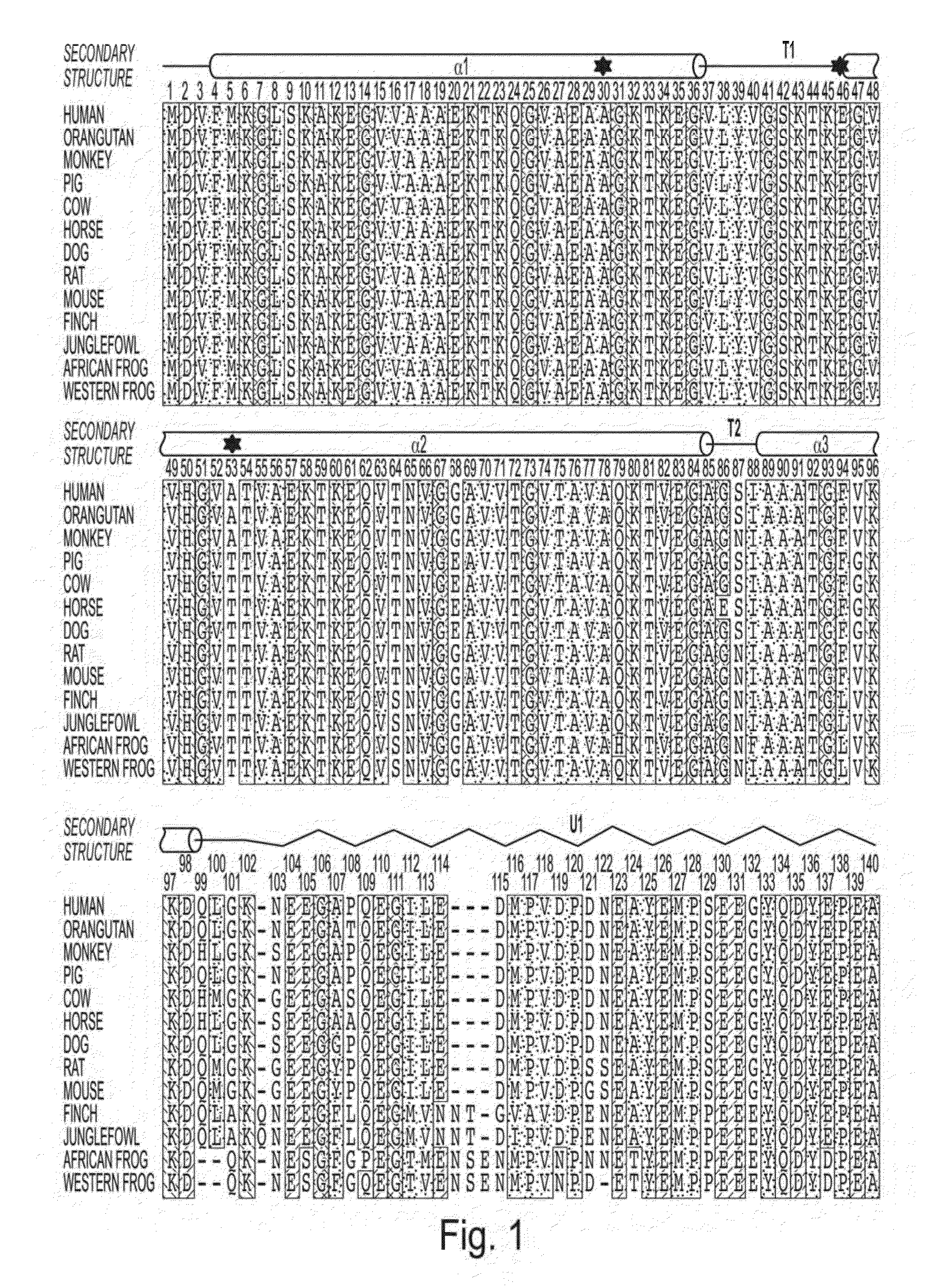
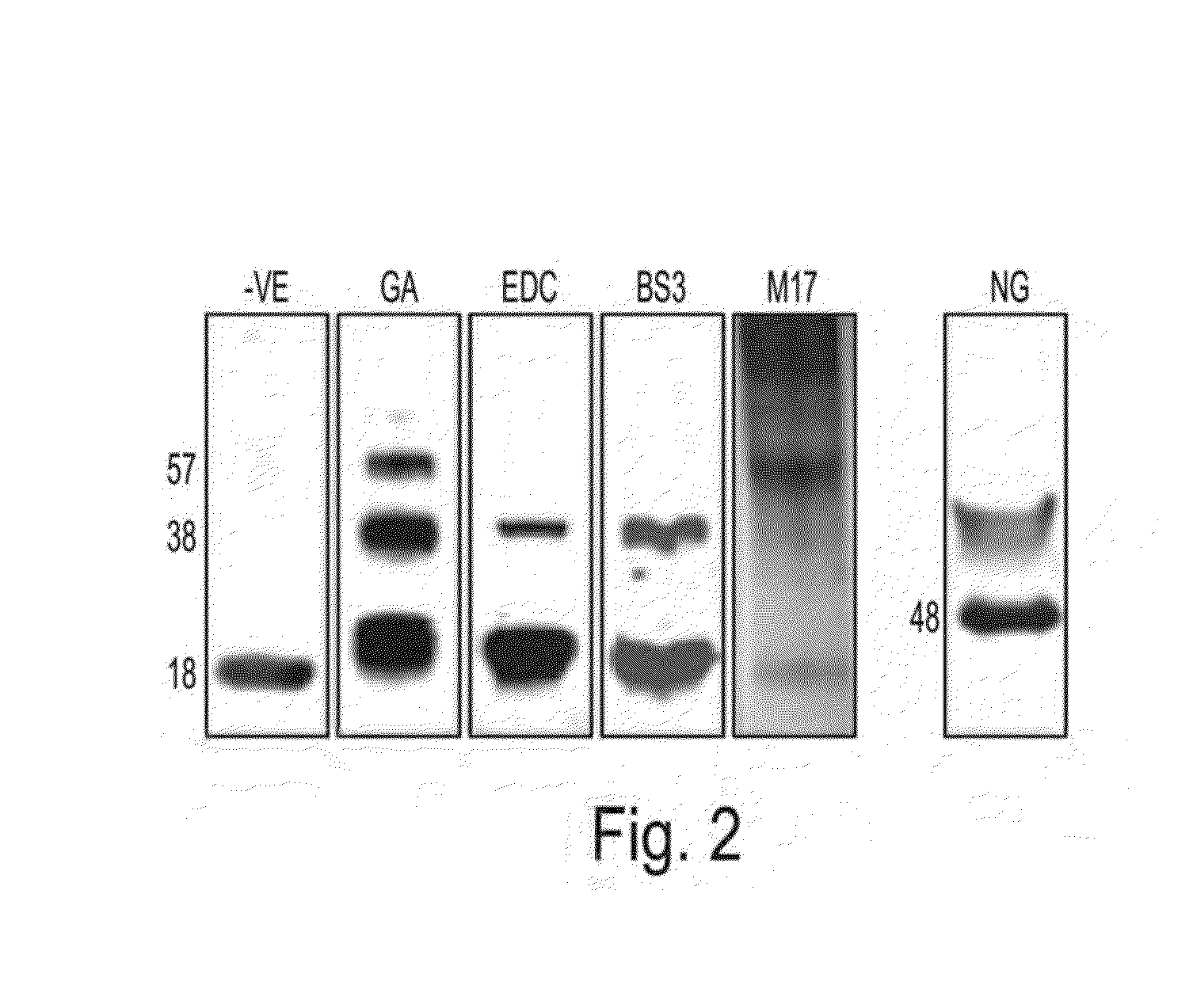
Tetrameric alpha-synuclein and use thereof
a technology of tetrameric alpha-synuclein and tetrameric alpha-synuclein, which is applied in the field of tetrameric alpha-synuclein, can solve problems such as toxic aggregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation of an α-Synuclein Oligomer
[0209]We expressed α-synuclein as an N-terminal GST-fusion and have developed a purification procedure aimed at avoiding denaturing conditions and maintaining the protein in a ‘physiological-like’ condition, in buffer containing 100 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, and 0.1% n-octyl-glucopyranoside (BOG). We note that the concentration of BOG present (˜3 mM) is well below the critical micelle concentration (˜25 mM). The same buffer was used in all subsequent protein purification steps as well as for storage. After proteolytic removal of the GST tag, α-synuclein was purified to homogeneity on a size-exclusion column, from which it eluted as a single, sharp, and symmetrical peak suggesting a homogenous particle. The specific protease site required for GST tag removal leaves a ten-residue sequence, GPLGSPEFPG (SEQ ID NO: 5), prior to the N-terminal methionine of the canonical α-synuclein sequence. However, evidence from NMR resonance assign...
example 2
Characterization of Native α-Synuclein Tetramer
[0282]To identify the assembly form of αSyn under non-denaturing conditions and avoid the potential breakdown of physiological complexes by detergents, we employed native gel electrophoresis (Native-PAGE). Since αSyn is endogenously expressed in a variety of cultured cell types, we chose to analyze the dopaminergic human neuroblastoma line, M17D (10), as well as the