Single Molecule Detection Using Molecular Motors
a single molecule and molecular motor technology, applied in the direction of specific use bioreactors/fermenters, organic chemistry, after-treatment of biomass, etc., can solve the problems of non-specific binding, requirement, and inconvenient use of dna hybridization assays,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
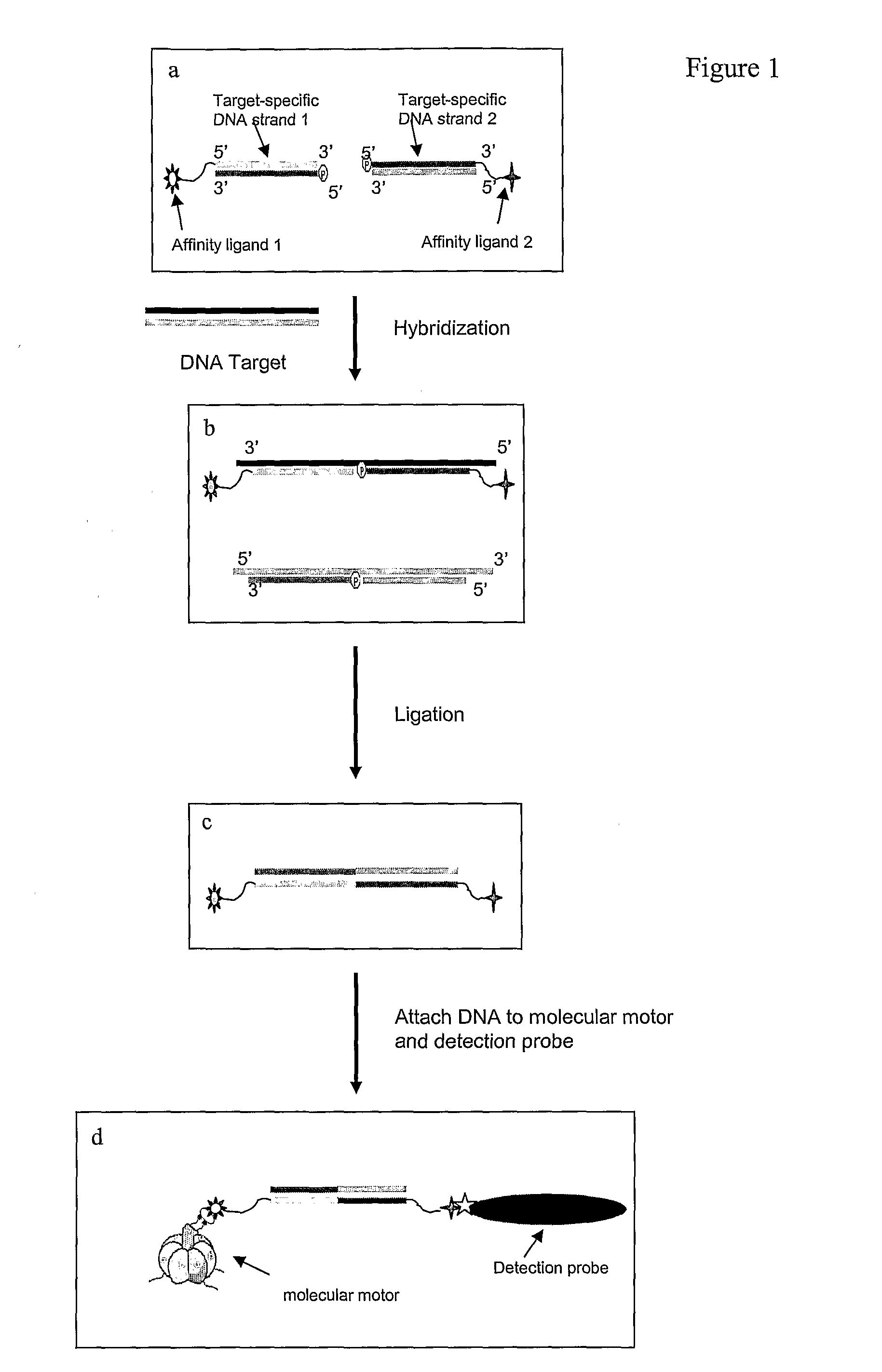
[0059]As shown in FIG. 1, one embodiment of the disclosed methods comprises the following steps:[0060]1. As indicated in FIG. 1a, a first affinity tag is attached to the 5′ end of the first target-specific DNA strand. A second affinity tag is attached to the 3′ end of second target-specific DNA strand (FIG. 1a).[0061]2. In FIG. 1b the first and second target-specific nucleic acid strands are hybridized to the target nucleic acid so that the 3′ end of the first target-specific strand is directly adjacent to the 5′ end of the second target-specific strand.[0062]3. In FIG. 1c the first and second target-specific DNA strands are ligated, to generate a double-stranded DNA sequence that contains the first and second affinity tags at each end.[0063]4. In FIG. 1d the double-stranded DNA that contains the affinity tags is then used as a bridge between a molecular motor and the detection probe used to detect the motion generated from the motor via the affinity tags. The first affinity tag att...
example 2
[0065]The following are two examples for detecting multiple target nucleic acids simultaneously:
[0066]Approach 1: Detection probes comprising gold rods of different sizes are used to detect ligated DNAs that are specific to pBR322 and Lambda DNA simultaneously using the following procedures:
1. Gold nanorods of different lengths are prepared because the length determines the wavelength of light scattered from it. The short and long gold rods are prepared to enable them to bind to digoxigenin (DIG) and dinitrophenyl-X (DNP-X), respectively.
