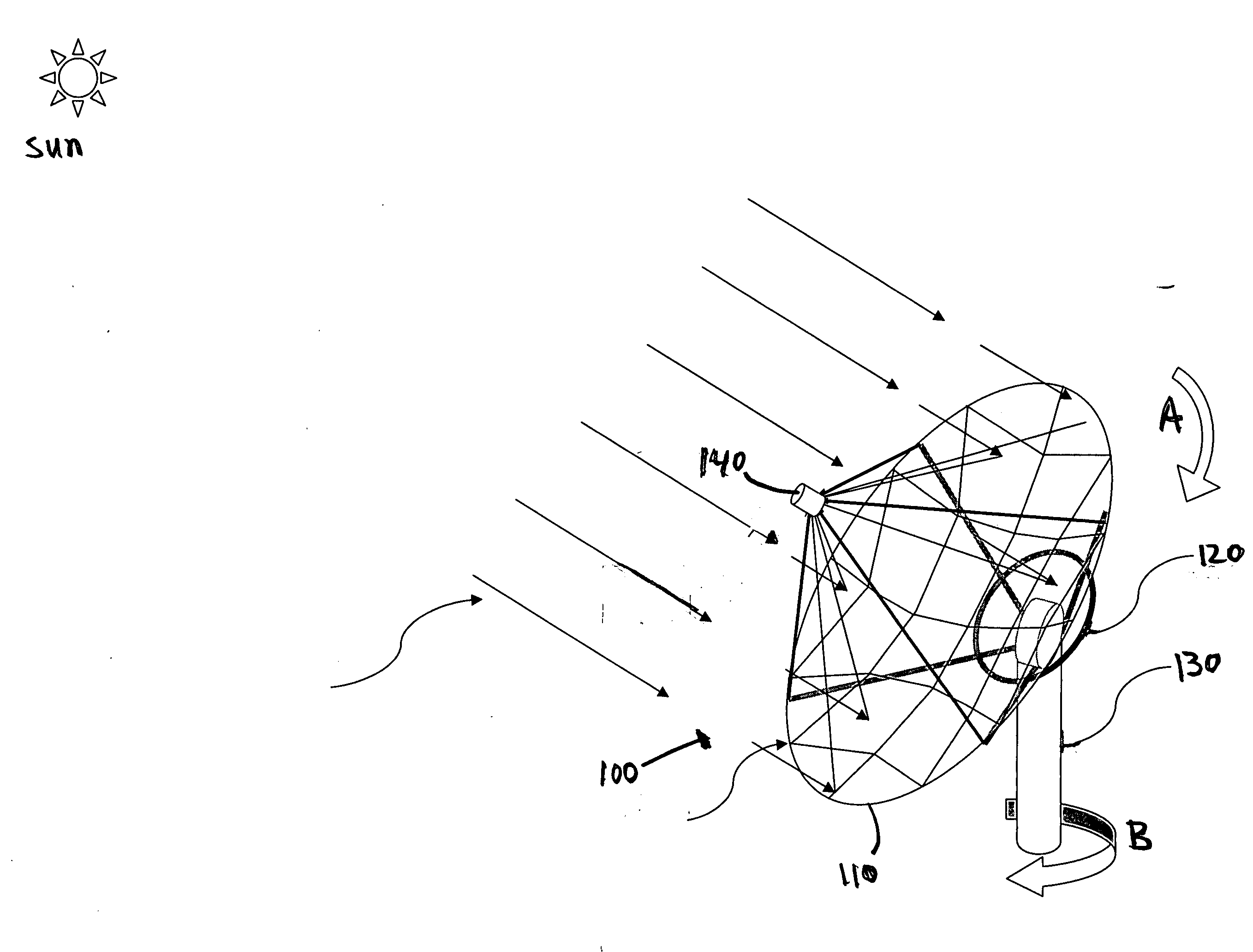
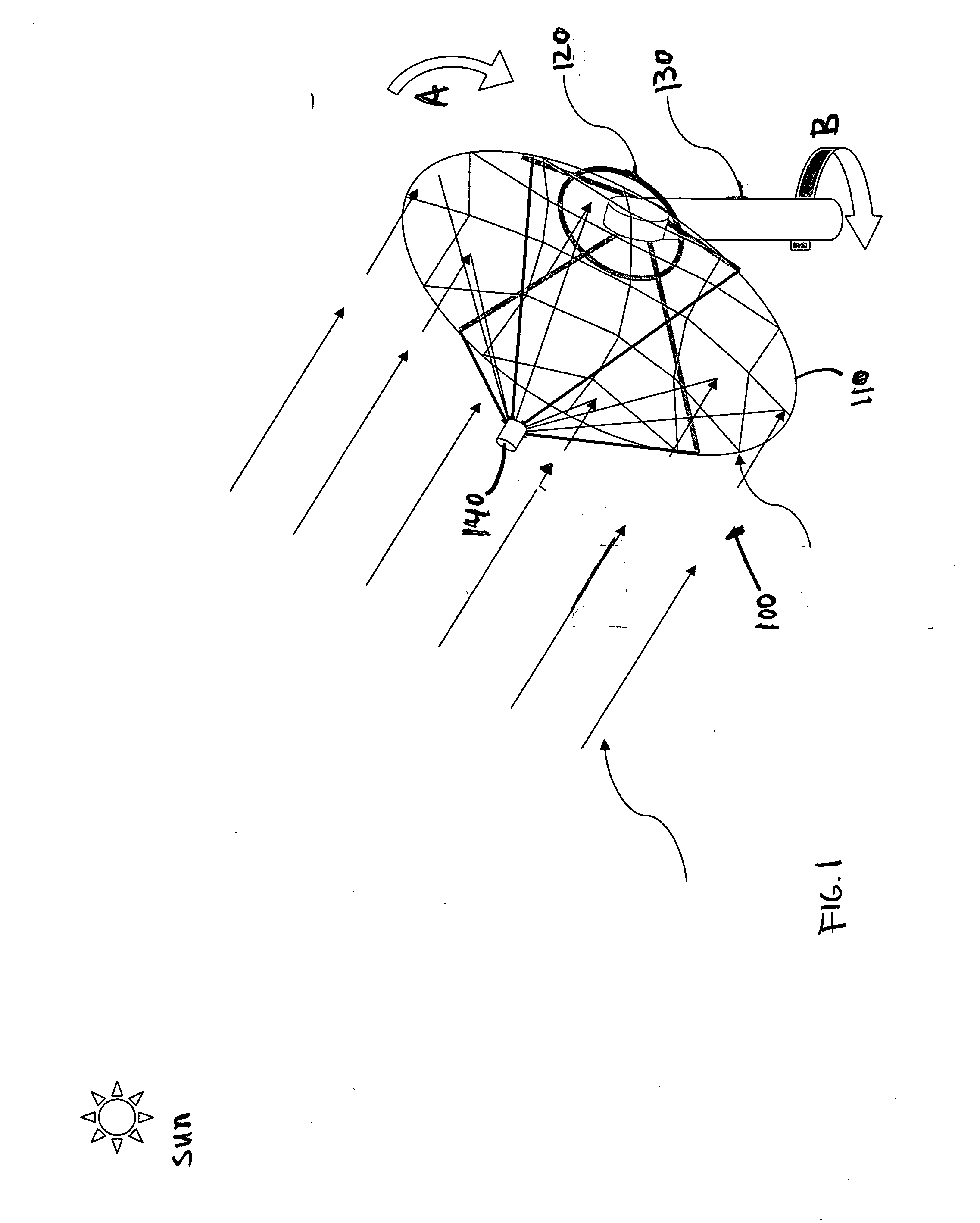
Aligned multiple flat mirror reflector array for concentrating sunlight onto a solar cell
a technology of solar cells and mirror reflectors, applied in solar heat systems, solar thermal energy generation, light and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of complex, known reflector arrays, and thus expensive manufacture and deployment, and achieve the effect of better appreciation of contributions to the ar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0044]The triangular configuration of the second embodiment is further shown in FIG. 6A. Panel 515 is mounted to the outer ring 550 at contact points 550c and 550d, and to the inner ring 540 at contact point 540e. Connection between the panel 515 and the contact point 540e may include bolting the panel 515 to the contact point 540e by means of bolt 600. Space between the contact point 540e and the panel 515 provides adjustability to the orientation of the panel 515.
[0045]In accordance with the second embodiment of the invention, the inner and outer rings 540 and 550 are aligned concentrically and supported by a support frame 610. To achieve a concave structure, the outer ring 550 is disposed in a plane above the inner ring 540 relative to a tilt axis 620.
