Chitosan covalently linked with small molecule integrin antagonist for targeted delivery
a small molecule integrin and covalent linking technology, which is applied in the direction of biocide, drug composition, metabolic disorder, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the risk of metastasis, affecting and unable to be easily transported to the cytoplasm of cells by themselves, so as to improve the delivery effect of small molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
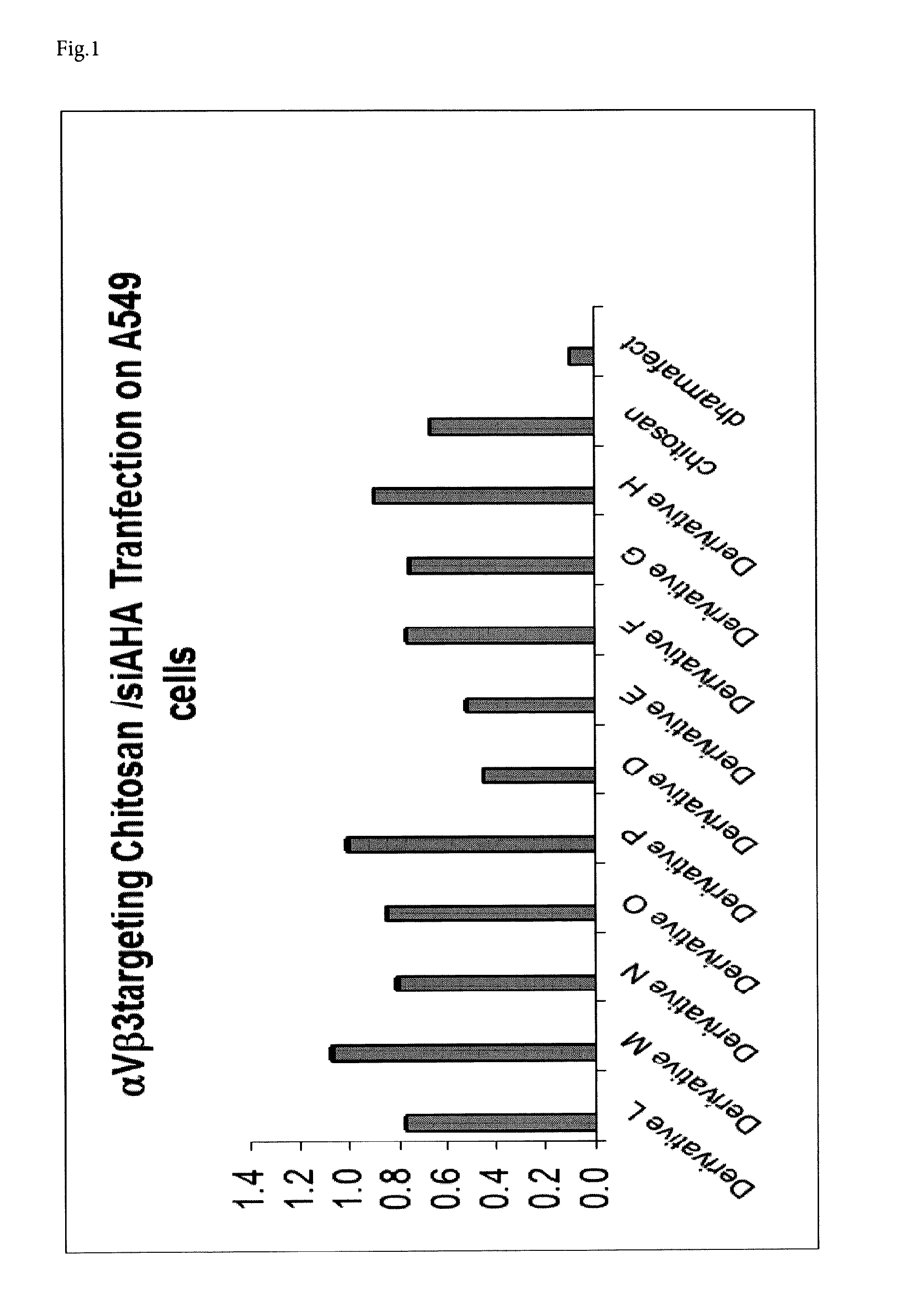
Cs(NM)-αvβ3 Ligand 3 (0.3% Loading) (Chitosan Derivative D)
Step 1: Cs(NM)-Pr-S-Ac (0.26%)
[0248]
[0249]In an Erlenmeyer flask was added Protosan (novamatrix (NM) (200 mg, 1.13 mmol), 1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-ol (153 mg, 1.13 mmol, Eq: 1.0), 3-(acetylthio)propanoic acid (836 μg, 5.64 μmol, Eq: 0.005), and water (50 mL). The mixture was stirred until a clear colorless solution formed, and then was diluted with Acetonitrile (50.0 mL). To this was added EDC (3.25 mg, 16.9 μmol, Eq: 0.015) and the reaction was stirred at RT for 13 hr. The reaction was partially acidified with 1 mL of 0.1 M HCl, concentrated, transferred to a dialysis bag (10K MWCO, Thermo Scientific, Snake Skin), and dialyzed against 4 L of 2.5% NaCl solution for 3 h, 2% for 5 h, 1% for 6 h, 0.5% 12 h, water 12 h 4 times. The dialysate was lyophilized yielding off white fibrous solid, 158 mg. The loading was determined by 1H NMR integration of the methyl of the thioacetate at 2.21 ppm as compared to the methyl of the N...
