Feed additive composition
a technology of additive composition and feed, which is applied in the direction of accessory food factors, animal feeding stuff, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems that the interaction between dfms and enzymes has never been fully understood, and achieve the effect of improving the performance of an animal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
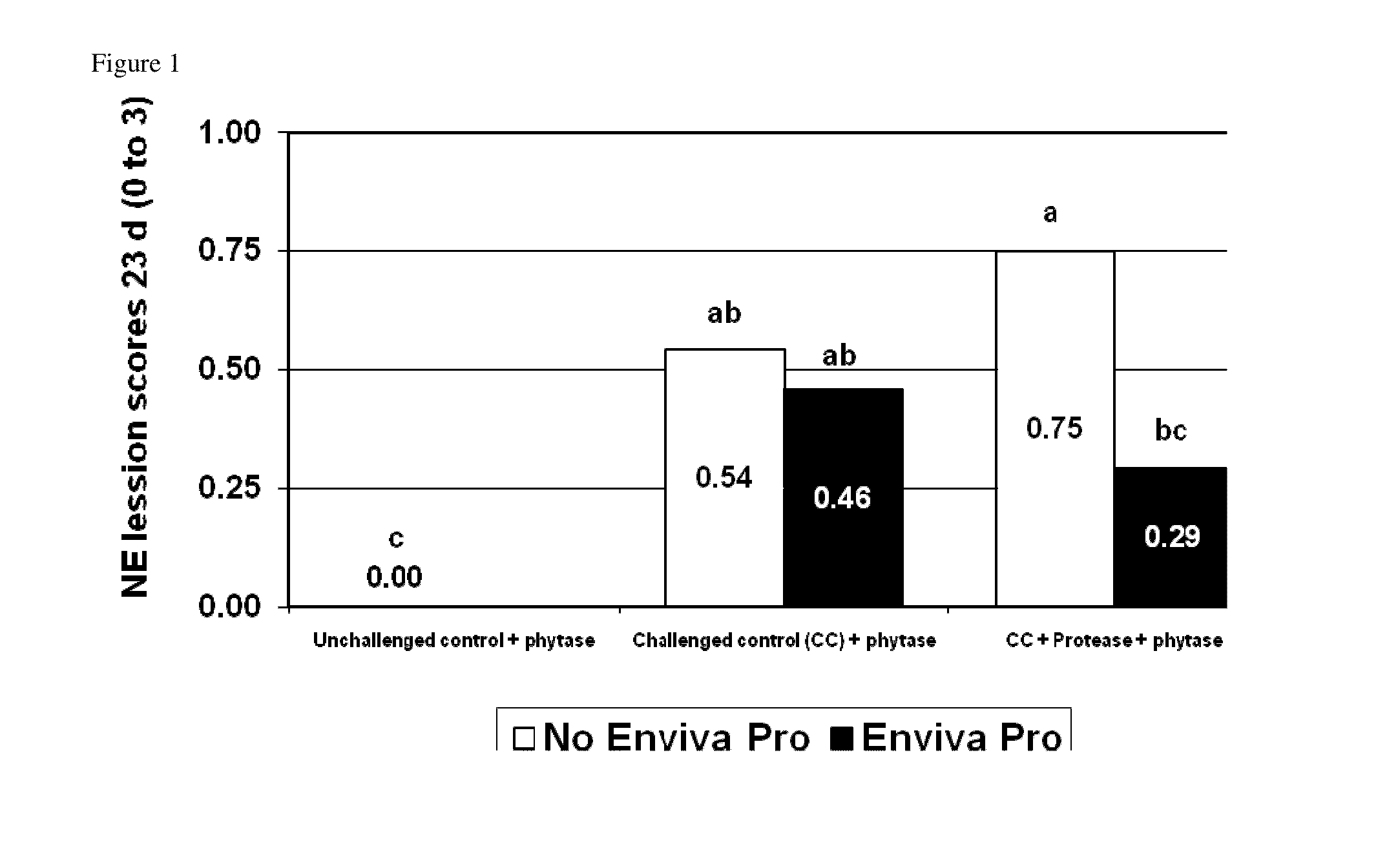
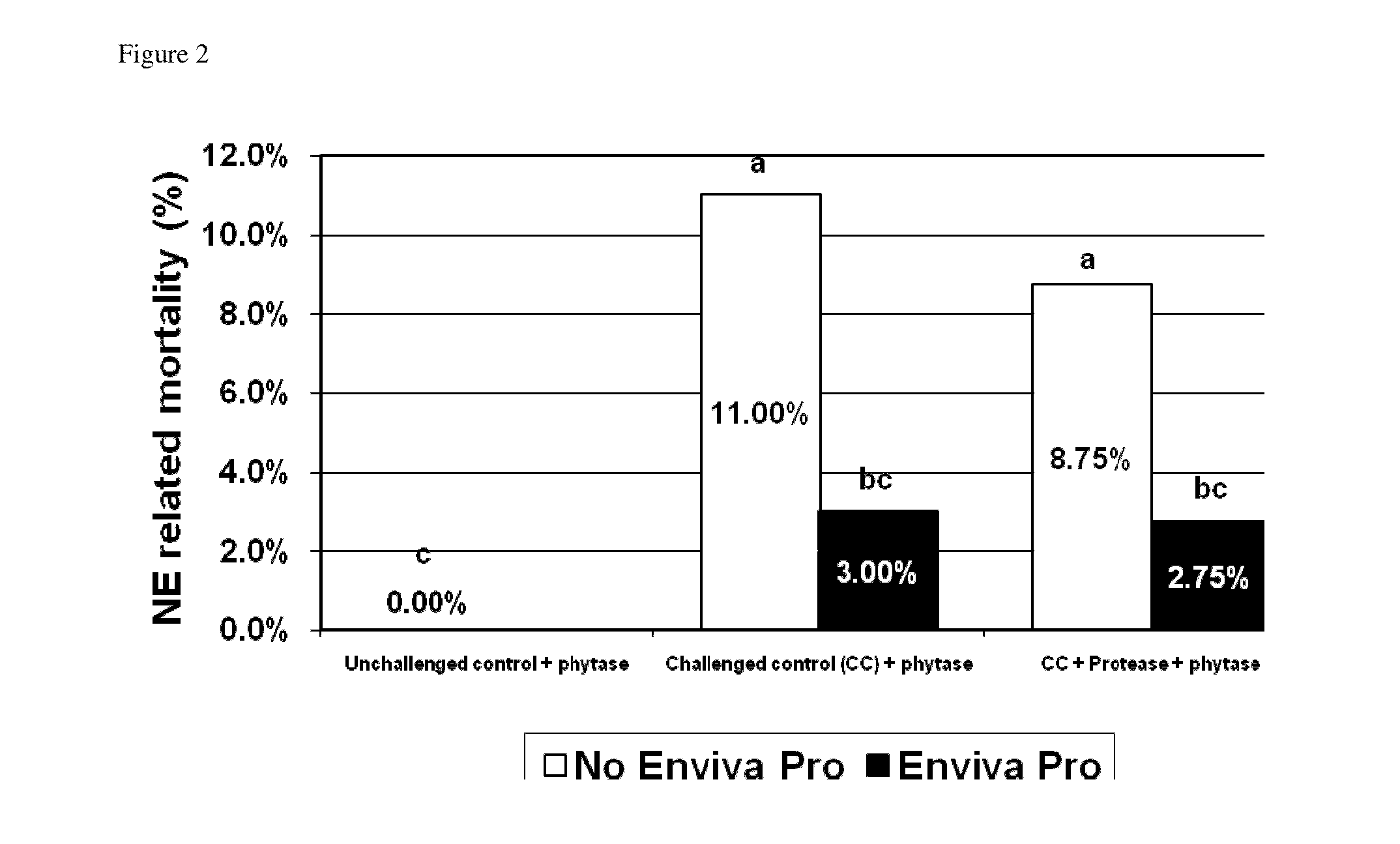
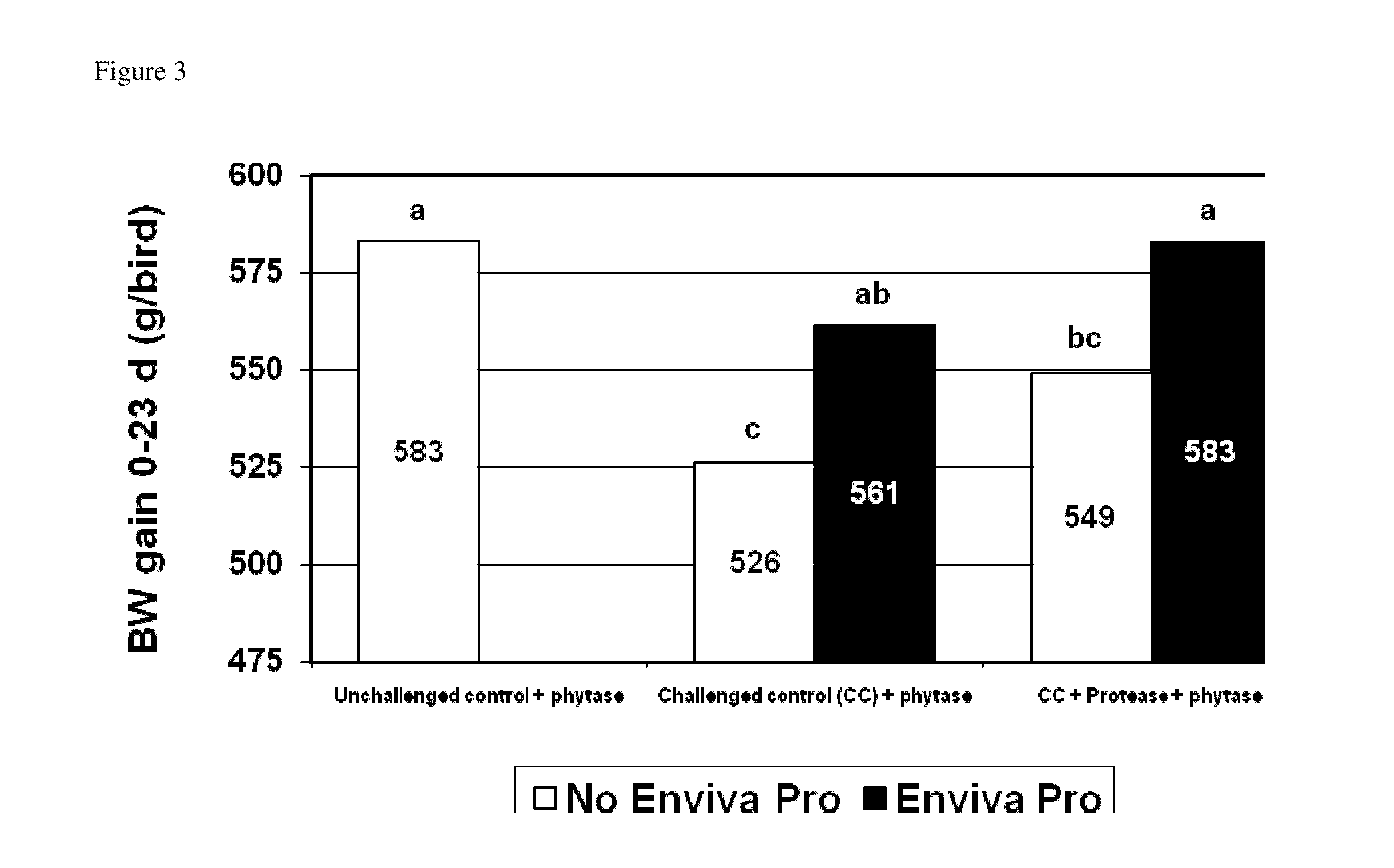
[0329]Three thousand six hundred one-day-old Cobb male chicks are purchased from a commercial hatchery. At study initiation, fifty males are allocated to each treatment pen by blocks. The study consisted of the following treatments (Table 1):
TABLE 1Experimental design of Example 1.perfringensAdditionalTreatmentChallengePhytase1enzyme2DFM31No500 FTU / kgNoneNone2Yes500 FTU / kgNoneNone3Yes500 FTU / kgProteaseNone(5000 u / kg)4Yes500 FTU / kgNoneEnviva Pro(7.5 × 104CFU / g)5Yes500 FTU / kgProteaseEnviva Pro(5000 u / kg)(7.5 × 104CFU / g)1Phytase from E. coli.2protease from Bacillus subtilis.3Enviva Pro ® is combination of Bacillus subtilis strains Bs2084, LSSAO1 and 15AP4, provided by Danisco A / S.