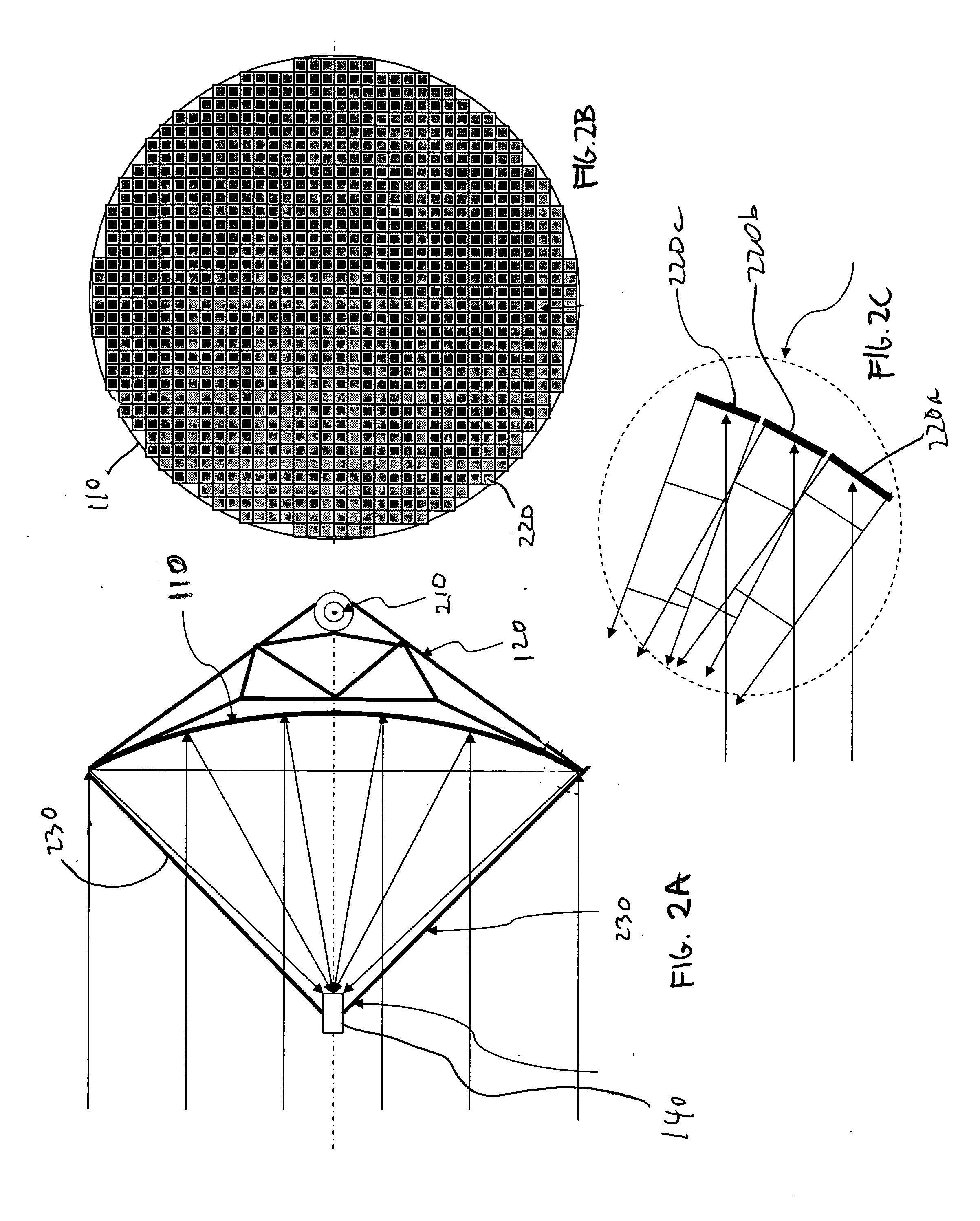
[0046]A third alternative embodiment of the invention is shown in FIGS. 7A and 7B. A square concentrating platform 700 includes a 32×32 array of mirrors 710 supported by a flat support structure 720. As shown in FIG. 8, mirrors 710 ...
third embodiment
[0055]the invention shown in FIGS. 7A and 7B and in FIG. 8 provides a 32×32 array of 1024 square mirrors d 710 distributed on the flat support structure 720. In this configuration there is provided a space between adjacent mirrors to avoid one mirror blocking the reflected light of the adjacent mirror. The minimum space between the edges of two adjacent mirrors is calculated as
v=d′ sin(θ / 2)tan θ, (4)
where d′ is the mirror width described in equation (2) and θ is the angle between incident light and reflected light. For the flat structure, θ is simply calculated as following.
θ=tan−1(R / H). (5)
In case of a tilt angle θ=45°, the mirror reduced width d′=0.765d, space v=0.383, d′=0.293d, sunlight projection d″=0.707d and cell width v+d″=d. The values for other tilt angles are listed in Table I shown in FIG. 11. As the mirror is tilted, the space between adjacent mirrors becomes larger and sunlight projection smaller. The cell width as the sum of the two is unchanged. The mirrors are dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com