Diamond clusters defining various shapes
a technology of diamond clusters and diamonds, applied in the field of diamond jewelry, can solve the problems of difficult process and high cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
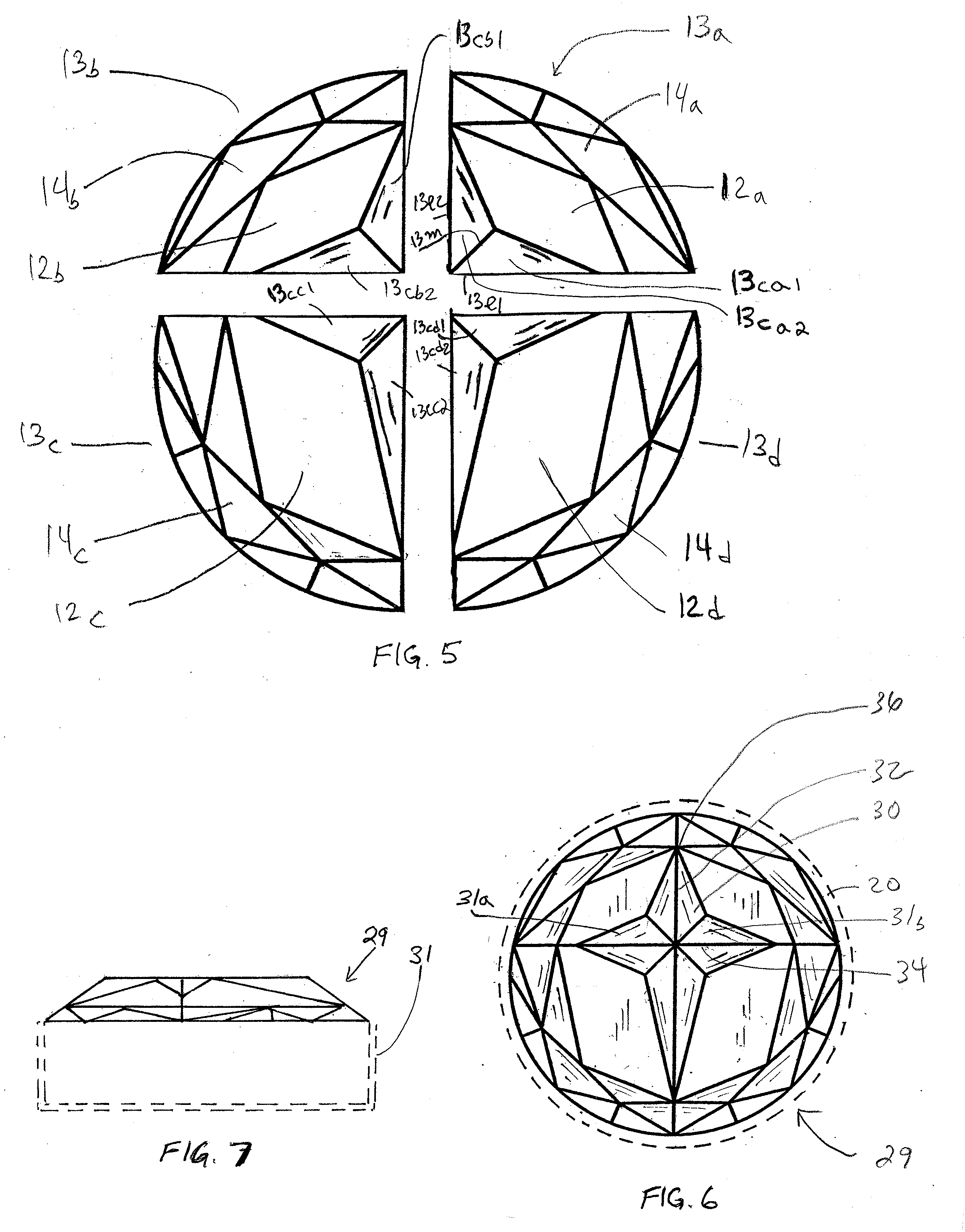
[0019]FIG. 1 illustrates diagrammatically a conventional round diamond 10 with its table 12, crown 14 and pavilion 16. The diamond 10 can be mounted in a round setting 20 with the table 10 and crown 14 jutting above the setting and the culet 22 protruding at the bottom, all as widely known and shown in FIG. 2. FIG. 3 shows the bottom view. The conventional diamond can be drilled or laser cut to define a cross shape 18 in its table 12 as shown in FIG. 4, but doing so would require a large sized and therefore expensive diamond and a very laborious and expensive process as noted above.
[0020]In departure from the prior art, the present invention utilizes, as depicted in the exploded view of FIG. 5, four diamond sections or quadrant sections 13a, 13b, 13c and 13d. Each diamond quadrant has a respective table facet 12a, 12b, 12c and 12d, and a respective crown section 14a, 14b, 14c and 14d. Most importantly, each diamond quadrant includes two respective cross facets, for example, 13a1 and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com