Solid elastic lens element and method of making same
a technology of elastic lens element and solid layer, applied in the field of solid layer lens element, can solve the problems of unreliable and unpredictable system of lens element use, unreliable solid layer and motorized system,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
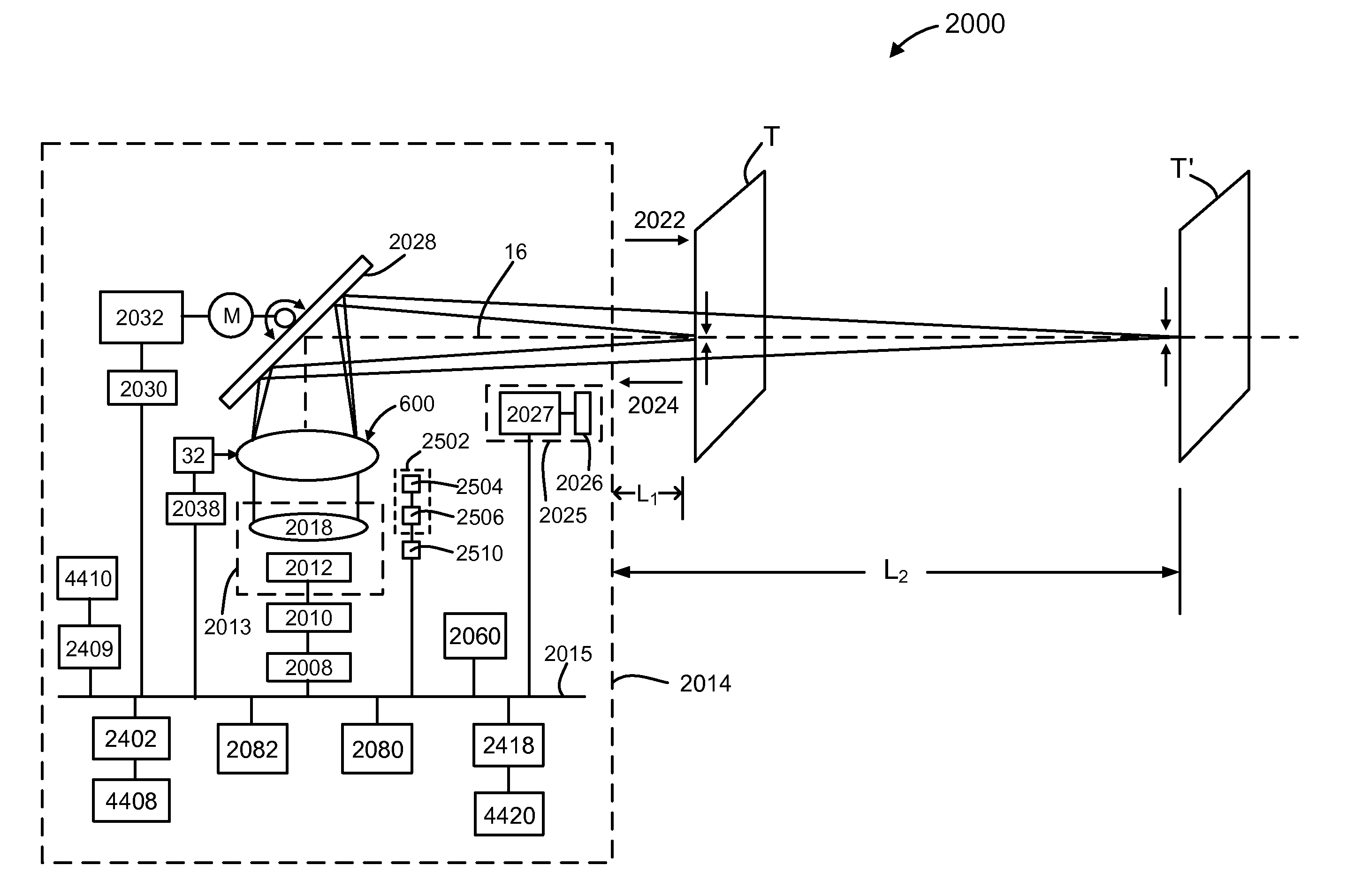
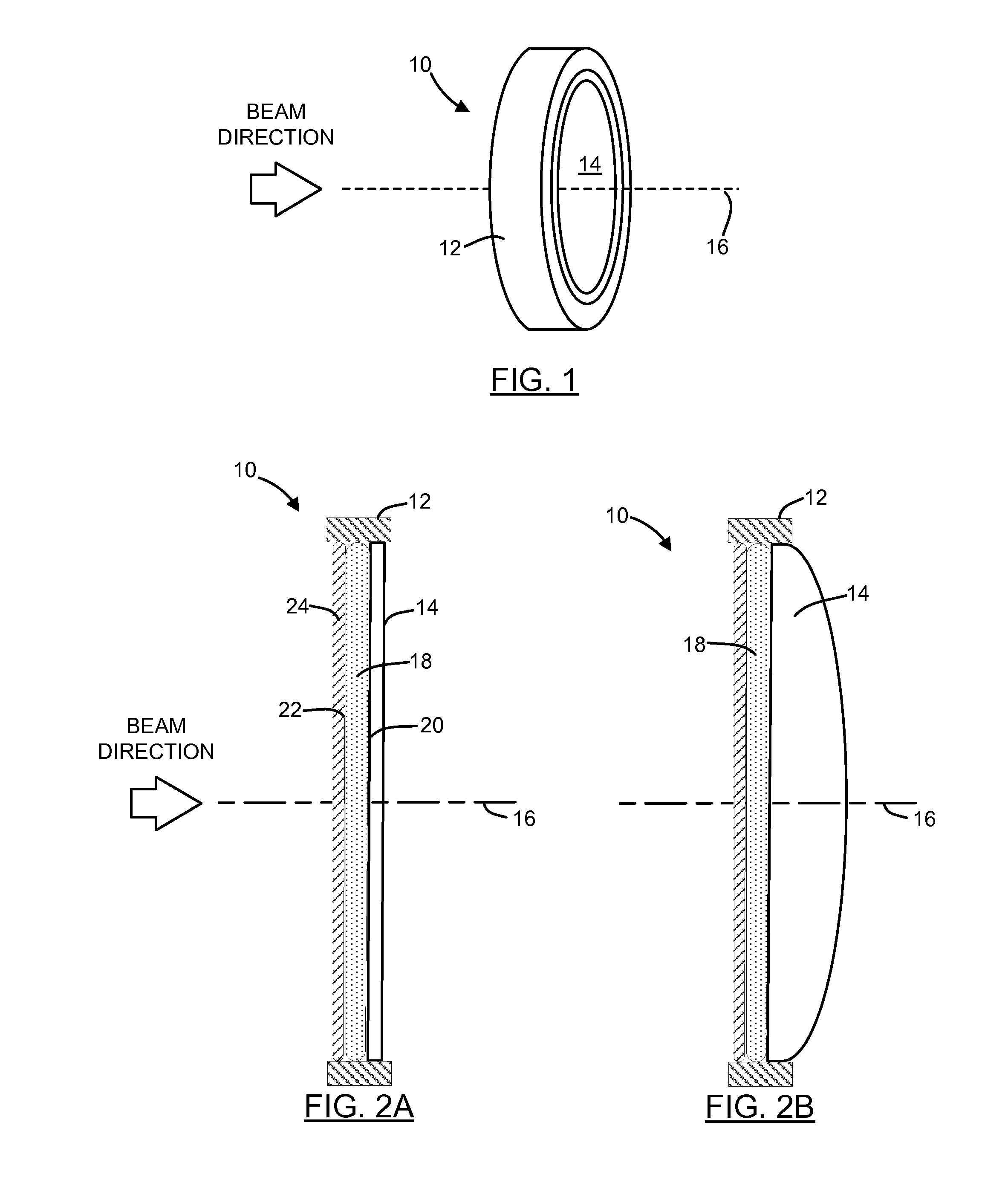
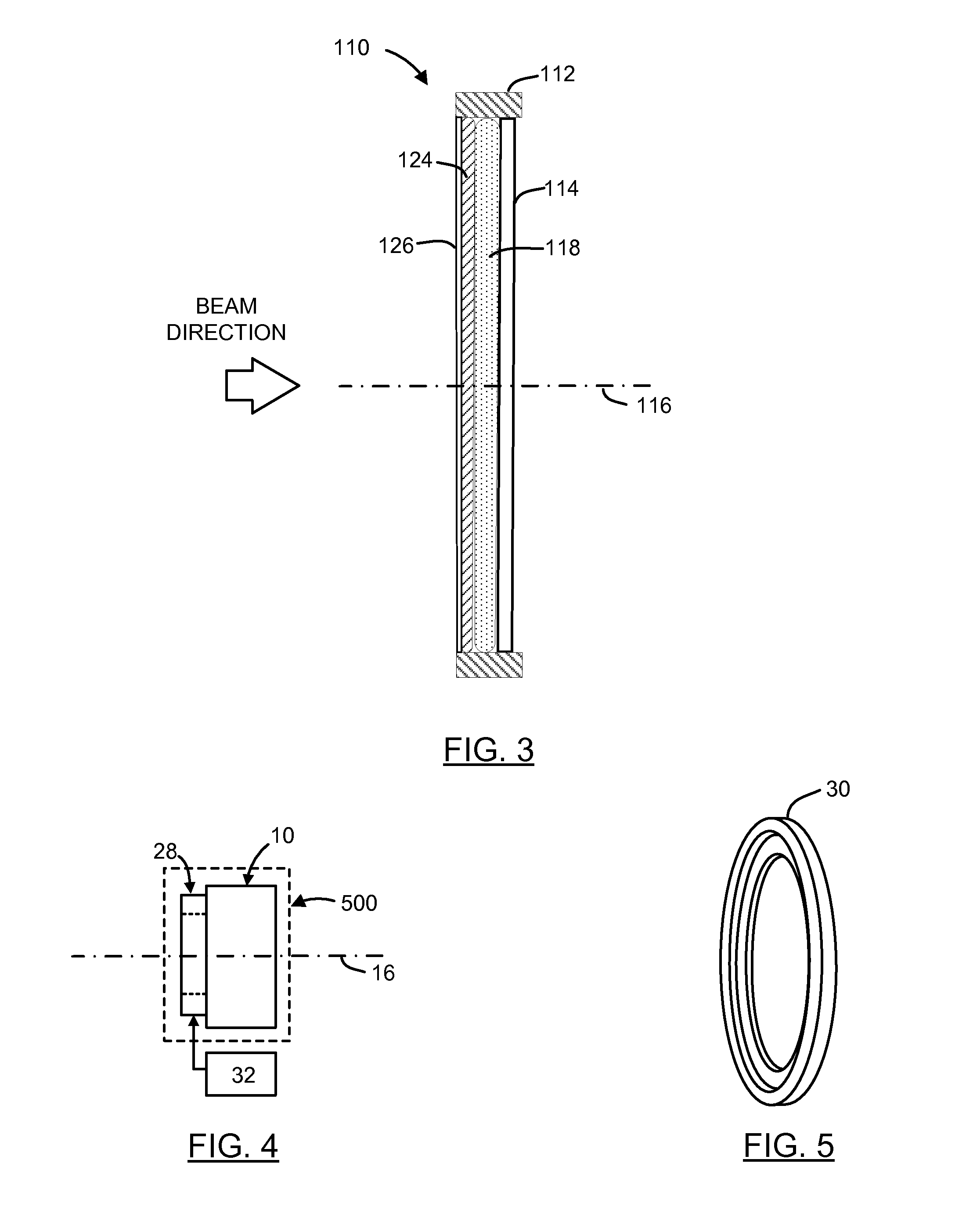
[0039]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2A, there is shown a perspective and cross sectional side views respectively of a lens element 10. The lens element 10 includes a housing 12, two light transmissive elastic solid lenses, and a light transmissive cover 14. In the illustrated embodiment, the housing 12 is a simple ring-like construction into which the cover 14 is press-fit. The two lenses are nested against the cover 14. Other constructions for the housing 12 are possible, as will be explained in detail below. Together, the two elastic solid lenses and the cover 14 define an optical axis 16.
[0040]The light transmissive cover 14 may be provided by a solid light transmissive material with or without optical power, or by a deformable membrane capable of exhibiting curvature for definition of a lens surface having optical power, such as that illustrated in FIG. 2B. In the illustrated embodiment, the light transmissive cover 14 is a solid piece of glass.
[0041]A first elastic solid lens 18 is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com