Digital map shape vector encoding method and position information transfer method
a vector encoding and digital map technology, applied in the field of transmitting position information of digital maps, can solve the problems of increasing the volume of road shape data, requiring a large social cost of maintenance, and requiring the use of node numbers and link numbers, so as to achieve the effect of reducing the volume of data to be transferred and compressed efficiently
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0062]In a first embodiment, description will be given to a method of compressing data by variable-length coding.
[0063]In a method of transmitting position information of a digital map according to the invention, first of all, the shape of a road is expressed in shape data having a statistical deviation. The reason is that a compressibility is to be increased when the shape data are compressed and coded.
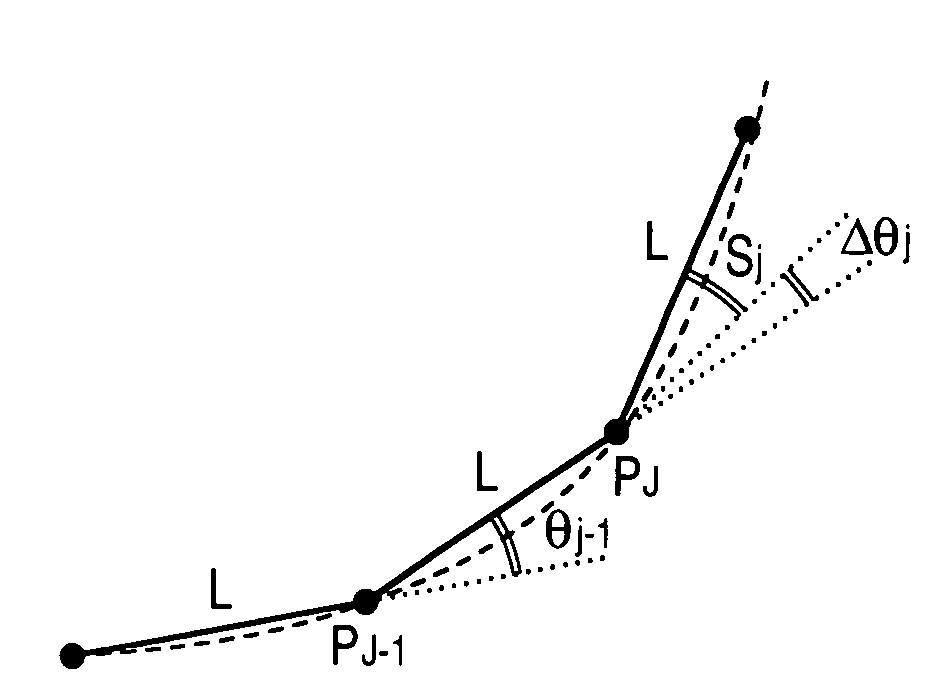
[0064]In the case in which the shape of the road is to be represented by a coordinate point arranged on the road, the position of each coordinate point (PJ) can be uniquely specified by two dimensions of a distance from an adjacent coordinate point (PJ−1) and an angle as shown in FIG. 41. In FIG. 41, the angle indicates an angle Θj based on an “absolute azimuth” for setting a due north (upper in the drawing) azimuth to 0 degree and designating an angle of 0 to 360 degrees clockwise. Thus, the expression of a coordinate point by using the distance and the absolute azimuth is referred ...
second embodiment
[0080]In a second embodiment, description will be given to a method of compressing data by using a run-length method.
