Dual-axis planar motor providing force constant and thermal stability
a planar motor and force constant technology, applied in the direction of dynamo-electric machines, electrical apparatus, magnetic circuits, etc., can solve the problems of thermal drift, inconvenient component replacement, inaccurate positioning operation of the planar motor along the two axes of motion, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing thermal dri
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
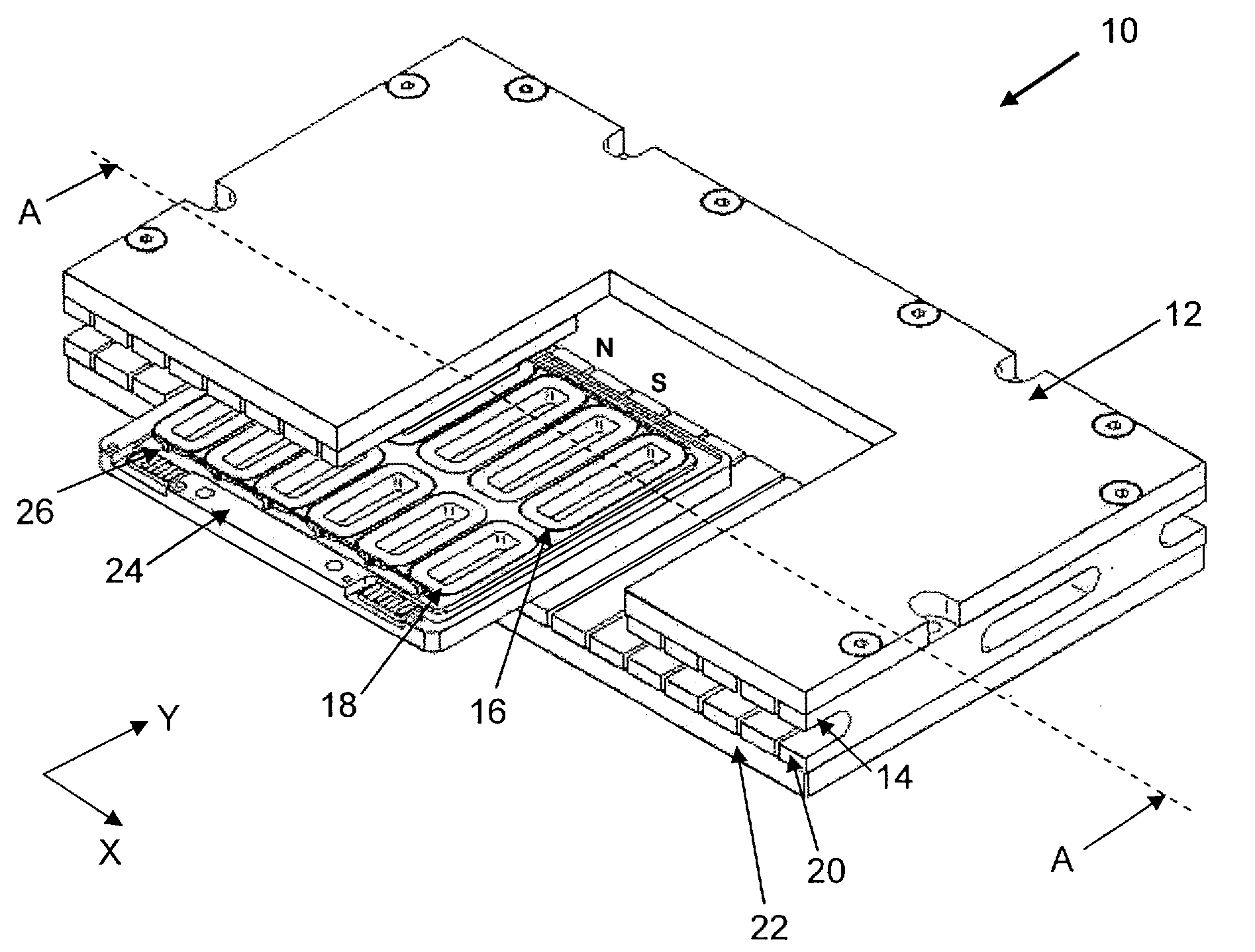
