Method and device for spreading fiber strands
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
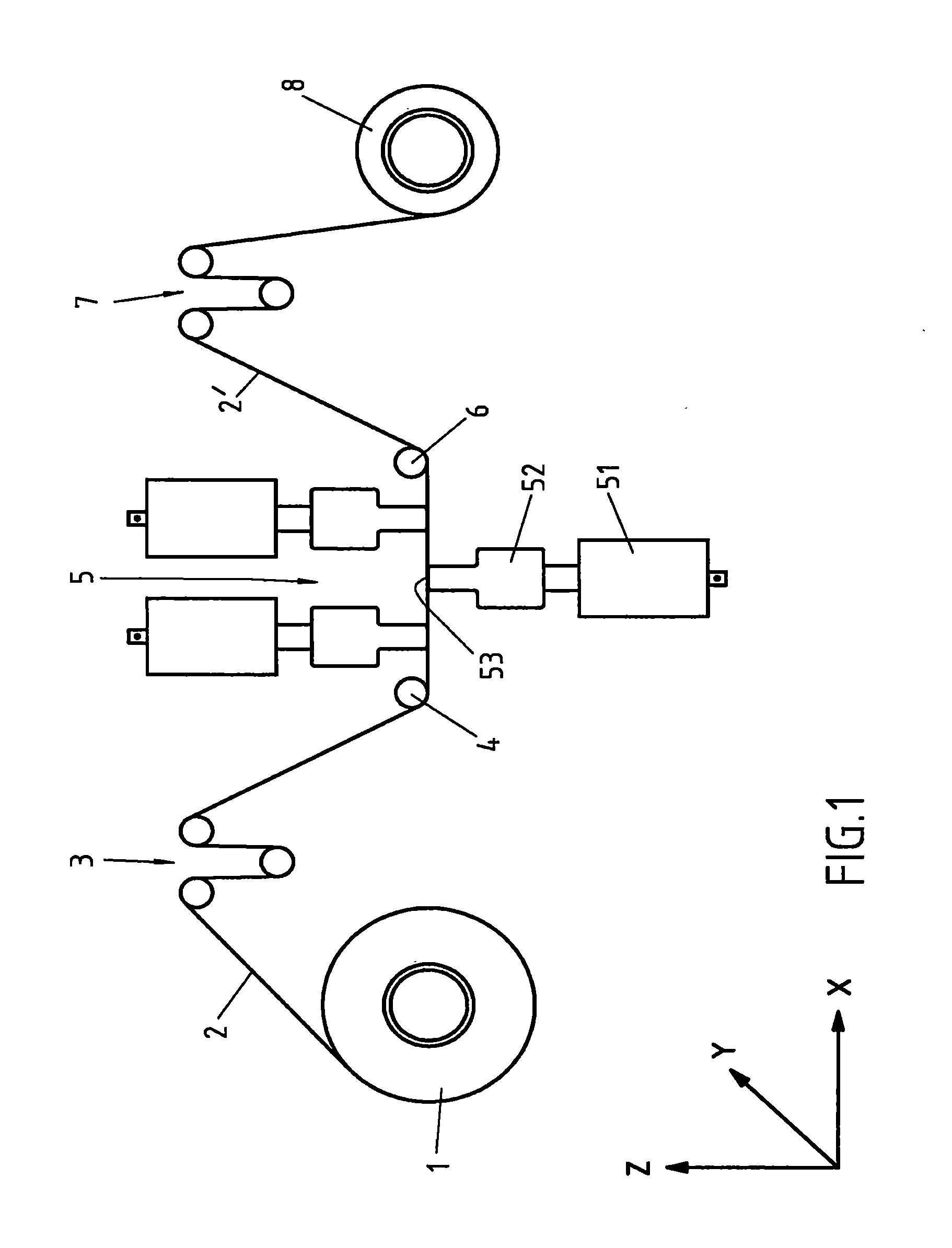
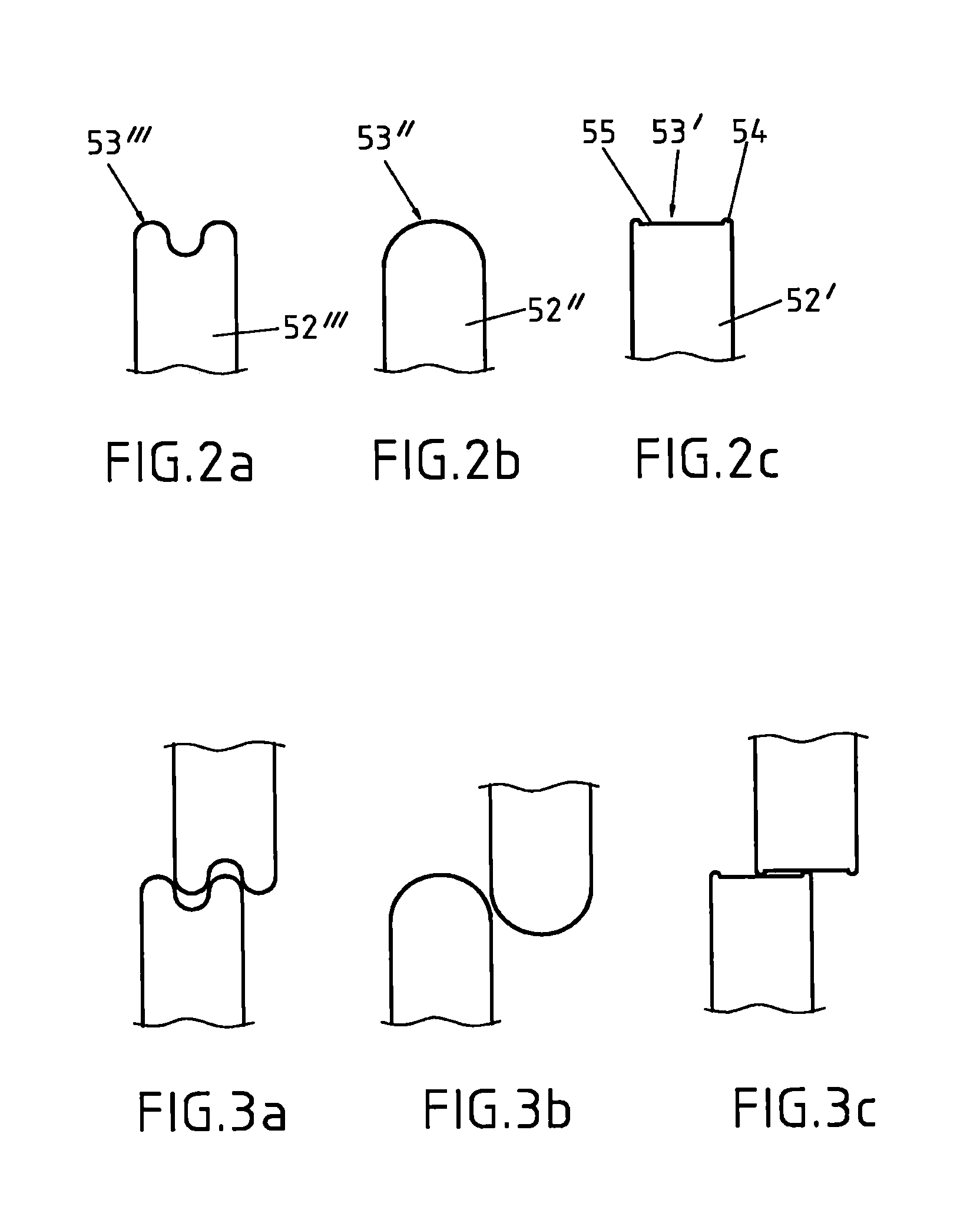
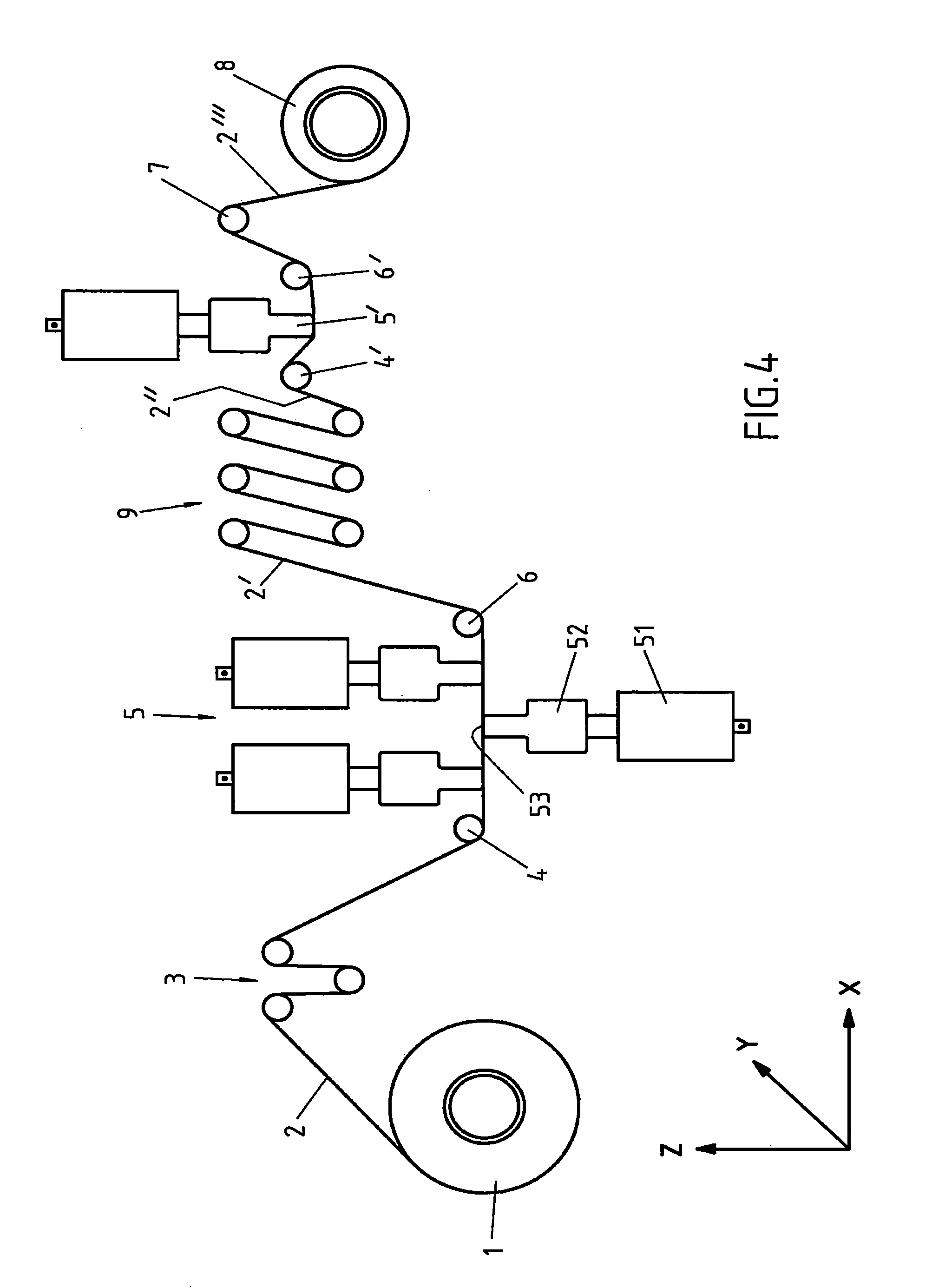
[0026]The invention is not restricted to these exemplary embodiments. The basic sketch in FIG. 1 depicts the fundamental passage of a fiber strand 2 to be spread, through the spreader station 5, proceeding from the unwinding unit 1, out to the winding unit 8. The fiber strand 2 in this case pertains to a 12K fiber strand, that is, the fiber strand consists of 12,000 filaments, which are arranged continuously in the fiber strands 2, side by side, and each one surrounded by a release agent. This release agent prevents the fiber strand 2 from being damaged during its movement. The employed fiber strand 2 is delivered on a spool of the unwinding unit 1 and is unwound from this spool. Due to the unwinding of the fiber strand 2 from the spool, different unwinding positions would result with each revolution. In order that this fiber strand 2 is always supplied to the same position of the following dancing roller 3, which conducts it to the spreader station 5, so that the fiber strand 2 is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com