Neoplasia screening compositions and methods of use
a composition and composition technology, applied in the field of neoplasia screening compositions and methods of use, can solve the problems of invasive procedures that lack sensitivity and accuracy, neoplasia is a significant cause of human morbidity and mortality, and neoplasias, including bladder, renal and prostate cancer, can achieve the effects of improving the sensitivity and accuracy of patient diagnosis, and improving the sensitivity and accuracy o
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Bladder Cancer Statistical Analysis
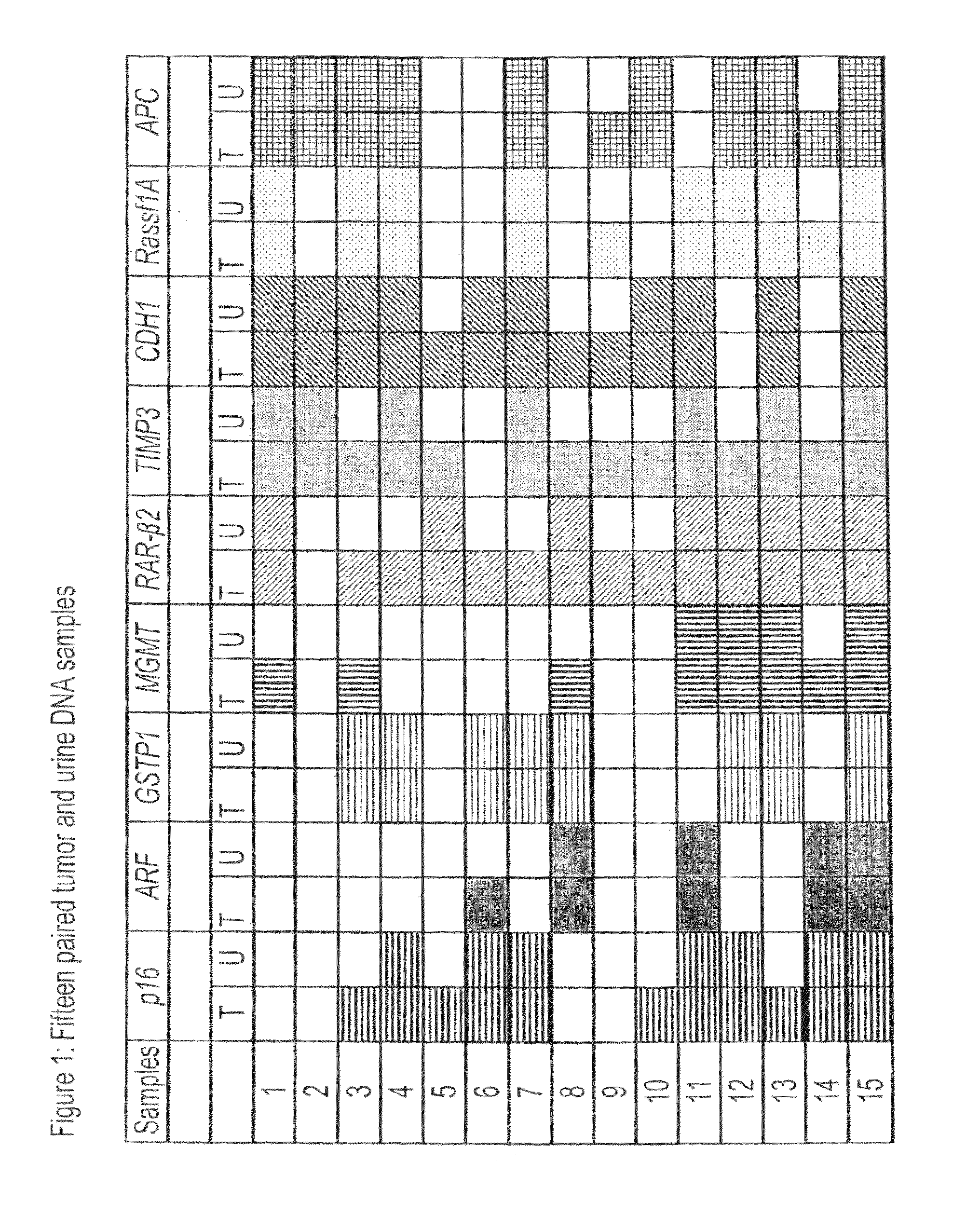
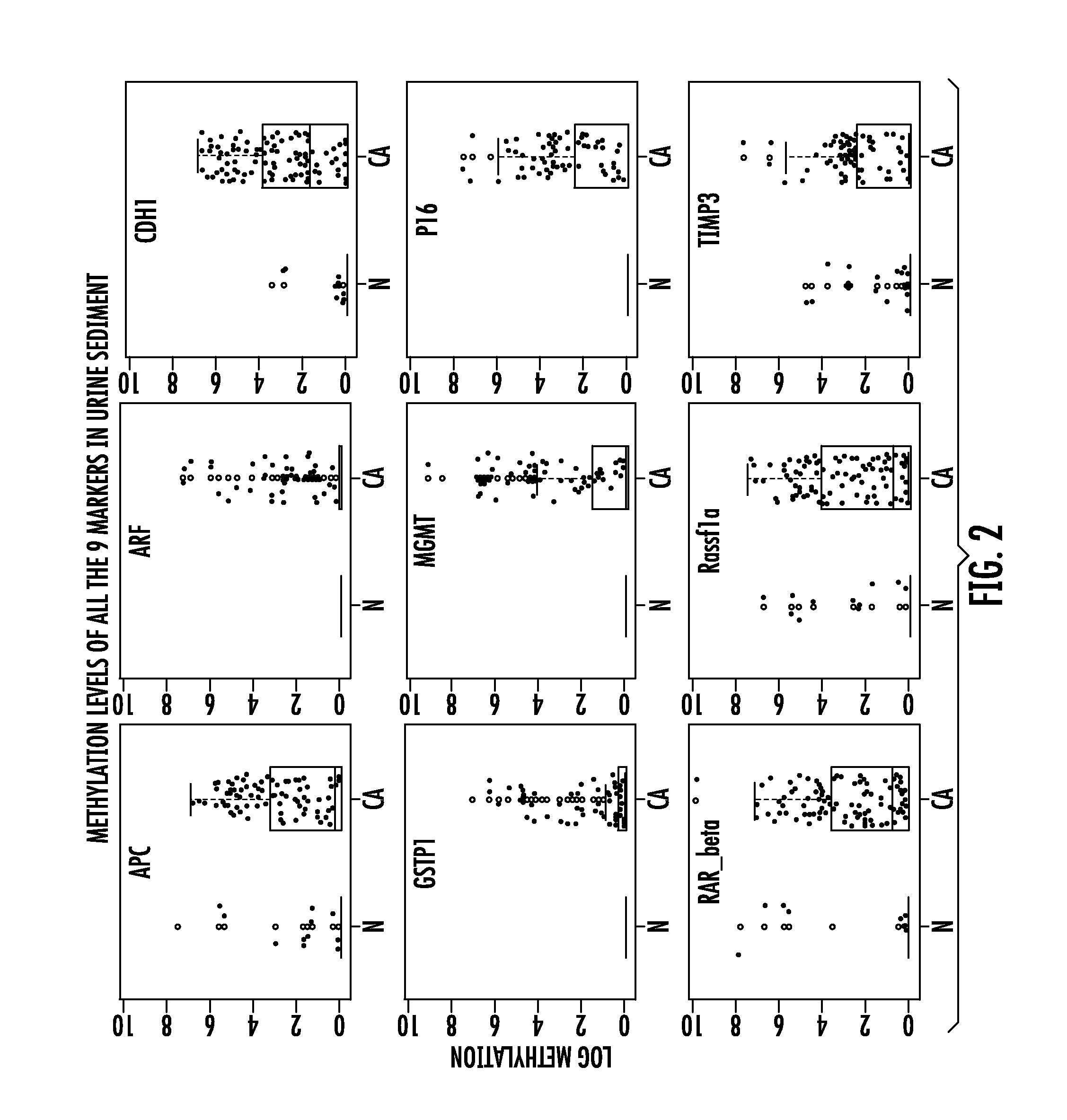
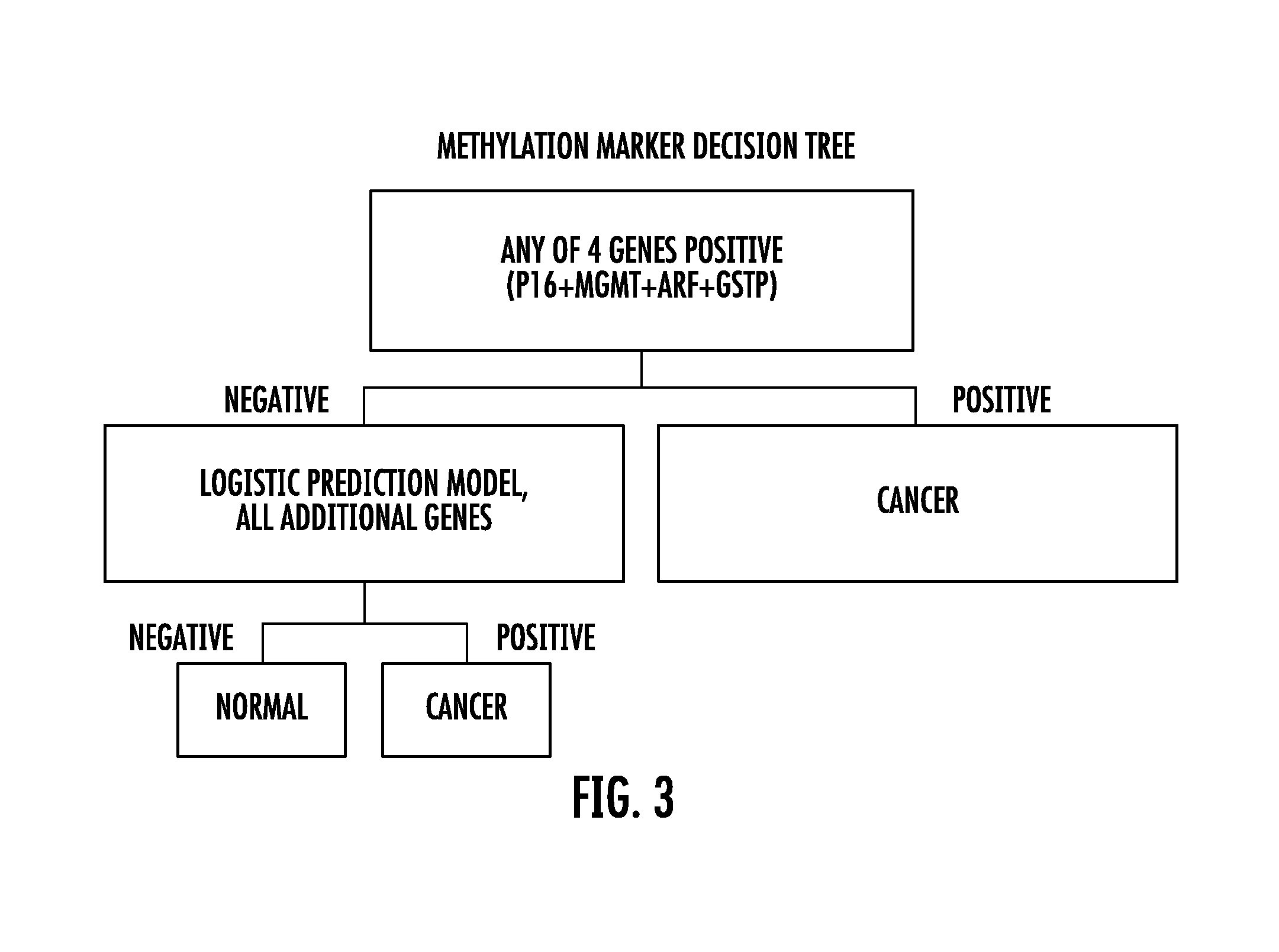
[0219]The major statistical endpoint in this study was the quantitative methylation levels for each gene in cancer cases and in controls. From these levels, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed for each of nine genes for the detection of bladder cancer. The value of using a binary cutoff (zero methylation) versus the quantitative level was also explored, via multivariate logistic models. Since four of the genes showed 100% specificity, a two step decision rule was constructed. In the first step, four genes with 