Non-Standard Amino Acid Conjugates of Amphetamine and Processes for Making and Using the Same
a technology of amino acid conjugates and amphetamine, which is applied in the field of non-standard amino acid conjugates of amphetamine and processes for making and using the same, can solve the problems of increased blood pressure and heart rate, euphoric drug “, and cardiovascular effects, and reduce abuse liability. , to achieve the effect of preventing the rebound effect, reducing or eliminating the pharmacological activity of amphetamine, and preventing cardiovascular stress and euphoria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
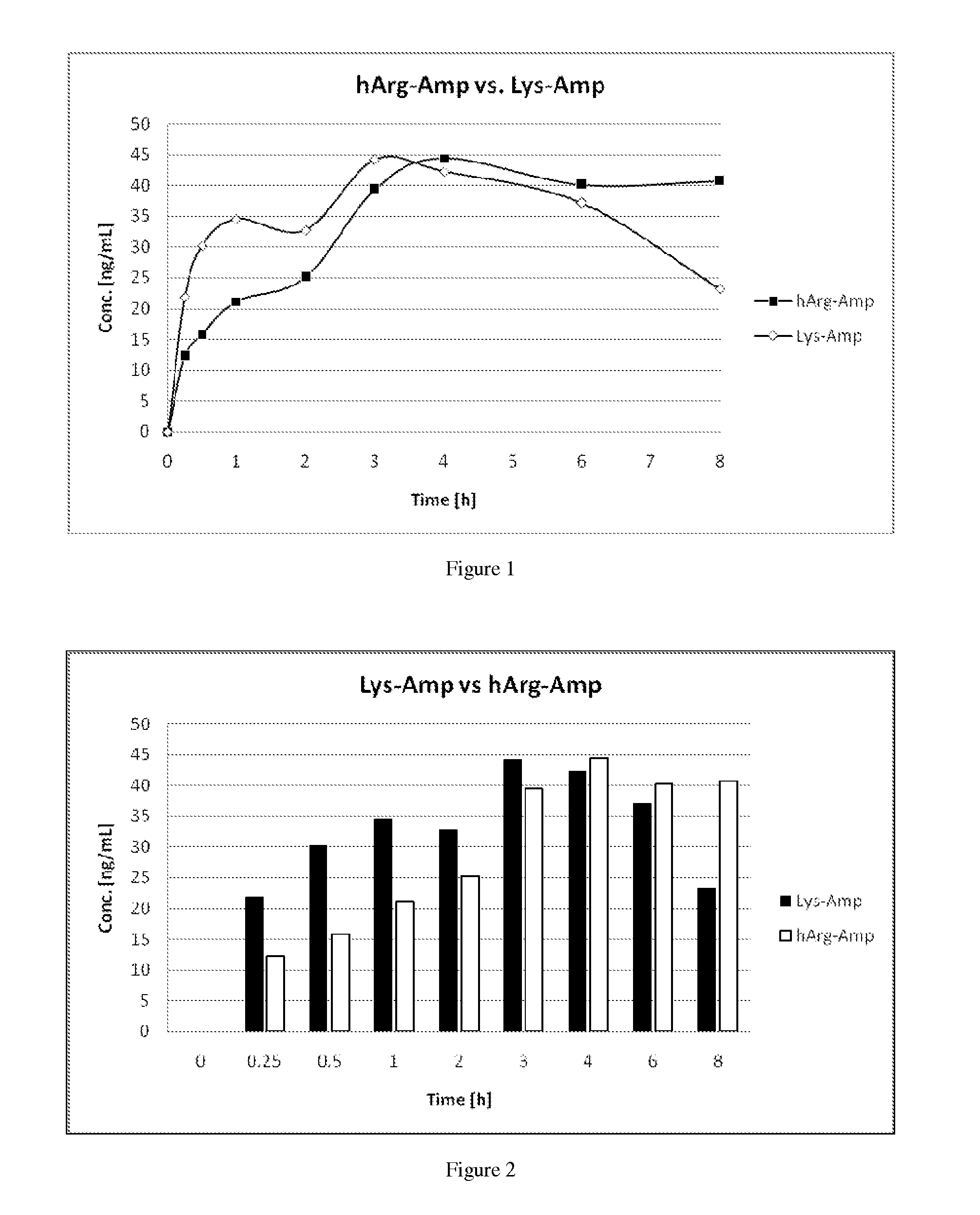
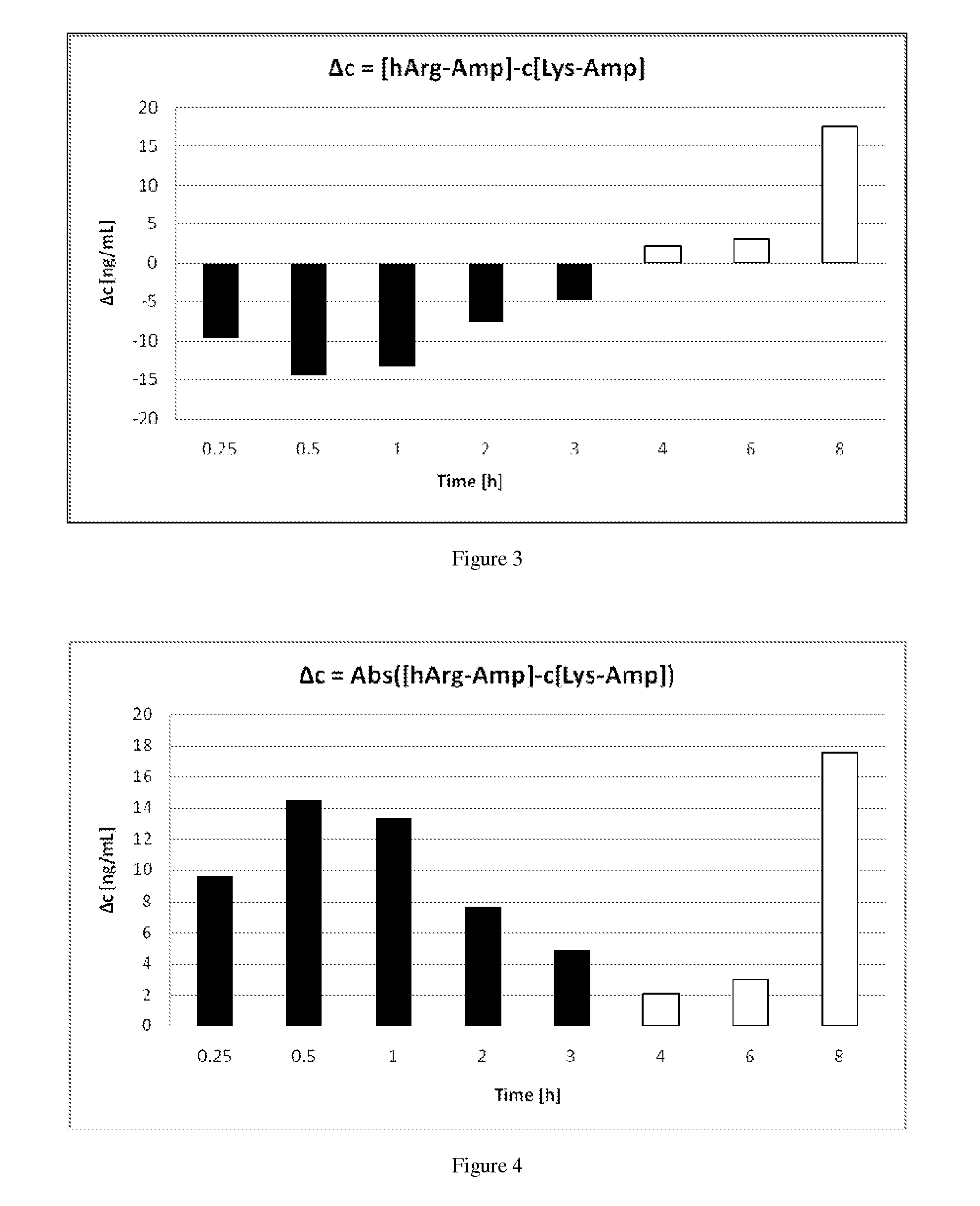
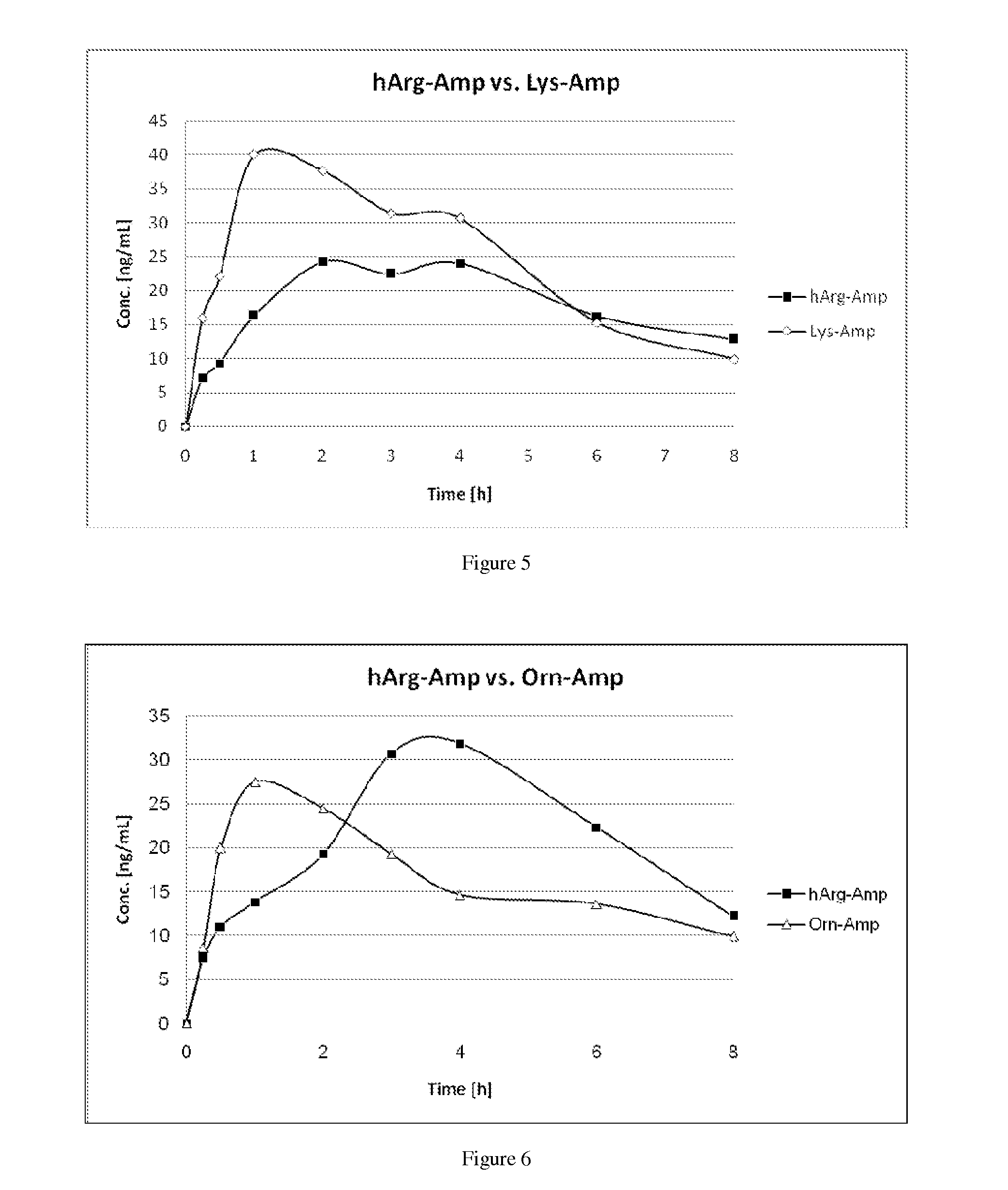
Comparative Study of Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Released D-Amphetamine Following Administration of a Non-Standard Amino Acid Conjugate (hArg-Amp) and a Standard Amino Acid Conjugate (Vyvanse™, Lys-Amp)
