Polyhydroxyalkanoate production methods and materials and microorganisms used in same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
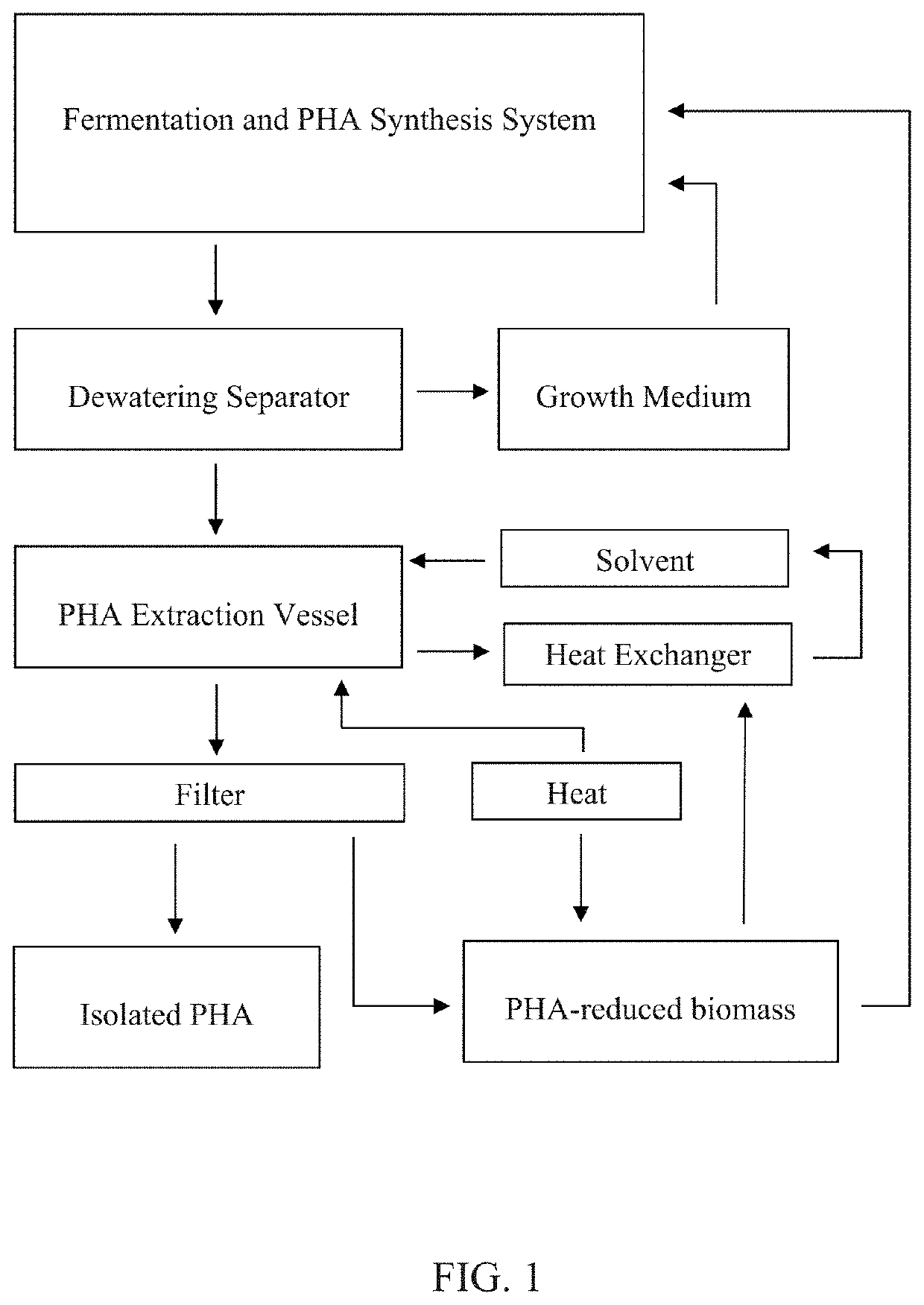
[0296]A fermentation system comprising one or more vessels are partially filled with one or more liquid growth mediums, wherein the medium comprises methanotrophic, autotrophic, methanotrophic, and / or other heterotrophic or biomass-utilizing microorganisms containing PHA, and, per liter of water, 0.7-1.5 g KH2PO4, 0.7-1.5 g K2HPO4, 0.7-1.5 g KNO3, 0.7-1.5 g NaCl, 0.1-0.3 g MgSO4, 24-28 mg CaCl2*2H2O, 5.0-5.4 mg EDTA Na4(H2O)2, 1.3-1.7 mg FeCl2*4H2O, 0.10-0.14 mg CoCl2*6H2O, 0.08-1.12 mg MnCl2*2H2O, 0.06-0.08 mg ZnCl2, 0.05-0.07 mg H3BO3, 0.023-0.027 mg NiCl2*6H2O, 0.023-0.027 mg NaMoO4*2H2O, 0.011-0.019 mg CuCl2*2H2O. One or more of the mediums are anaerobic and / or aerobic, and carbon containing gases, including methane, carbon dioxide, and volatile organic compounds, as well as optionally air or oxygen, are fed into all or part of the system to induce the growth and reproduction of microorganisms through the utilization of carbon-containing gases, as well as the production of PHA.
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com