Transparent sharing of memory pages using content comparison
a technology of memory pages and content comparison, applied in the field of memory management, can solve the problems of system memory being usually fast, having weaknesses, and being volatil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
performance example
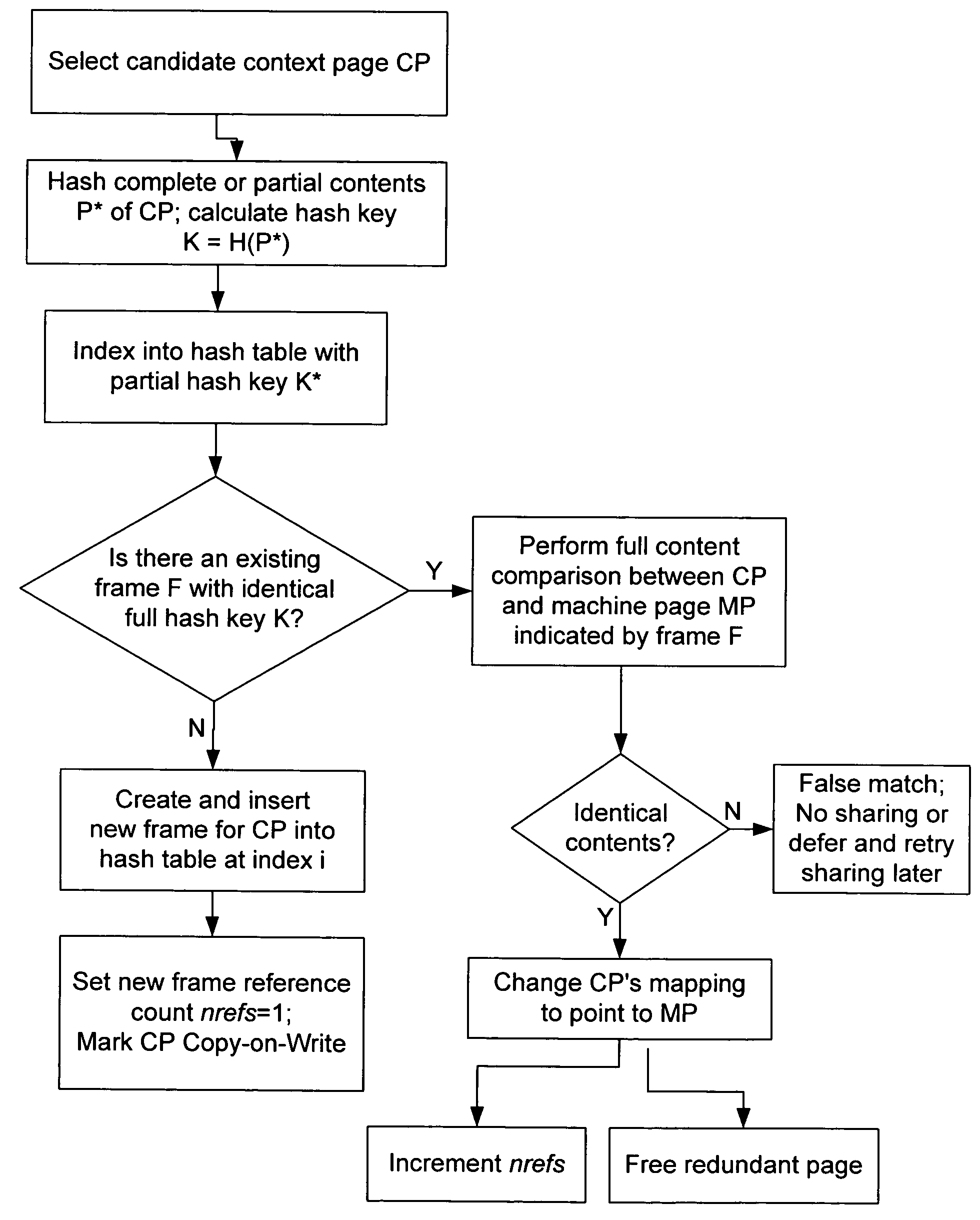
[0166]One working prototype of the invention exported an interface for configuring page sharing parameters and querying status information. The output given below is a snapshot taken when running the invention on a private build of VMware ESX Server running on a dual-processor x86 platform with support for page sharing and with the speculative hint frame optimization procedure described above.
[0167]In the test from which this snapshot was taken, three VMs were each running from a non-persistent virtual disk and using Windows 2000 as the VOS. Two of the VMs were configured for 128 MB memory, the remaining VM being configured for 64 MB. Each VM ran a simple workload consisting of the Microsoft Internet Explorer web browser, Windows Task Manager, and a command prompt window. Each VMM used a randomized policy to select candidate pages for sharing, and scanned pages at a maximum rate of 50 pages per second.
[0168]The overhead required to use the invention in this test was as follows:
[0169...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com