[0120]The Pharmacokinetic Parameters of D-Amphetamine Following Oral Administration of a non-standard amino acid conjugate of the present technology and a standard amino acid conjugate, Vyvanse™ (Lys-Amp), commercially available from Shire, Incorporated of Wayne, Pa. are studied in this example. The non-standard amino acid conjugate used in this example is the hydrochloride salt of hArg-Amp. The results are recorded in the table below:
TABLE 1Non-standard amino acidParameter% amp1Vyvanse ™ % total Amp2AUC0-8 h94%100%AUC0-4 h77%100%AUCinf95%100%Cmax76%100%Tmax400% 100%1Percent amphetamine released relative to Vyvanse ™ (at an equimolar concentration of amphetamine contained in the non-standard amino acid prodrug compared to the total amphetamine contained in Vyvanse ™)2Percent ampheta...
example 2
Preparation of Boc-Orn(Boc)-Amp
[0123]Boc-Orn(Boc)-OH (1.5 g, 4.518 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (15 ml). EDCI (1.299 g, 6.777 mmol), NHS (0.572 g, 4.969 mmol), d-amphetamine (0.732 g, 5.422 mmol) and DIEA (0.87 ml, 4.969 mmol) were then added sequentially. The clear reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 16 hours (hrs). The reaction mixture was quenched with pH 3 water (40 ml), and the product was extracted with EtOAc (3×70 ml). The combined extracts were washed with pH 3 water, saturated NaHCO3 followed by water. The EtOAc layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Solvent was removed to obtain 1.82 g of protected amide as a white solid.
[0124]The white solid was analyzed by 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ. The results show 1.1-1.2 (m, 3H, Amp α-CH3), 1.3-1.5 (m, 18H, Boc CH3), 1.6-1.8 (m, 4H, Orn δ CH2), 2.75 (m, 2H, Amp β CH2), 3.05-3.1 (m, 2H, Orn δ CH2), 3.2 (m, 1H, Amp a CH), 4.1 (m, 1H, Orn α CH), 7.1-7.4 (m, 5H, Amp Ar—H). These NMR shifts are consistant with the structure of Orn-Am...
example 3
Preparation Of Orn-Amp
[0125]Boc-Orn(Boc)-Amp (1.35 g, 3 mmol) was dissolved in EtOAc (200 ml) and to the slightly cloudy solution was added MsOH (0.43 ml, 6.6 mmol) drop wise. The reaction mixture became a clear solution which was stirred at room temperature for approximately 20 hrs. Solvent was removed and the residue was triturated in hexanes. Off-white solid product was formed which was filtered under vacuum and washed with hexanes. The solid was dried in vacuum oven for 20 hrs to obtain 0.88 g of Orn-Amp.2MsOH (1-ornithine-d-amphetamine dimesylate).
[0126]The product obtained was tested by 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ. The result shows 1.1 (m, 3H, Amp α-CH3), 1.4-1.6 (m, 4H, Orn β, γ CH2), 2.35 (s, 6H, CH3SO3H CH3), 2.6-2.8 (m, 4H, Amp β and Orn δ), 3.75 (m, 1H, Amp α), 4.05 (m, 1H, Orn α), 7.1-7.3 (m, 5H, Amp Ar—H), 7.6-8.5 (br peaks, amide and amine); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ 18.45 (Orn γ), 21.49 (Orn β), 27.30 (Amp β), 37.38 (Amp CH3), 37.77 (Amp α), 41.20 (Orn δ), 51.54 (Orn α), 125.29 (p-A...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| attention deficit disorder | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| disorder | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| prodrugs/compositions | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com