[0330]Bird weights by pen were recorded at study initiation, 23 d, 35 d, and termination (42 d). The pen was the unit of measure. Broiler diets were fed as crumbles (starter) or pellets (grower and finisher). Diets met or exceeded NRC standards (Table 2). The mixer was flushed to prevent c...
example 2
Materials and Methods
[0346]One digestibility trial with broiler chickens is conducted to determine the effects of protease and DFMs treatments on top of phytase on nutrient utilisation. The cages are housed in environmentally controlled rooms. The birds receive 20-hour fluorescent illumination and, are allowed free access to the diets and water. On day 1, a broiler live coccidiosis vaccine is given to all chicks orally. The study consists of the following treatments (Table 3).
TABLE 3Experimental design of Example 2.TreatmentPhytase1ProteaseDFM21500 FTU / kgNoneNone2500 FTU / kgProtease 13 (5000 u / kg)None3500 FTU / kgProtease 13 (5000 u / kg)None4500 FTU / kgProtease 24 (15000 u / kg)None5500 FTU / kgNoneEnviva Pro(1.5 × 105 CFU / g)6500 FTU / kgProtease 13 (5000 u / kg)Enviva Pro(1.5 × 105 CFU / g)7500 FTU / kgProtease 13 (5000 u / kg)Enviva Pro(1.5 × 105 CFU / g)8500 FTU / kgProtease 24 (15000 u / kg)Enviva Pro(1.5 × 105 CFU / g)1Phytase from E. coli provided by Danisco A / S.2Enviva Pro ® is combination of Bacillus ...
example 3
Materials and Methods
[0352]One digestibility trial with broiler chickens is conducted to determine the effects of phytase+protease and DFMs treatments on nutrient utilisation. The cages are housed in environmentally controlled rooms. The birds receive 20-hour fluorescent illumination and, allowed free access to the diets and water. On day 1, a broiler live coccidiosis vaccine is given to all chicks in a spray cabinet. The study consists of the following treatments (Table 5).
TABLE 5Experimental design of Example 3.TreatmentPhytase1Protease2DFM1NoneNone2500 FTU / kg5000 u / kg3NoneNoneEnviva Pro3 (1.5 × 105 CFU / g)4500 FTU / kg5000 u / kgEnviva Pro3 (1.5 × 105 CFU / g)5NoneNoneCalsporin4 (5.0 × 106 CFU / g)6500 FTU / kg5000 u / kgCalsporin4 (5.0 × 106 CFU / g)7NoneNoneGallipro Tect5 (8.0 × 105 CFU / g)8500 FTU / kg5000 u / kgGallipro Tect5 (8.0 × 105 CFU / g)1Phytase from E. coli.2Protease from Bacillus subtilis provided by Danisco A / S.3Enviva Pro ® is combination of Bacillus subtilis strains Bs2084, LSSAO1 and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| constant humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com