Electric power source used with vehicles
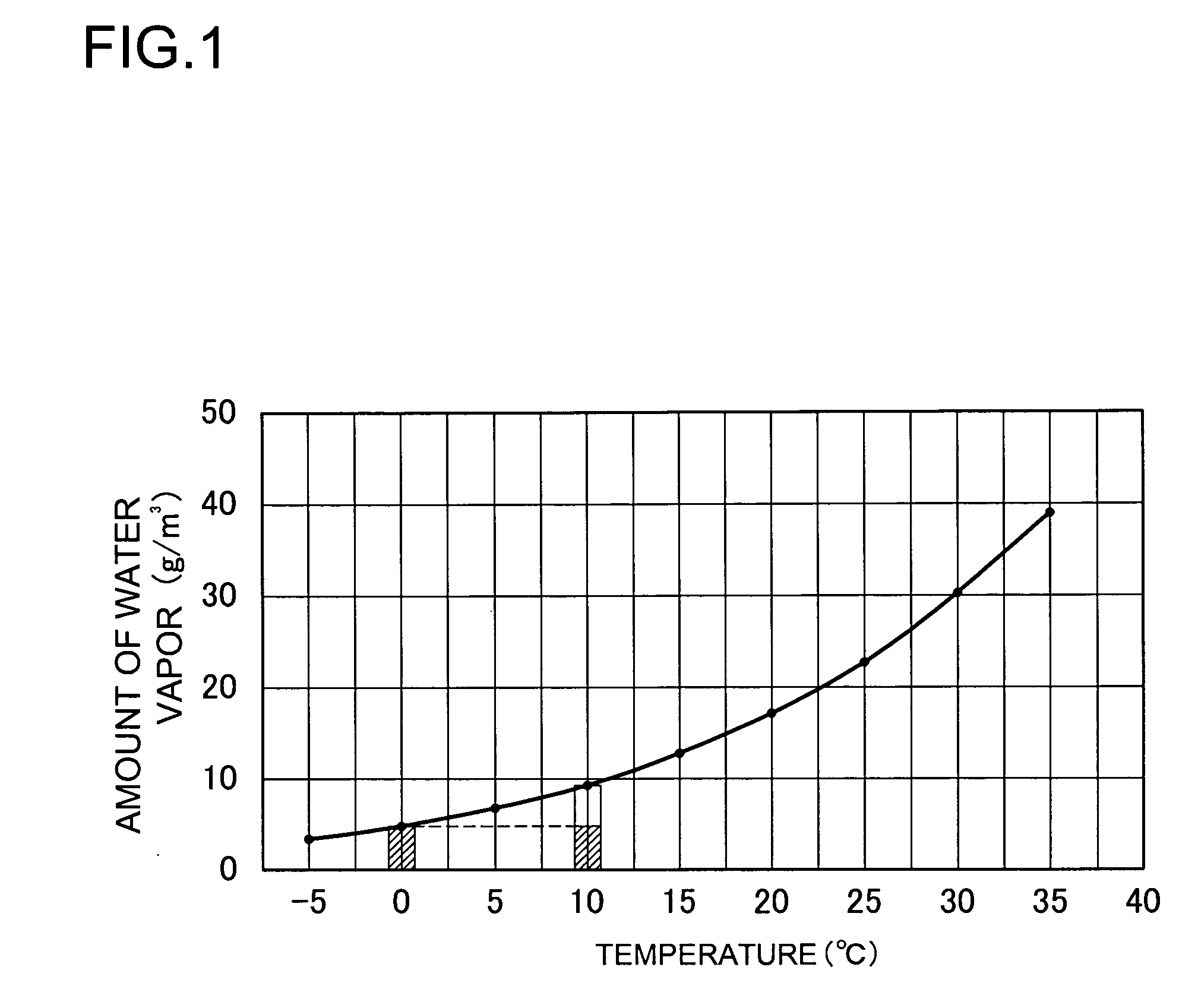
a technology of electric power source and vehicle, which is applied in the direction of cell temperature control, electrical equipment, cell components, etc., can solve the problems of shortening the life of the battery, dew formation, and inability to ensure the safety of the battery, so as to reduce the temperature elevation of the battery, simplify the structure, and achieve the effect of reducing the preset temperature of the plate temperature sensor 73
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
