeutic areas. There is growing interest in utilizing these formulations for the delivery of biologics, gene therapies, and other complex molecules. This expansion requires overcoming challenges related to stability, compatibility, and manufacturing processes specific to hypertonic environments.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing emphasis on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of hypertonic formulations on cellular and tissue levels. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing formulation design and predicting potential side effects. Advanced imaging techniques and in vitro models are being employed to gain deeper insights into these mechanisms, paving the way for more targeted and efficient hypertonic formulations.
Market Analysis for Hypertonic Pharmaceutical Products
The market for hypertonic pharmaceutical products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing prevalence of conditions requiring osmotic therapy and the rising demand for innovative drug delivery systems. Hypertonic formulations, characterized by their higher solute concentration compared to physiological fluids, have found applications across various therapeutic areas, including ophthalmology, pulmonology, and wound care.
In the ophthalmology sector, hypertonic eye drops have gained traction for treating dry eye syndrome and corneal edema. The global dry eye syndrome market, a key driver for hypertonic ophthalmic solutions, is projected to expand substantially due to the aging population and increased screen time. Hypertonic saline solutions for inhalation have shown promise in managing cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis, contributing to the growth of the respiratory care market.
The wound care segment has also witnessed increased adoption of hypertonic dressings and gels, particularly for chronic wound management. These products leverage osmotic pressure to promote wound healing and reduce bacterial load, addressing the growing need for advanced wound care solutions in an aging population with rising incidence of chronic wounds and diabetic ulcers.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for hypertonic pharmaceutical products, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present lucrative growth opportunities, driven by improving healthcare access and rising awareness of advanced treatment options.
Key market trends include the development of combination therapies incorporating hypertonic formulations, such as hypertonic saline with bronchodilators for respiratory conditions. There is also a growing focus on patient-friendly delivery systems, including pre-filled nebulizers and easy-to-use eye drop dispensers, to improve compliance and treatment outcomes.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative startups. Major players are investing in research and development to expand their product portfolios and gain a competitive edge. Strategic collaborations and licensing agreements are becoming increasingly common as companies seek to leverage complementary expertise and accelerate product development.
Despite the positive growth outlook, challenges remain. These include the need for robust clinical evidence to support the efficacy of hypertonic formulations in new therapeutic areas and potential regulatory hurdles in certain markets. Additionally, pricing pressures and reimbursement issues may impact market growth, particularly in cost-sensitive regions.
Current Challenges in Hypertonic Formulation Development
The development of hypertonic formulations presents several significant challenges in the pharmaceutical industry. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining the stability of the formulation over extended periods. The high solute concentration in hypertonic solutions can lead to increased chemical reactivity, potentially causing degradation of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or excipients. This instability may result in reduced efficacy or even the formation of harmful byproducts.
Another critical challenge is the potential for tissue irritation and discomfort upon administration. Hypertonic formulations can cause osmotic stress on cells and tissues, leading to pain, inflammation, or damage at the site of application. This is particularly problematic for parenteral formulations and ophthalmic preparations, where patient comfort and compliance are crucial factors.
The viscosity of hypertonic formulations also poses difficulties in manufacturing and administration. High solute concentrations can significantly increase the solution's viscosity, complicating processes such as filtration, filling, and dispensing. For injectable formulations, high viscosity may necessitate larger gauge needles, potentially causing more pain during administration.
Osmotic effects present another set of challenges. Rapid water movement due to osmotic gradients can lead to localized dehydration or swelling of tissues, depending on the route of administration. This can affect drug absorption kinetics and bioavailability, potentially altering the intended therapeutic effect.
Formulation scientists must also grapple with the limited solubility of some APIs in hypertonic environments. The high concentration of solutes can reduce the solubility of certain drugs, leading to precipitation or crystallization. This not only affects the stability of the formulation but can also impact its safety and efficacy.
The selection of appropriate excipients for hypertonic formulations is another complex task. Excipients must be carefully chosen to maintain stability, enhance solubility, and mitigate potential adverse effects of hypertonicity. However, the range of suitable excipients may be limited due to regulatory constraints and compatibility issues with the hypertonic environment.
Lastly, scale-up and manufacturing of hypertonic formulations present unique challenges. Ensuring homogeneity and consistent osmolality across large batches can be difficult, requiring specialized equipment and processes. Additionally, the high solute concentrations may accelerate equipment wear and corrosion, necessitating more frequent maintenance and potentially increasing production costs.
