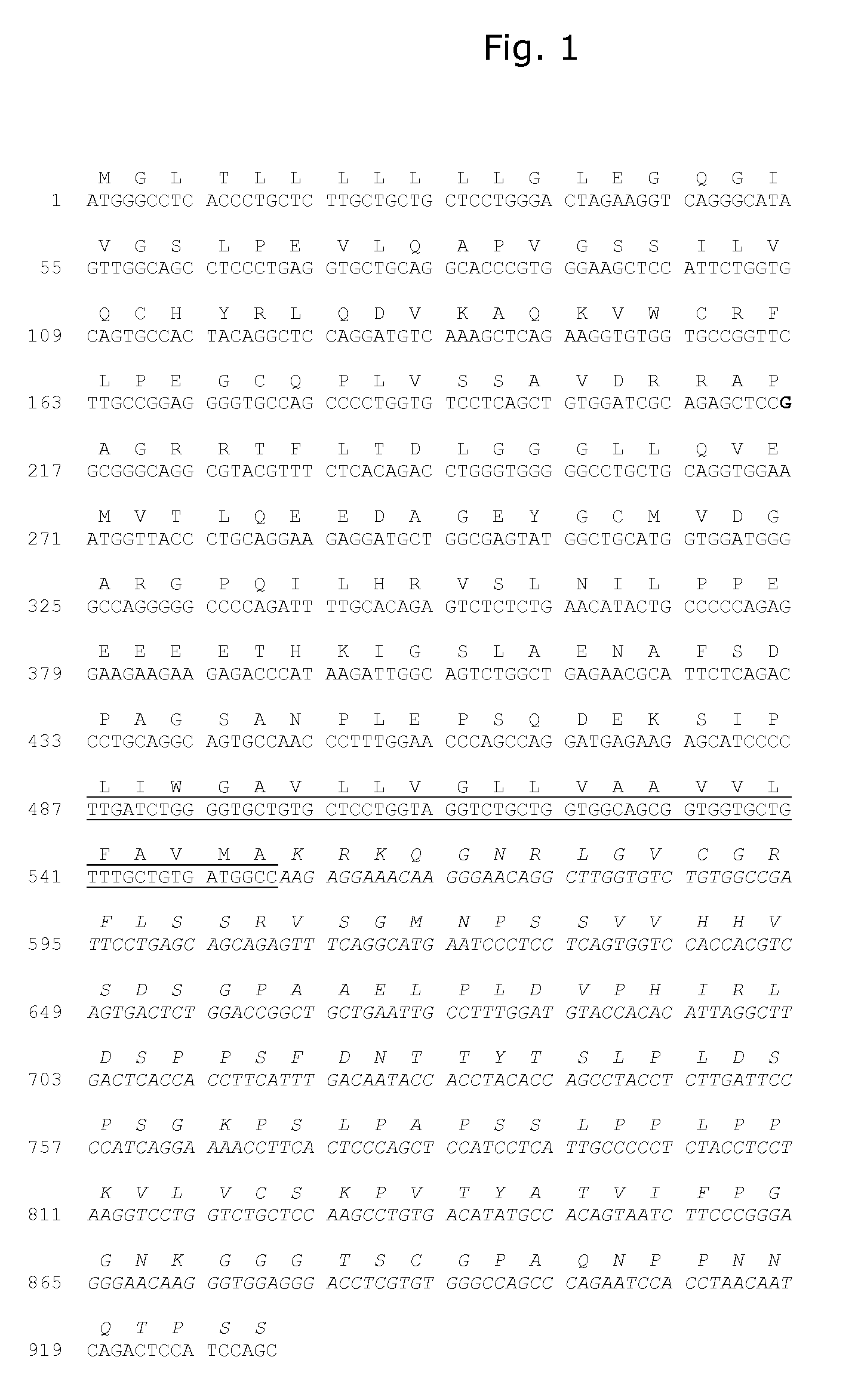Targeting tissue factor to activated platelets
a technology of activated platelets and tissue factors, which is applied in the direction of fusions for specific cell targeting, peptides/protein ingredients, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient production at this point, insufficient blood coagulation, and potentially life-threatening bleeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0303]A fusion protein comprising (i) at least one tissue factor polypeptide, or biologically functional variant(s) or fragment(s) thereof, and (ii) a ligand that is capable of binding (iii) a receptor, and / or a fragment or variant thereof, wherein the receptor is present only on the surface of activated platelets.
embodiment 2
[0304]The fusion protein according to embodiment 1, wherein (iii) is TLT-1 or a fragment or variant thereof.
embodiment 3
[0305]The fusion protein according to embodiment 2, wherein (iii) is TLT-1 (16-162).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cell density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com