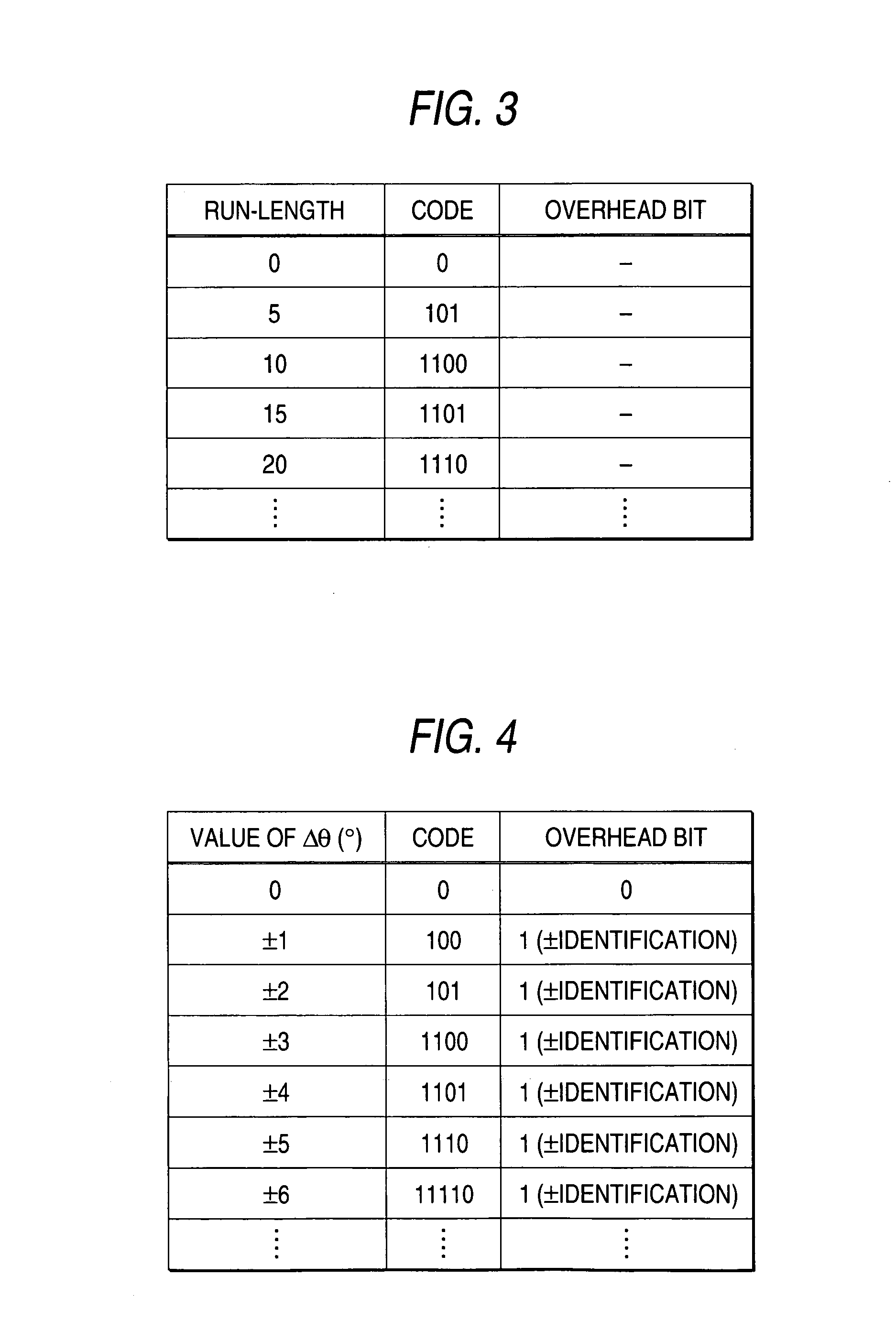
[0081]In the example of the first embodiment, in the case in which Δθj is coded to express the shape data, “0” continues in a straight road or a road curved with the same curvature. In such a case, a data compressibility is higher in an expression of “0 continues twenty times” than “00000 . . . ”. Herein, run-length coding is carried out to compress data.
[0082]FIG. 3 shows a code table for the run-length which defines that the same number continuing five times (a run-length of 5) is displayed as “101”, for example. FIG. 4 shows the same code table for Δθ as that in FIG. 2.
[0083]A data array is determined as run-length →Δθ→ run-length →Δθ→. . . , for example. When Δθ is
[0084]“0, 0, 0, 0, 0, −2, −2, 0, +3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, −1 . . . ”,
[0085]it is expressed in “101·0—0·1011—0·1011—0·0—0·11000—1101·0—0·1001 . . . ”→
[0086]“10100101101011000110...
third embodiment
[0093]In a third example, description will be given to a device for executing the position information transmitting method according to the invention.
[0094]FIG. 6 shows a position information transmitter / receiver for exchanging event generation information on a road together with another device 30 as an example of the device.
[0095]The device comprises an offline processing portion 20 for generating a code table to be used for compressing and coding road shape data in an offline, and an online processing portion 10 for transmitting traffic information by using the code table data generated by the offline processing portion 20. The offline processing portion 20 includes a digital map data base 22, a storage portion 21 for storing past traffic information, a code table calculating portion 23 for generating code table data to be used for compression and coding, and a code table data base 24 for storing the code table data thus generated.
[0096]On the other hand, the online processing por...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com