Existing Hypertonic Formulation Strategies
01 Hypertonic solutions for medical applications
Hypertonic formulations are used in various medical applications, including wound healing, osmotic therapy for cerebral edema, and treatment of dehydration. These solutions have a higher solute concentration than body fluids, creating an osmotic gradient that can draw fluid out of tissues or promote fluid absorption.- Hypertonic solutions for medical applications: Hypertonic formulations are used in various medical applications, including wound healing, reducing edema, and treating dehydration. These solutions have a higher solute concentration than body fluids, creating an osmotic gradient that draws water out of tissues. This property is utilized in treatments for conditions such as cerebral edema and in perioperative fluid management.
- Hypertonic formulations in ophthalmic treatments: Hypertonic solutions are employed in ophthalmic treatments, particularly for managing corneal edema and reducing intraocular pressure. These formulations typically contain high concentrations of osmotically active agents like glycerin or sodium chloride. They work by drawing excess fluid from the cornea or anterior chamber, improving visual acuity and relieving ocular discomfort.
- Hypertonic formulations for respiratory therapy: Hypertonic saline solutions are used in respiratory therapy, especially for patients with cystic fibrosis and other respiratory conditions. These formulations help to thin and mobilize mucus, improve airway hydration, and enhance mucociliary clearance. The increased osmolarity of the solution draws water into the airway surface liquid, facilitating easier expectoration of mucus.
- Hypertonic formulations in cell culture and preservation: Hypertonic solutions play a crucial role in cell culture techniques and preservation of biological materials. These formulations are used to create osmotic stress in cells for various research purposes, including studies on cell volume regulation and osmotic adaptation. In cryopreservation, hypertonic solutions help to dehydrate cells before freezing, reducing intracellular ice formation and improving cell viability upon thawing.
- Hypertonic formulations in food and beverage industry: Hypertonic solutions are utilized in the food and beverage industry for various purposes. These include creating preserved foods through osmotic dehydration, developing sports drinks for rapid rehydration, and formulating functional beverages with specific osmotic properties. The high solute concentration in these formulations can help in extending shelf life, enhancing flavor, and providing specific nutritional benefits.
02 Hypertonic formulations in ophthalmic treatments
Hypertonic solutions are utilized in ophthalmic treatments, particularly for conditions like dry eye syndrome and corneal edema. These formulations help reduce excess fluid in the cornea and conjunctiva, alleviating symptoms and improving ocular surface health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hypertonic solutions for respiratory therapy
Hypertonic saline solutions are employed in respiratory therapy, especially for patients with cystic fibrosis and other respiratory conditions. These formulations help improve mucociliary clearance, reduce airway inflammation, and enhance lung function.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypertonic formulations in cell culture and preservation
Hypertonic solutions play a crucial role in cell culture techniques and preservation of biological samples. These formulations help maintain cell viability, control osmotic pressure, and protect cells during cryopreservation processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hypertonic formulations for sports and exercise recovery
Hypertonic solutions are used in sports nutrition and exercise recovery. These formulations help replenish electrolytes, promote rapid rehydration, and enhance post-exercise recovery by facilitating fluid absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Hypertonic Pharmaceutical Industry
The competitive landscape for hypertonic formulations in pharmaceutical innovation is characterized by a mature market with significant growth potential. Major players like Eli Lilly & Co., Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., and Novartis AG are investing heavily in research and development to advance this technology. The market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for novel drug delivery systems and improved therapeutic outcomes. The technology maturity varies among companies, with established pharmaceutical giants leading in innovation, while smaller firms like Intarcia Therapeutics, Inc. and QuantX Biosciences US, Inc. are emerging with specialized solutions. The global market size for hypertonic formulations is expanding, fueled by applications in various therapeutic areas and the need for enhanced drug efficacy and patient compliance.
Eli Lilly & Co.
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Innovative Approaches in Hypertonic Drug Delivery
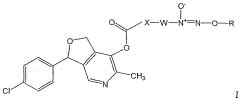
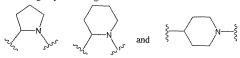
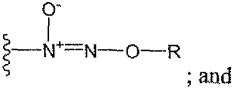
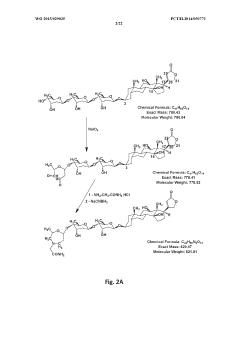
- Development of nitric oxide linked cicletanine and its derivatives, including various pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates, for controlled and sustained delivery, which can be administered to treat the mentioned conditions by forming quaternary ammonium salts or acid addition salts, and their use in combination with other pharmacologically active compounds.