100% specificity were used to identify an initial group of cancers. Among the patients in whom none of these genes were methylated, a logistic regression (Cox, D. R. The Analysis of Binary Data. London: Methuen, 1970) utilizing the remaining genes was performed. ROC curves were produced by combining sensitivity and 100% specificity achieved from the first step with the logistic regression results from the second st...
example 2
Renal Carcinoma Statistical Analysis
[0224]All of the statistical tests were performed using Excel software (Microsoft, Redmond, Wash.). The sensitivity of QMSP-based detection of hypermethylation in urine and serum was calculated as number of positive tests / number of cancer cases. The specificity was calculated as number of negative tests / number of cases without genitourinary cancer for urine (and absence of any cancer for serum).
Example 3
Prostate Carcinoma Patients and Sample Collection
[0225]Fifty six patients undergoing prostatectomy for prostate adenocarcinoma and 16 patients undergoing cystoprostatectomy for bladder carcinoma at the Johns Hopkins Hospital between November 2001 and May 2002 (Harden et al., J Natl Cancer Inst, 95: 1634-7, 2003) were included in this study. Immediately after resection, sextant biopsies (apex, mid, and base from right and left sides) were taken from all 72 of the resected prostates and kept frozen at −80° C. The biopsies were sectioned to extract DN...
example 3
Prostate Carcinoma Statistical Analysis
[0228]The medians and ranges of the methylation ratios for the samples was determined. Associations between these values were tested by using the Mann-Whitney U test, and P values<0.05 were considered to be significant.
Example 4
Prostate Sample Collection and DNA Preparation
[0229]Urine samples of fifty-two patients with prostate cancer who underwent curative surgery at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine were evaluated. Detailed data on these patients are listed in Table 11. Urine samples from ninety-one age-matched individuals (median age, 56.5 years; range, 28 to 84 years) without a history of genitourinary malignancy were used as controls. Of these ninety-one individuals, nine were diagnosed with benign prostate hyperplasia, ten harbored atypical cells by urine cytology examination, five had primary cancers in other sites (non-small-cell carcinoma of lung, n=1; basal cell carcinoma of skin, n=1; malignant melanoma of leg, n=1; Kap...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com