Method and device for detecting heart rhythm irregularities
a heart rhythm and irregularity technology, applied in the field of methods and devices for detecting heart rhythm irregularities, can solve the problems of increased risk of heart failure, dementia, and the cost of ecg equipment, and achieve the effect of reducing errors and high utility value in the medical industry
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0043]I. Determining the Occurrence (Absence) of an Irregular Pulse Peak
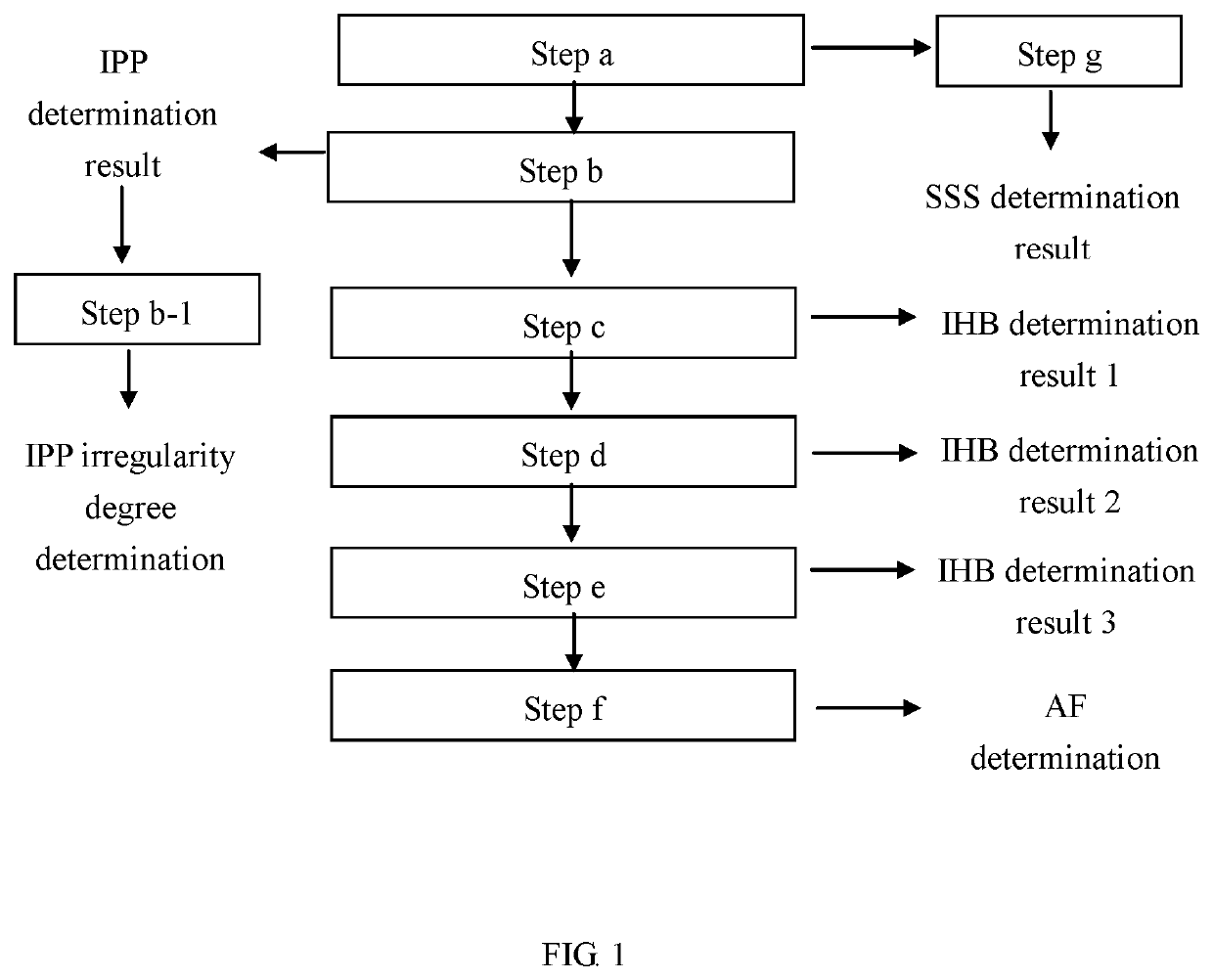
[0044]Referring to steps a and b in FIG. 1, the method of the present invention for detecting heart rhythm irregularities can be used to detect an irregular pulse peak, and the determination steps are as follows:
[0045][Step a]:
[0046]Pulse peaks are measured continuously for 25 seconds to obtain a pulse peak sequence and a pulse peak time interval sequence P(i) corresponding to the pulse peak sequence, where i is an integer ranging from 1 to N.
[0047]Referring to the pulse signal graph in FIG. 6, pulse signals are detected while the bladder is gradually pressurized (i.e., inflated). Pulse peaks are measured continuously for 25 seconds such that a pulse peak sequence and a pulse peak time interval sequence P(i) corresponding to the pulse peak sequence are obtained, where i is an integer ranging from 1 to 15. During the 25-second period, the first pulse peak detected (indicated by the letter a in FIG. 6) and the sec...
embodiment 2
[0059]II. Embodiment 2-Determining the Occurrence (or Absence) of Irregular Heartbeat
[0060]Referring to step c in FIG. 1, the method of the present invention for detecting heart rhythm irregularities can be used to detect irregular heartbeat, and the determination step is as follows:
[0061][Step c]:
[0062]Following step b, IPP determination is performed on each pulse peak time interval in the pulse peak time interval sequence P(i), i.e., on the first through the Nth pulse peak time intervals. The number B of the irregular pulse peaks identified in the sequence P(i) is counted. Then, the ratio of the number B of the identified irregular pulse peaks to the total number N of the time intervals in the sequence P(i) is calculated. If the ratio is larger than or equal to a threshold value, it is determined that irregular heartbeat (IHB) has occurred. The threshold value in this embodiment is 20%, but the present invention has no limitation on this value. Mathematically, the determination of...
embodiment 3
[0066]III. Embodiment 3-Determining the Occurrence (or Absence) of Atrial Fibrillation
[0067]Referring to steps d to f in FIG. 1, the method of the present invention for detecting heart rhythm irregularities can be used to detect atrial fibrillation, and the determination steps are as follows:
[0068][Step d]:
[0069]After step c (i.e., after determining the occurrence or absence of IHB in the sequence P(i)), measurement is stopped for 10 seconds. Then, pulse peaks are measured continuously for 25 seconds to obtain another pulse peak sequence and a pulse peak time interval sequence Q(i) corresponding to this pulse peak sequence, where i is an integer ranging from 1 to N. The occurrence (or absence) of IHB in the sequence Q(i) is determined as in step c.
[0070][Step e]:
[0071]Measurement is stopped for 10 seconds, and then pulse peaks are measured continuously for 25 seconds to obtain yet another pulse peak sequence and a pulse peak time interval sequence R(i) corresponding to this pulse pe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com