- Development of digoxin and digitoxin derivatives that are selective inhibitors of the α2 isoform of Na,K-ATPase, with modifications such as perhydro-1,4-oxazepine derivatives, which show increased selectivity and reduced toxicity, allowing for topical application to reduce intra-ocular pressure and potentially serve as cardiotonic agents.
Regulatory Considerations for Hypertonic Pharmaceuticals
The regulatory landscape for hypertonic pharmaceuticals is complex and multifaceted, requiring careful navigation by pharmaceutical companies to ensure compliance and market success. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe, have established specific guidelines for the development, manufacturing, and marketing of hypertonic formulations.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the classification of hypertonic pharmaceuticals. Depending on their intended use and mechanism of action, these formulations may be categorized as drugs, medical devices, or combination products. This classification significantly impacts the regulatory pathway and requirements for approval.
Safety and efficacy are paramount concerns for regulatory agencies when evaluating hypertonic formulations. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data from preclinical and clinical studies demonstrating the product's safety profile and therapeutic efficacy. This includes assessing potential adverse effects related to the hypertonic nature of the formulation, such as tissue irritation or electrolyte imbalances.
Quality control and manufacturing processes are subject to stringent regulatory scrutiny. Pharmaceutical companies must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement robust quality management systems to ensure consistent production of hypertonic formulations that meet predetermined specifications.
Labeling and packaging requirements for hypertonic pharmaceuticals are particularly critical. Regulatory agencies mandate clear and accurate labeling that includes information on osmolality, electrolyte composition, and appropriate usage instructions. This is essential for preventing medication errors and ensuring patient safety.
Stability testing is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for hypertonic formulations. Manufacturers must demonstrate the product's ability to maintain its physicochemical properties, sterility, and therapeutic efficacy throughout its intended shelf life under various environmental conditions.
Post-market surveillance and pharmacovigilance are ongoing regulatory requirements for hypertonic pharmaceuticals. Companies must have systems in place to monitor and report adverse events, conduct post-approval studies if required, and update product information based on real-world data.
Regulatory considerations also extend to the global market, with different countries and regions having varying requirements for hypertonic formulations. Pharmaceutical companies must navigate these differences and may need to adapt their regulatory strategies to meet local standards and expectations.
As the field of hypertonic pharmaceuticals continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt. Companies must stay informed about emerging regulatory trends and be prepared to engage with regulatory agencies in scientific discussions to address novel aspects of hypertonic formulations.
Safety and Efficacy Evaluation of Hypertonic Formulations
The safety and efficacy evaluation of hypertonic formulations is a critical aspect of pharmaceutical development. These formulations, characterized by their higher osmotic pressure compared to physiological fluids, require thorough assessment to ensure their therapeutic benefits outweigh potential risks.
Safety evaluations for hypertonic formulations focus on both local and systemic effects. Local effects may include tissue irritation, pain at the administration site, or damage to blood vessels. Systemic effects can range from electrolyte imbalances to more severe complications such as hypernatremia or fluid shifts. Preclinical studies in animal models are essential to identify potential toxicities and determine safe dosage ranges.
Clinical trials for hypertonic formulations typically follow a phased approach. Phase I studies assess safety and tolerability in healthy volunteers, while Phase II and III trials evaluate efficacy and further safety in patient populations. These trials often include careful monitoring of vital signs, electrolyte levels, and fluid balance to detect any adverse effects promptly.
Efficacy evaluation of hypertonic formulations depends on their intended therapeutic use. For instance, hypertonic saline solutions used in the treatment of cerebral edema are assessed for their ability to reduce intracranial pressure. In contrast, hypertonic formulations for wound care are evaluated based on their capacity to promote healing and prevent infection.
Long-term safety monitoring is crucial for hypertonic formulations, particularly those intended for chronic use. Post-marketing surveillance helps identify rare adverse events that may not have been detected during clinical trials. This ongoing evaluation process ensures the continued safety and efficacy of the product in real-world settings.
Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, provide guidelines for the safety and efficacy evaluation of hypertonic formulations. These guidelines often require specific studies to address the unique challenges posed by these formulations, including osmotic effects and potential impacts on fluid and electrolyte balance.
In conclusion, the safety and efficacy evaluation of hypertonic formulations is a complex process that requires a multifaceted approach. It involves rigorous preclinical and clinical testing, careful consideration of both local and systemic effects, and ongoing monitoring throughout the product lifecycle. This comprehensive evaluation process is essential to ensure that hypertonic formulations provide meaningful therapeutic benefits while maintaining an acceptable safety profile.