Methods for freezing and thawing proteins
a protein and protein solution technology, applied in the field of uniform freezing and thawing protein solution, can solve the problems of protein changing its conformation and losing functional activity, clear problem of protein unfolding during freezing, and not practicable or economical method for intermediate storage of protein solution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
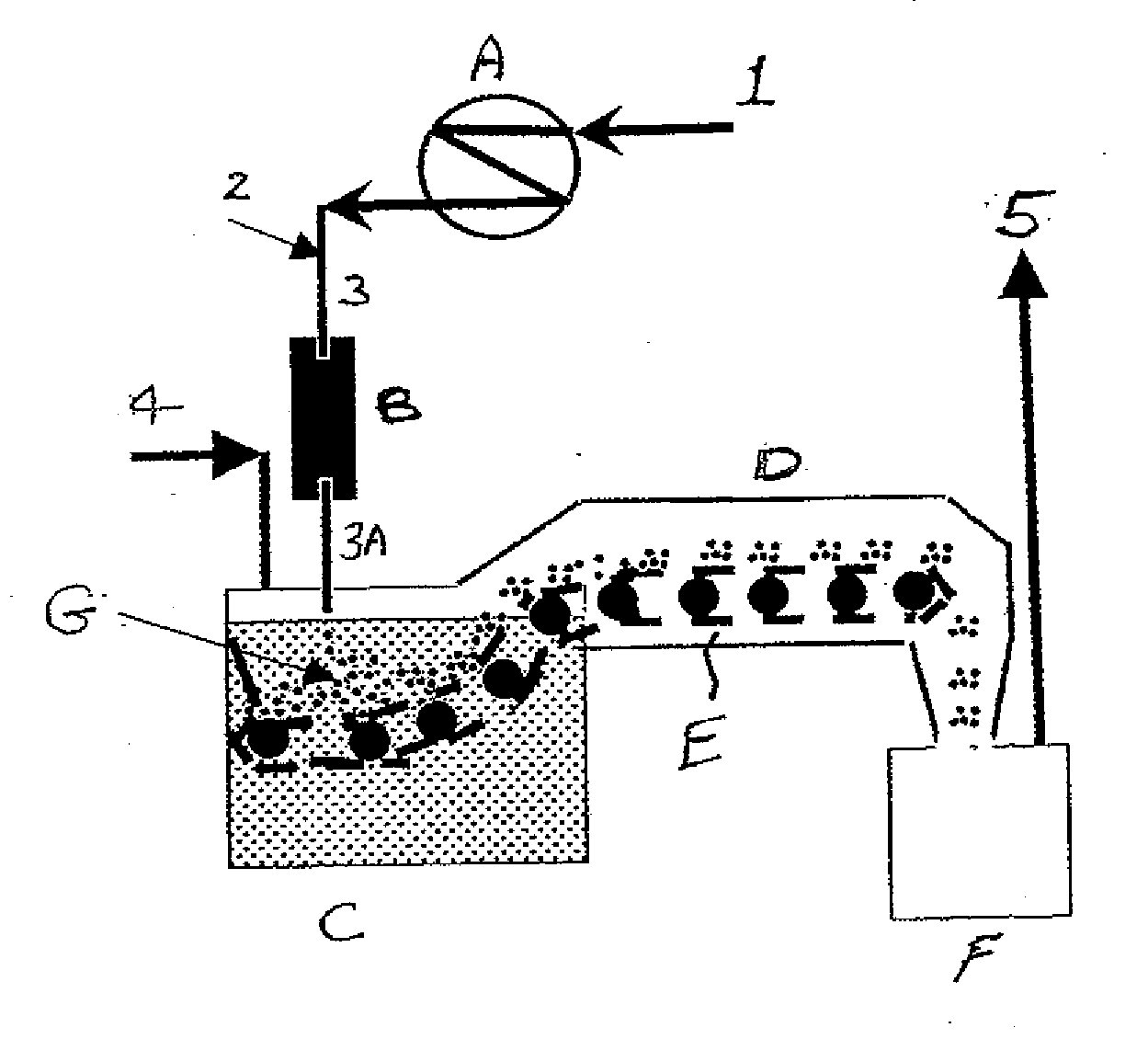
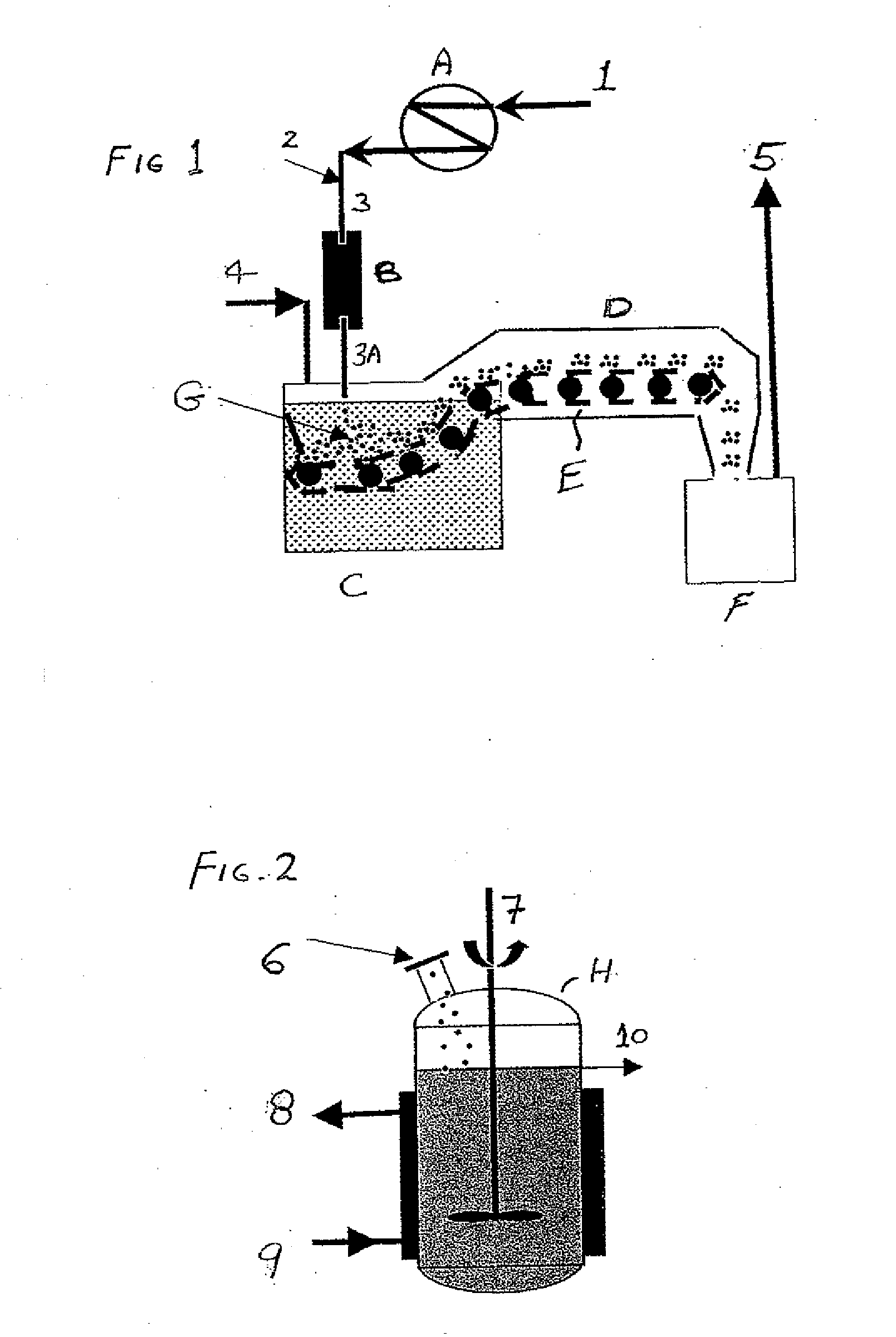
[0032]Turning to the figures, the methods of the invention are shown in detail. FIG. 1 shows a vitrification process for vitrifying protein pellets in liquid nitrogen. A protein solution is fed through line 1 to a heat exchanger A which reduces the temperature of the protein feed stream. A pre-cooled protein 2 solution having a temperature between −20° C. and −45° C. is fed into line 3 so the amount of cold necessary to reach −80° C. is reduced. The combined pre-cooled protein solution is fed through line 3 into droplet generator 4. The droplets are introduced through line 3A into an immersion bath C which contains sterile liquid nitrogen which is fed through line 4 into the immersion bath C.
[0033]The pre-cooled protein solution is dropped above or below the surface of the subcooled liquid nitrogen for 0.5 to 15 seconds through line 3A. The droplets are thus converted into vitrified pellets or beads G having a diameter of 0.5 to 15 mm. The vitrified pellets or beads G are carried al...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com