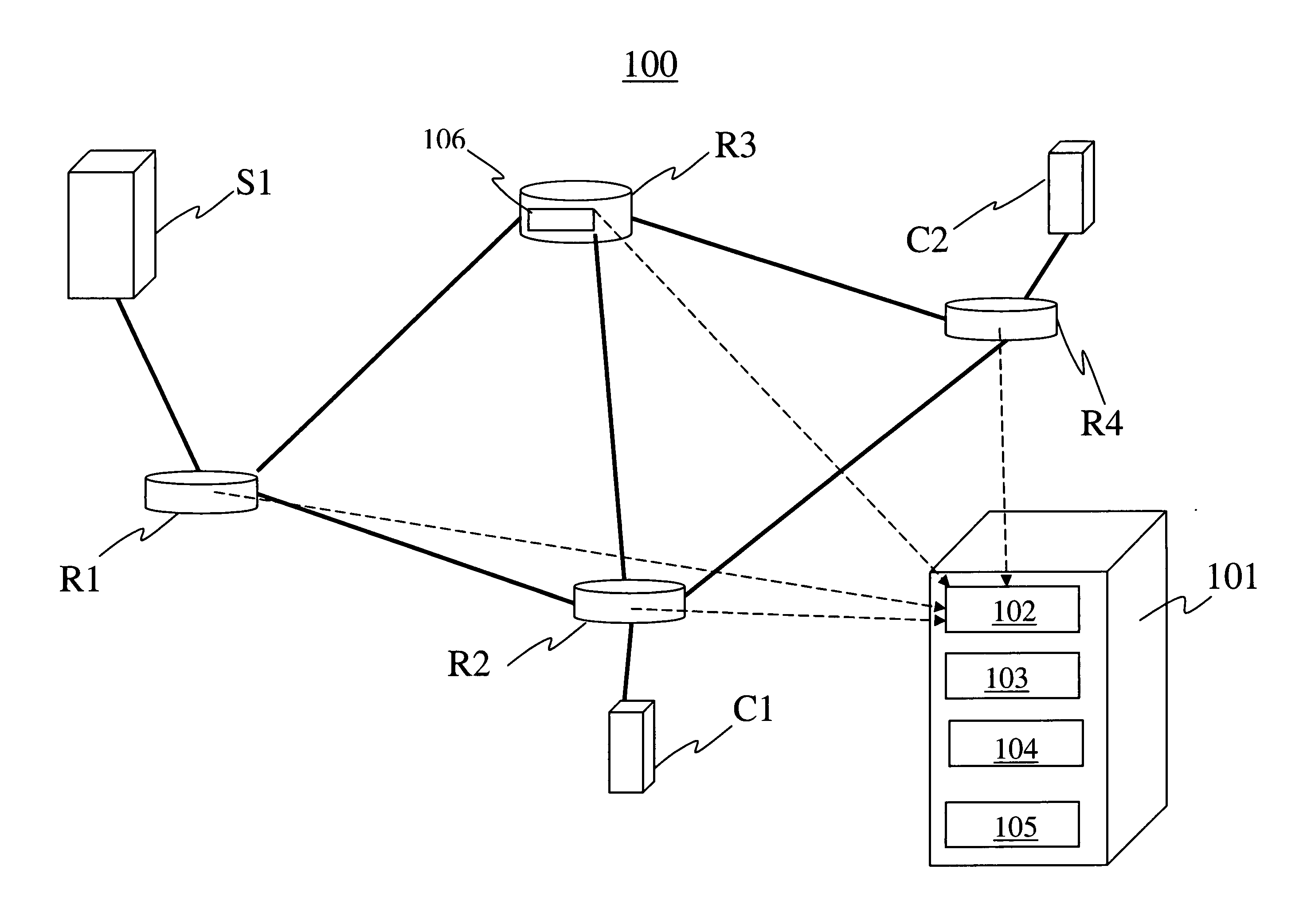
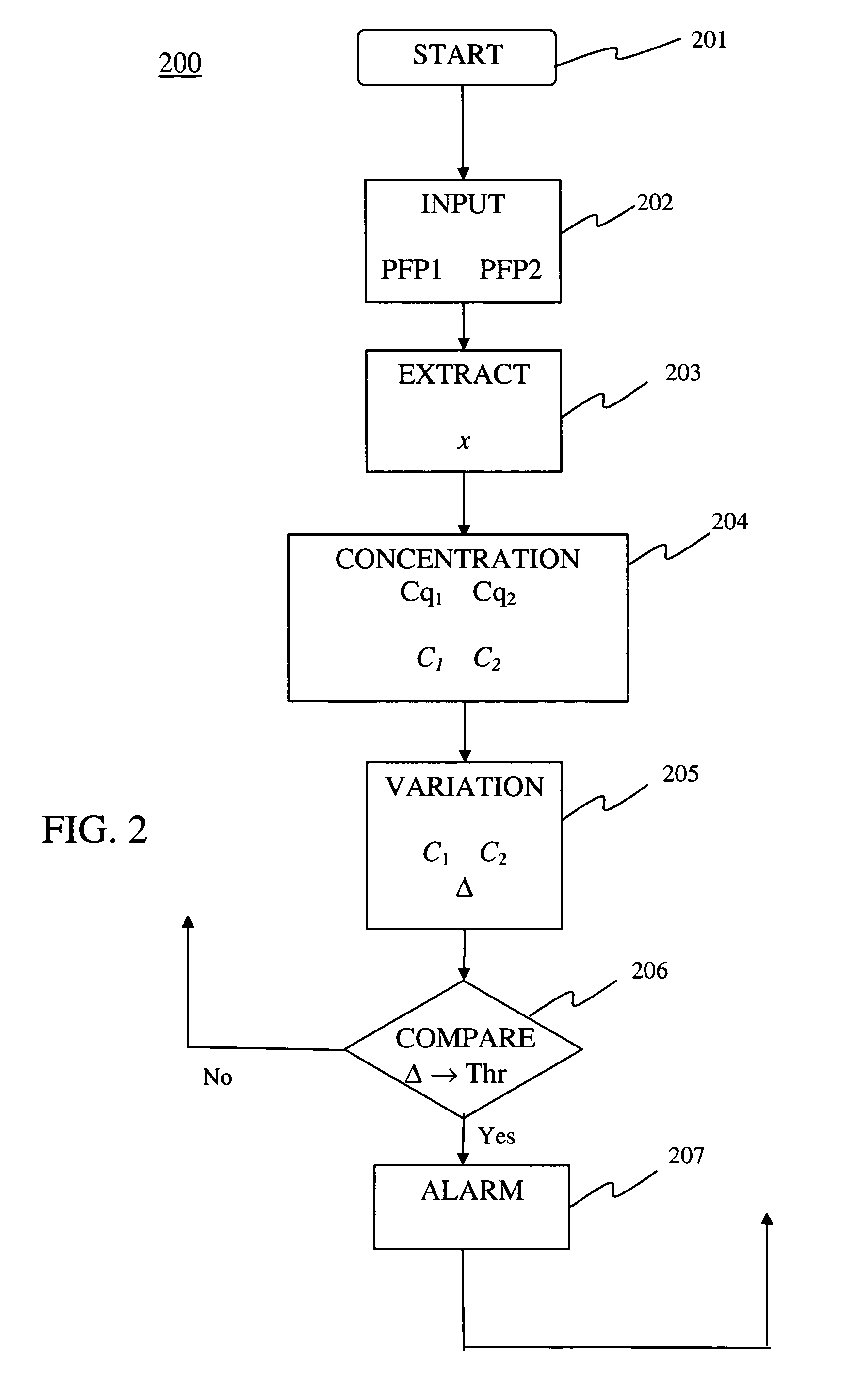
Method of detecting anomalies in a communication system using symbolic packet features
a communication system and feature detection technology, applied in the field of anomaly detection on packet switched communication systems, can solve the problems of insatiable known solutions, computational complexity and memory requirements, and the inability to describe the normal traffic in the communication network by stable, and achieve the reduction of computational complexity and memory requirements, and the effect of increasing reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0064]A first embodiment 300 of the detection method 200, is described herein below with reference to FIG. 3. Symbolic feature x is one of the above identified symbolic features extracted from flows of network packets, at a chosen network node, in (elementary) short time intervals of length ΔT, in some time units (e.g., ΔT is comprised 1 s−5 min), where ΔT can vary in time. In particular, as indicated above x can be the packet rate Rpacket, the average packet size Nsize, or the byte rate Rbyte suitably grouped, quantized, or hashed into a smaller set of symbolic values. For Rpacket and Rbyte, the zero values are allowed, if there are no packets with chosen features in the considered short time interval, whereas Nsize has to be positive and is not defined if in the considered short time interval there are no packets with chosen features. If the features relate to individual network packets, then ΔT corresponds to the packet inter-arrival time. The corresponding sequence of samples of...
second embodiment
[0096]According to a second example of the detection method 200, the two successive windows are defined in a different way with respect to the first embodiment.
