Multi-layer forming fabric with stitching yarn pairs integrated into papermaking surface
a technology of papermaking surface and forming fabric, applied in the field of papermaking, can solve the problems of short service life of the fabric, less suitable as forming fabric, particularly problematic wire marking, etc., and achieve the effect of little distortion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027]The present invention will be described more particularly hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings. The invention is not intended to be to the illustrated embodiments; rather, these embodiments are intended to fully and completely disclose the invention to those skilled in this art.
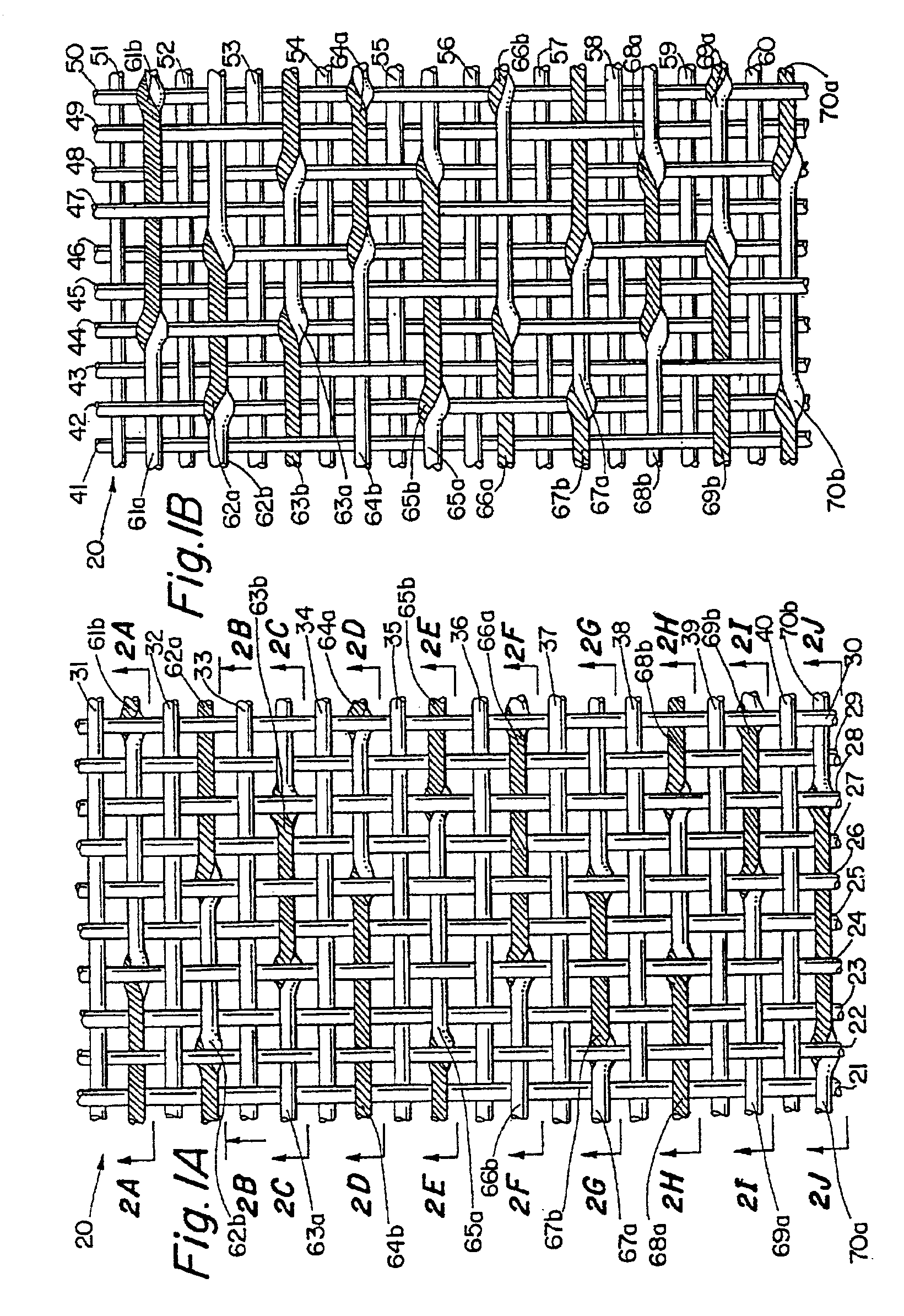
