Method of dispensing analytic reference material
a reference material and liquid technology, applied in the field of methods and devices for dispensing liquids, can solve the problems of contaminating a sample with shattered glass, time-consuming emptying, denaturation and degradation of those compounds,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
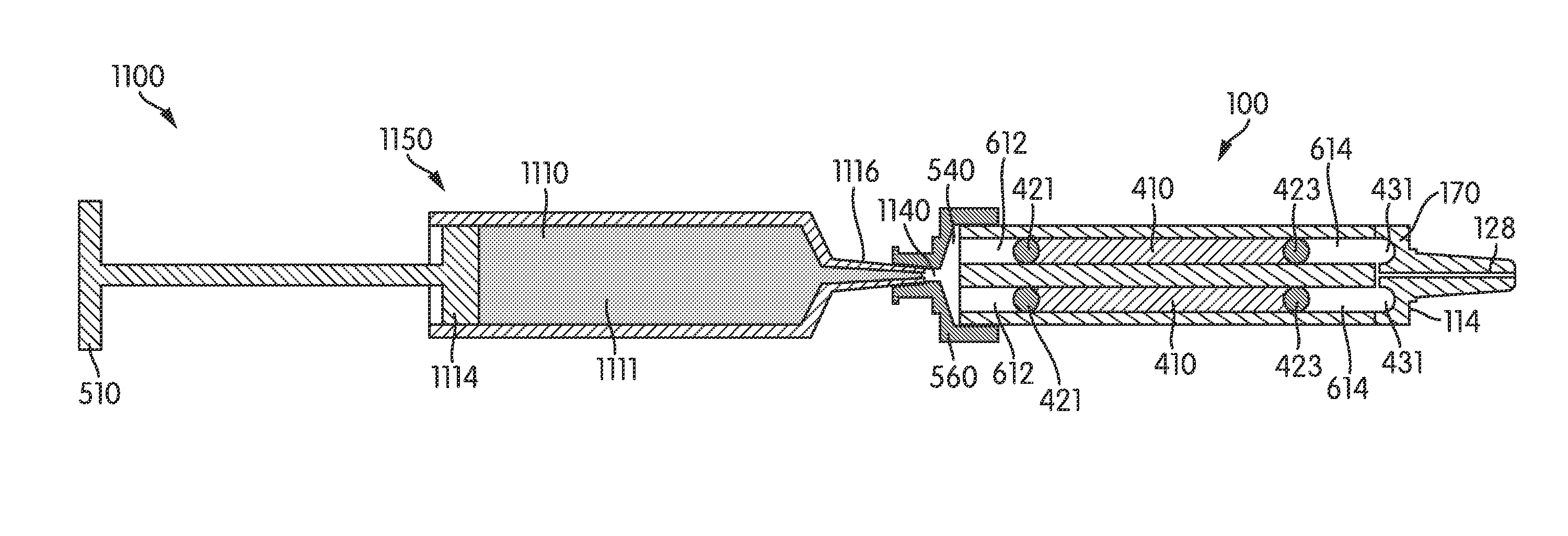
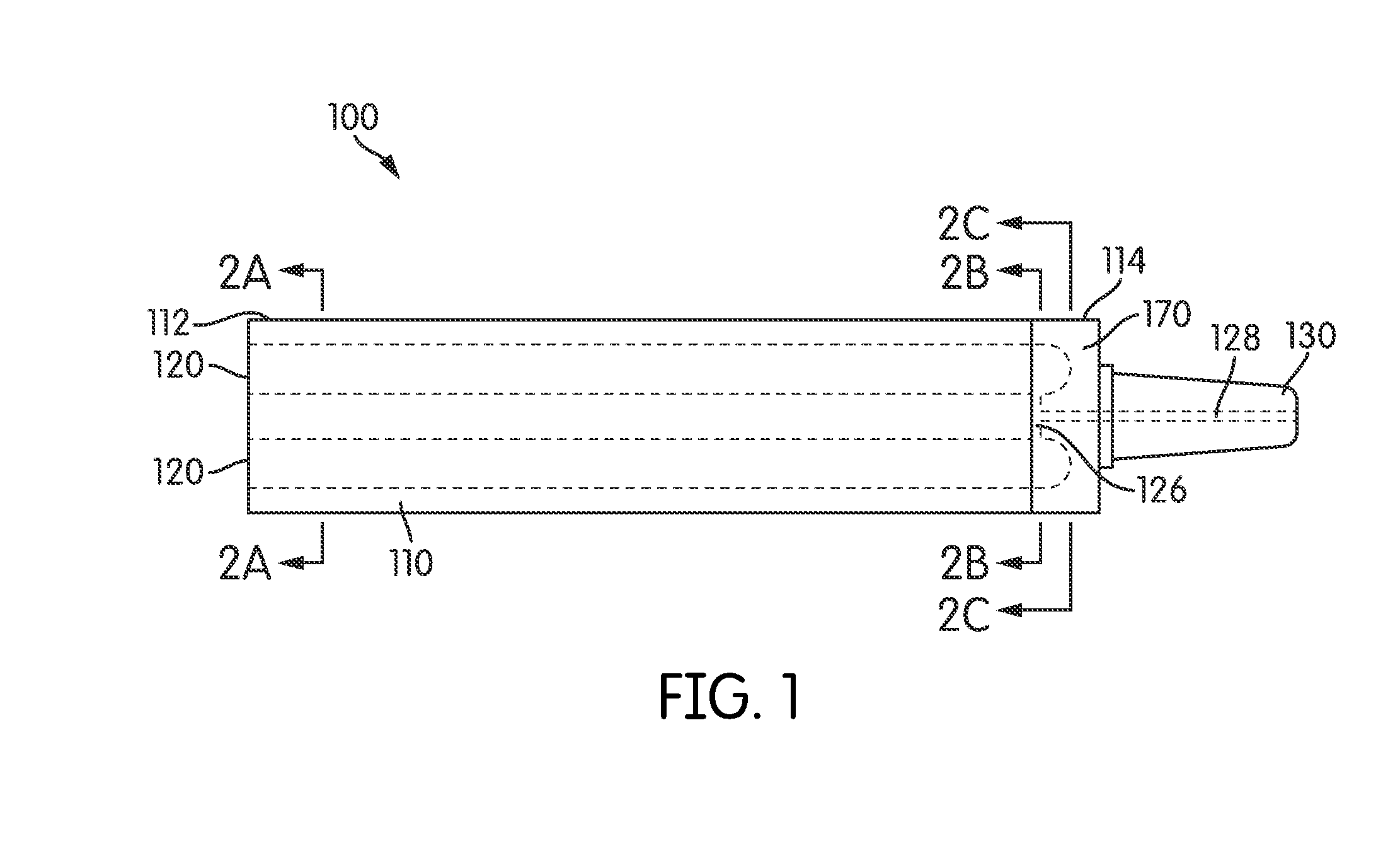
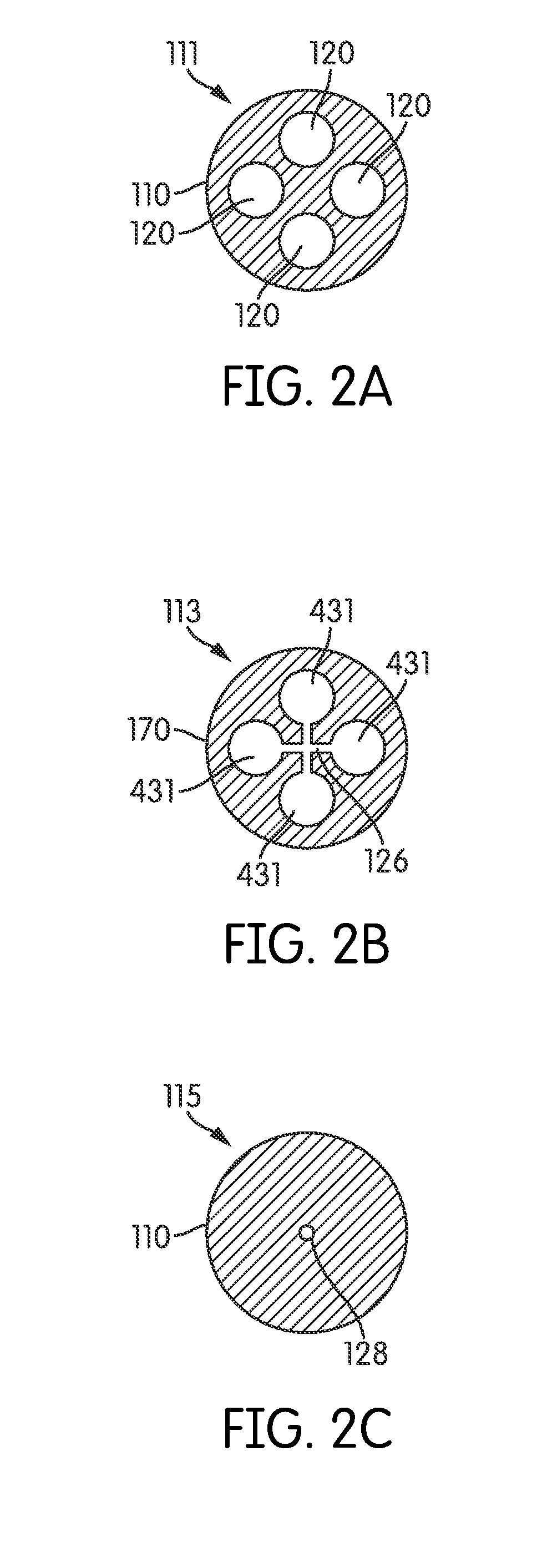
[0035]Referring to FIG. 1, an ampoule 100 includes an ampoule body 110 and a plurality of storage lumens 120 formed therein extending axially along the length of the body 110. The ampoule 100 has a proximal end 112 and a distal end 114. A connecting portion 130 extends outwardly from the distal end 114. The connecting portion 130 optionally connects to a hollow syringe needle (not shown) or other device or conduit through which the contents of the ampoule 100 are expelled and its shape is configured accordingly. The ampoule body 110 may be manufactured from any suitable material and may advantageously be formed of borosilicate glass. It will be appreciated, however, that other glass and plastic materials may also be employed. Depending on the materials of construction and / or the intended contents of the ampoule, the inner, outer or both surfaces of the ampoule 100, and particularly the surfaces of the storage lumens 120 exposed to the ampoule contents, may be chemically deactivated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com