commonly used cell lines HEK293, HeLa, and COS-7 that endogenously express αSyn. Each of these cell types contained a nondenatured αSyn-immunoreactive species migrating at ˜45 kDa in Blue Native PAGE (BN-PAGE). This was clearly the predominant form in all the cells, and very little or no ˜14 kDa monomer was detectable (FIG. 16A). We note that similar results were observed for heterologously expressed recombinant α-Syn that was purified from bacteria under non-denaturing conditions. Because these initial results in untransfected cells suggested an apparently stable oligomeric...
example 3
A Soluble α-Synuclein Construct Forms a Dynamic Tetramer
[0336]A heterologously expressed form of the human Parkinson disease-associated protein α-synuclein with a 10-residue N-terminal extension is shown to form a stable tetramer in the absence of lipid bilayers or micelles. Sequential NMR assignments, intramonomer nuclear Overhauser effects, and circular dichroism spectra are consistent with transient formation of α-helices in the first 100 N-terminal residues of the 140-residue α-synuclein sequence. Total phosphorus analysis indicates that phospholipids are not associated with the tetramer as isolated, and chemical cross-linking experiments confirm that the tetramer is the highest-order oligomer present at NMR sample concentrations. Image reconstruction from electron micrographs indicates that a symmetric oligomer is present, with three- or fourfold symmetry. Thermal unfolding experiments indicate that a hydrophobic core is present in the tetramer. A dynamic model for the tetramer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass histogram | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| period of time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com