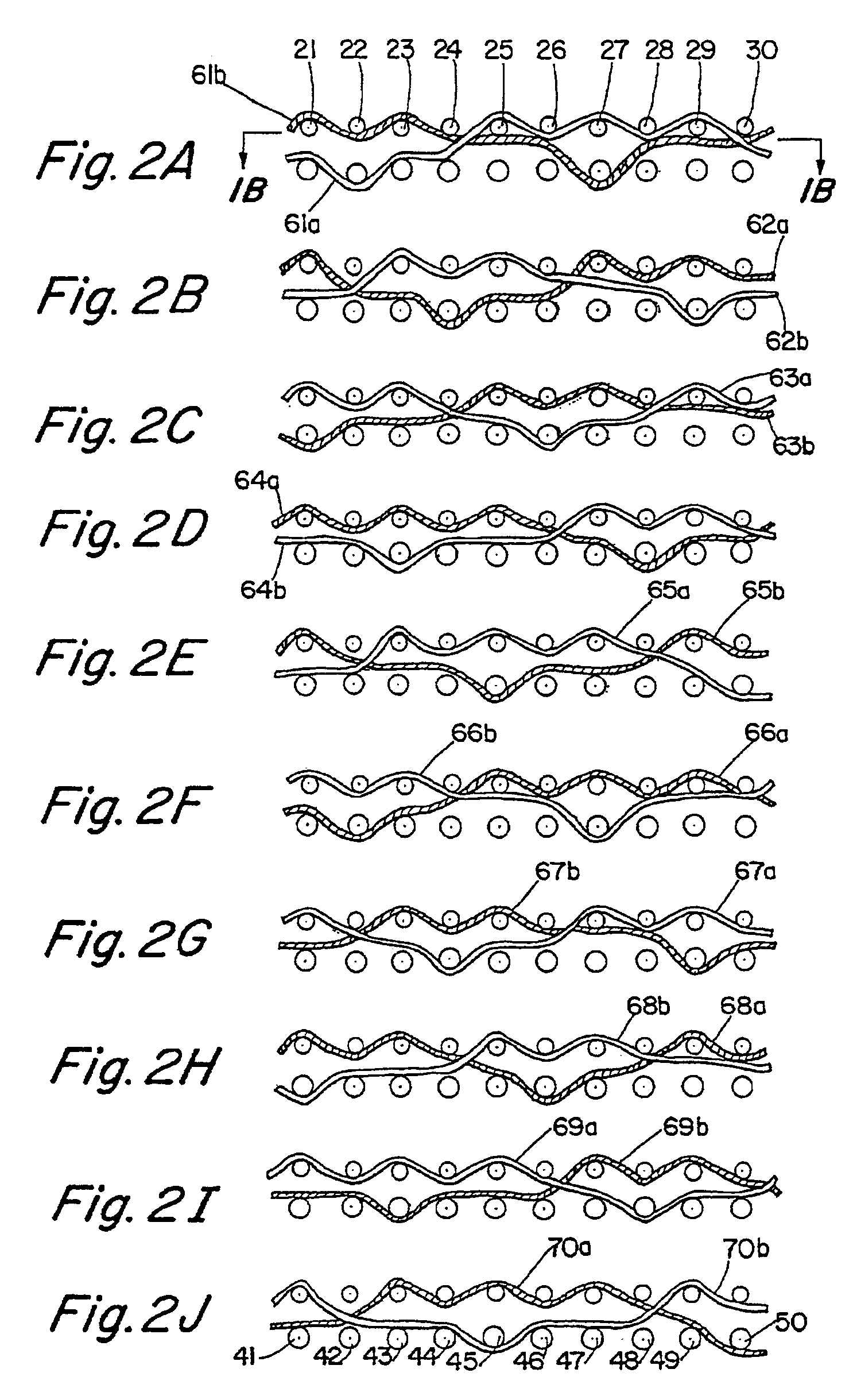
[0028]A 20 harness multi-layer forming fabric, generally designated at 20, is illustrated in FIGS. 1A and 1B, in which a single repeat unit of the fabric is shown. As seen in FIG. 1A, the repeat unit of the fabric 20 includes a top layer having ten top MD yarns 21-30 and ten top CMD yarns 31-40. These are interwoven such that each top CMD yarn passes over and beneath top MD yarns in an alternating fashion, with each top CMD yarn passing over and under the same top MD yarns. For example, top CMD yarn 31 passes under top MD yarn 21, over top MD yarn 22, under top MD yarn 23, over top MD yarn 24 and so on until it passes over top MD yarn 30. Similarly, top CMD yarn 32 passes under top MD...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com