Detonating cord and methods of making and using the same
a technology of detonating cords and fuses, which is applied in the direction of fuse detonation, explosion, blasting, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the velocity of detonation of detonating cords
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
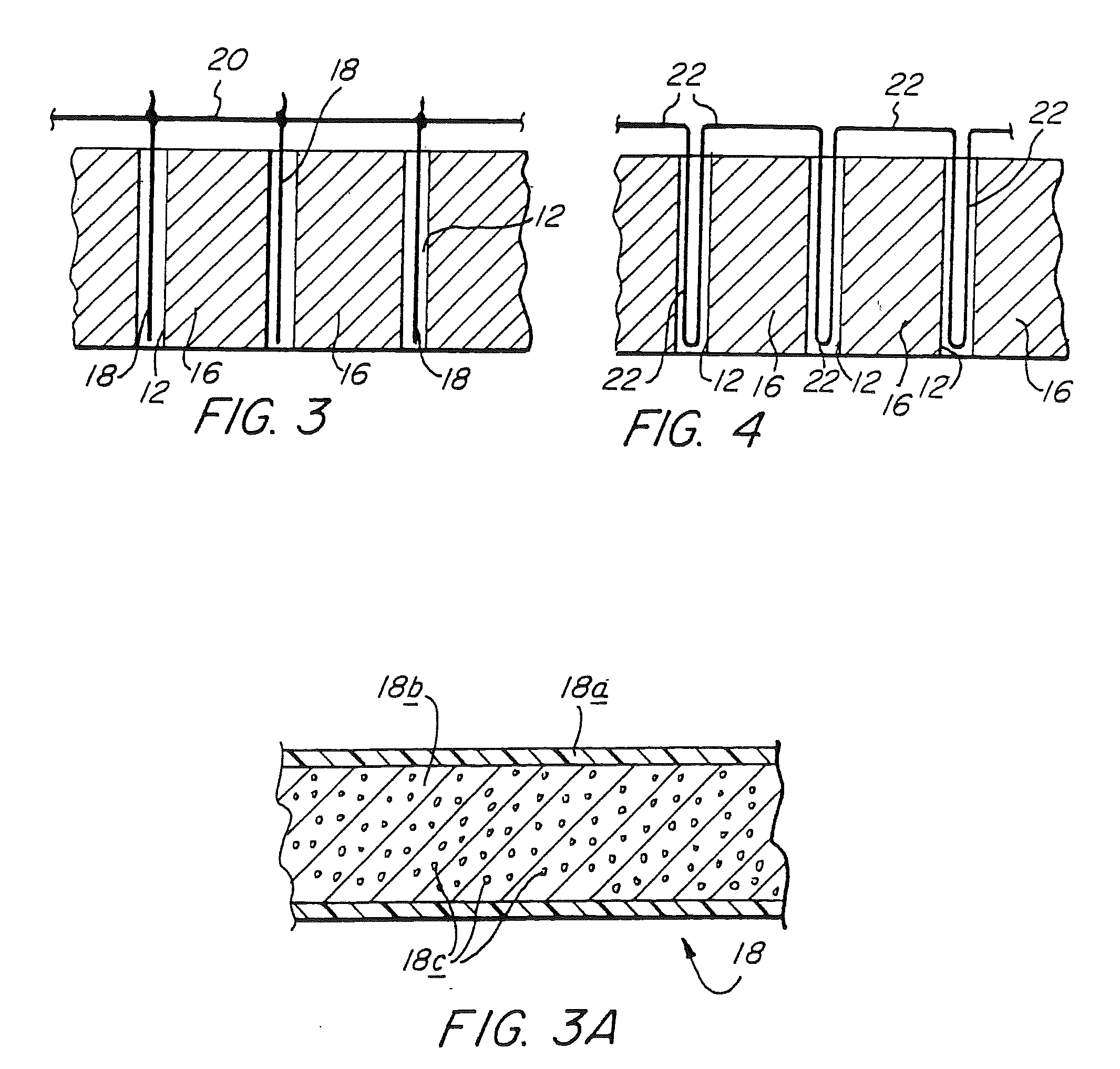
[0031]As noted above, the velocity of detonation of detonating cord can be controlled by mixing a diluent with the pulverulent explosive from which the explosive core of detonating cord is formed. By utilizing as the diluent inert particulate material or a second explosive less brisant than the first explosive, i.e., one having a lower velocity of detonation than the first explosive, the velocity of detonation of the detonating cord may be reduced. It has been discovered that by reducing the velocity of detonation, a reduction in the peak output pressures caused by detonation of the cord is attained without significantly affecting the total energy output of the cord. Such reduction of peak output pressure has been found to be highly desirable in certain circumstances, as it reduces undesired damage to areas of the rock immediately surrounding the cord. The benefits of the present invention are clearly shown, for example, in cutting what is referred to as “dimension stone” from in-gr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| velocities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com