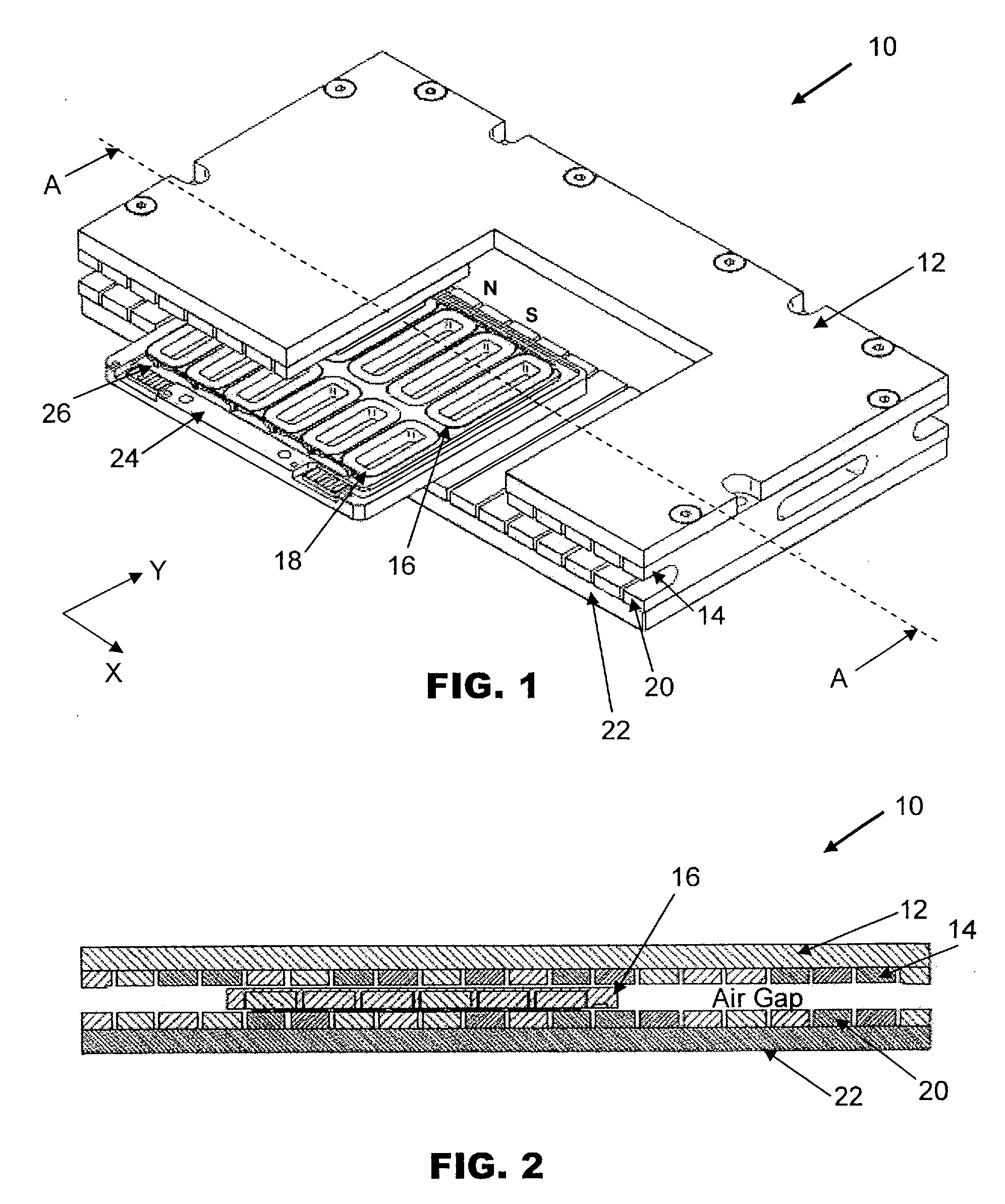
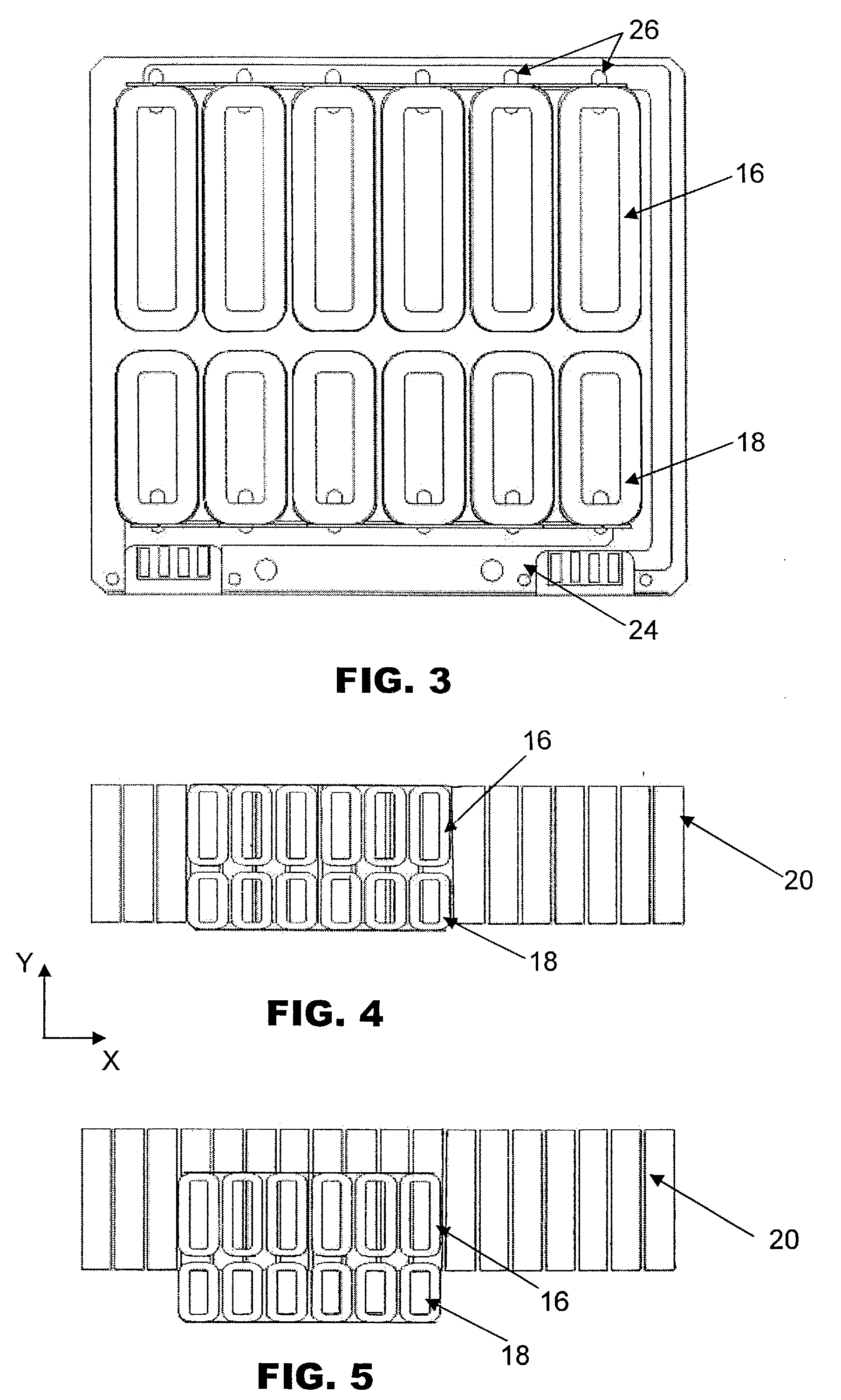
[0015]FIG. 1 is an isometric view of a multi-phase planar motor 10 according to the preferred embodiment of the invention with a portion of a top mount 12 and a first row of magnets 14 removed to reveal first and second sets of coils 16, 18 of a coil bracket 24. The planar motor 10 generally comprises the coil bracket 24 and a magnet assembly. The magnet assembly has first and second rows of magnets 14, 20 arranged along a first or X-axis and separated by a gap for generating magnetic flux lines between the rows of magnets. The first row of magnets 14 is mounted on the top mount 12 and the second row of magnets 20 is mounted on a bottom mount 22. Each row of magnets 14, 20 forms a continuous permanent magnetic track along the length of the top mount 12 and bottom mount 22 for guiding the movement of the coil bracket 24 located within the gap between the two rows of magnets 14, 20.
[0016]The first set of coils 16 is arranged along the X-axis corresponding to the length of the top and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com