[0097]According to this second embodiment, in step 202 at time j+1, the following first and second sample segments corresponding to packet flow portions PFP1 and PFP2, respectively, are considered:
(xi)i=mj+1−nj+1mj (22)
(xi)i=mj+1−nj+1mj+1 (23)
where the first segment (22) is the initial part of the second segment, without the ending part (xi)i=mj+1mj+1 or, equivalently, the last part of the preceding segment (xi)i=mj+1−nj+1mj+1, without the initial part (xi)i=mj−nj+1mj+1−nj+1.
[0098]FIG. 6 shows schematically two successive sliding windows W1 and W2, as in FIG. 4, with a difference that the first packet flow portion PFP1 is now associated with a shortened window W1′, extending from τ to T, whereas the second packet flow portion PFP2 is associated with W2 as in FIG. 4. In this way, the past data leaving the current sliding win...
third embodiment
[0101]In a third embodiment of the detection method 200, a moving window of increasing length is defined. Such moving window extends from a chosen initial time up to the current time, and each time, the ending point of the moving window advances τ units of time, where τ determines the resolution in time for detecting the anomalous changes in traffic. FIG. 7 shows schematically three exemplary successive windows Wj+1, and Wj+2 drawn in accordance with this third embodiment of the detection method 200. In FIG. 7, t denotes a generic time.
[0102]At each time, the packet flow portions PFP1 and PFP2 correspond to two successive moving windows. Accordingly, for a generic window index j, the packet flow portion PFP1 is defined by the segment
(xi)i=1mj (24)
which is associated with the jth moving window containing mj samples, and the packet flow portion PFP2 is defined by the segment
(xi)i=1mj+1 (25)
which is associated with the (j+1)th moving window containing mj+1 samples.
[0103]According to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com