)
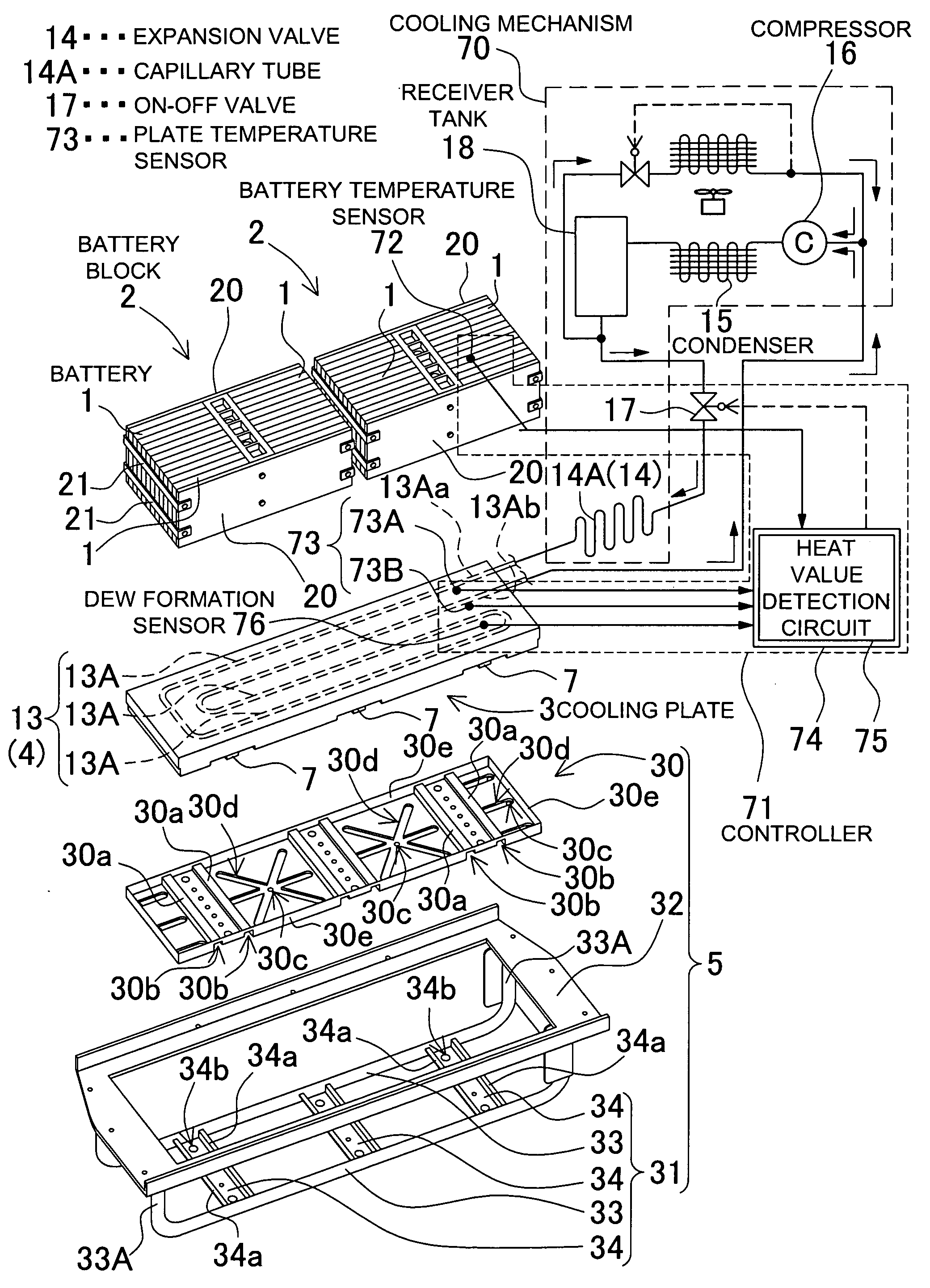
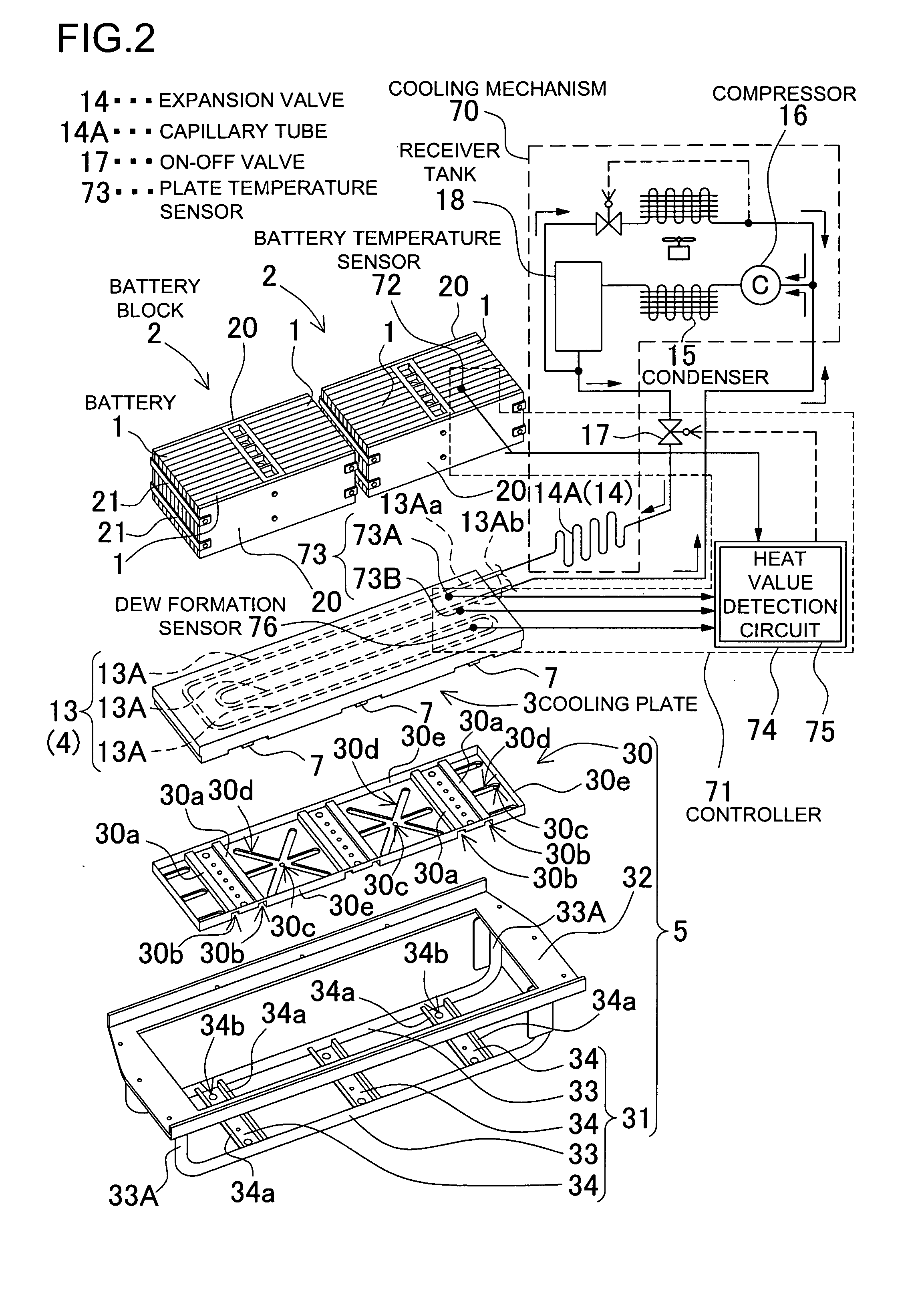
[0032]FIG. 2 through FIG. 5 show an electric power source used with a vehicle. FIG. 3 through FIG. 5 show a detail view of the electric power source illustrated in a schematic, exploded, perspective view in FIG. 2. The electric power source shown in these drawings includes: a battery block 2 composed of a rechargeable battery 1; a cooling plate 3 thermally coupled with and cooling the battery block 2; a cooling mechanism 70 for cooling the cooling plate 3; a controller 71 for controlling the cooling mechanism 70 to switch the cooling plate 3 into a cooled state and an uncooled state; and a frame structure 5 to which the cooling plate 3 is fixed. The electric power source forcibly cools the battery block 2 from a bottom face of the battery block by means of the cooling plate 3.
[0033]In regard to the cooling plate 3, a top surface plate 11 and a bottom plate 12 are interconnected at a periphery to define an interior portion as a sealed chamber 10. Incorporated in the sealed chamber 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com