example 2
Cs(NM)-αvβ3 Ligand 3 (0.6% Loading) (Chitosan Derivative E)
Step 1: Cs(NM)-Pr-S-Ac (0.47%)
[0253]The product (clear to opaque off white film / sheet solid, 176 mg) was prepared by a similar procedure as Cs(NM)-Pr-S-Ac (0.26%) from Protosan (200 mg, 1.13 mmol), 1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-ol (153 mg, 1.13 mmol, Eq: 1.0), 3-(acetylthio)propanoic acid (1.67 mg, 11.3 μmol, Eq: 0.01), and EDC (6.49 mg, 33.9 μmol, Eq: 0.03). (0.47%, N 4.30 nmol / mg).
Step 2: Chitosan(NM)-Pr-SH (0.47%)
[0254]The product (clear to opaque off white film / sheet solid) was prepared by a similar procedure as Cs(NM)-Pr-SH (0.26%) from Cs(NM)-Pr-S-Ac (0.47%) (47.5 mg). The material was used as is (0.47%, 23.7 nmol / mg).
Step 3: Cs(NM)-αvβ3 Ligand 3 (0.6% Loading) (Chitosan Derivative E)
[0255]The product (a white fibrous solid, 20 mg) was prepared by a similar procedure as Cs(NM)-Pr-S-αvβ3 Ligand 3 (0.3%) from Cs(NM)-Pr-SH (0.47%) (42 mg, 23.7 nmol / mg, 0.995 pimp and αvβ3 Ligand 3 (3.7 mg, 2.99 μmol, Eq. 3). (0.6% (29 nmol / ...
example 3
Cs(NM)-αvβ3 Ligand 3 (1.9% Loading) (Chitosan Derivative F)
Step 1: Cs(NM)-Pr-S-Ac (1.9%)
[0256]The product (clear to opaque off white film / sheet solid, 226 mg) was prepared by a similar procedure as Cs(NM)-Pr-S-Ac (0.26%) from Protosan (200 mg, 1.13 mmol), 1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-ol (153 mg, 1.13 mmol, Eq: 1.0), 3-(acetylthio)propanoic acid (5.02 mg, 33.9 μmol, Eq: 0.03), and EDC (19.5 mg, 102 μmol, Eq: 0.09). (1.9%, N 4.20 nmol / mg).
Step 2: Cs(NM)-Pr-SH (1.9%)
[0257]The product (clear to opaque off white film / sheet solid) was prepared by a similar procedure as Cs(NM)-Pr-SH (0.26%)) from Cs(NM)-Pr-S-Ac (1.9%) (48 mg). The material was used as is (1.9%, 95.3 nmol / mg).
Step 3: Cs(NM)-αvβ3 Ligand 3 (1.9% Loading) (Chitosan Derivative F)
[0258]The product (a white fibrous solid, 28 mg) was prepared by a similar procedure as Cs(NM)-Pr-S-αvβ3 Ligand 3 (0.3%) from Cs(NM)-Pr-SH (1.9%) (45 mg, 95.3 nmol / mg, 4.29 μmol) and αvβ3 Ligand 3 (15.9 mg, 12.8 μmol, Eq 3). (1.9%, 89 nmol / mg, N 3.7 μmo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com