2. Two pair of target-specific nucleic acids are prepared that are designed to hybridize specifically with pBR322 and Lambda DNA, respectively.
3. To enable the target-specific nucleic acid pairs to bridge between F1 ATPase and a gold nanorod, one target-specific nucleic acid from each pair is labeled with biotin while the other target-specific nucleic acid is labeled with DIG and DNP-X for pBR322 and Lambda DNA, respectively.
4. LCR is performed with...
examples 3
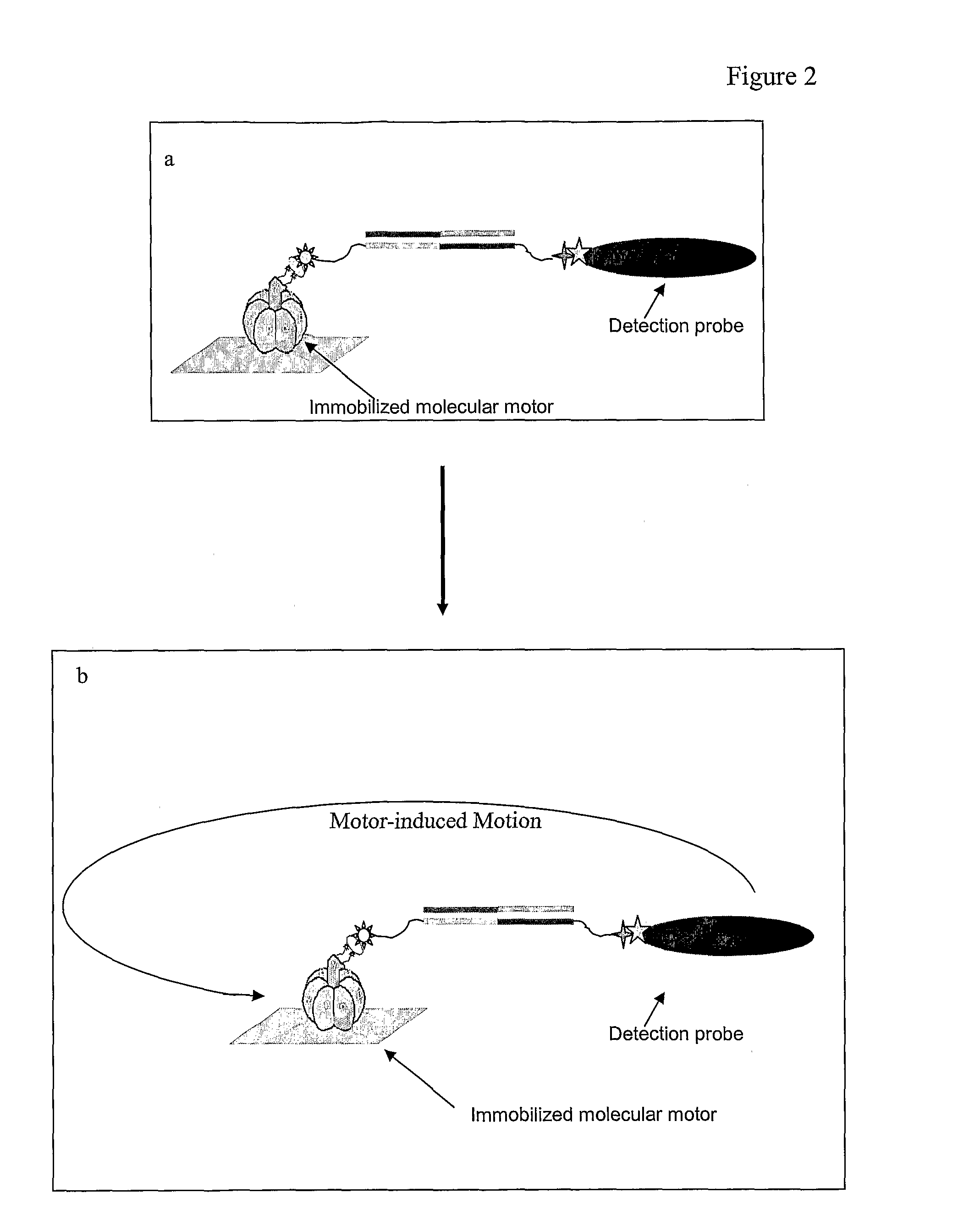
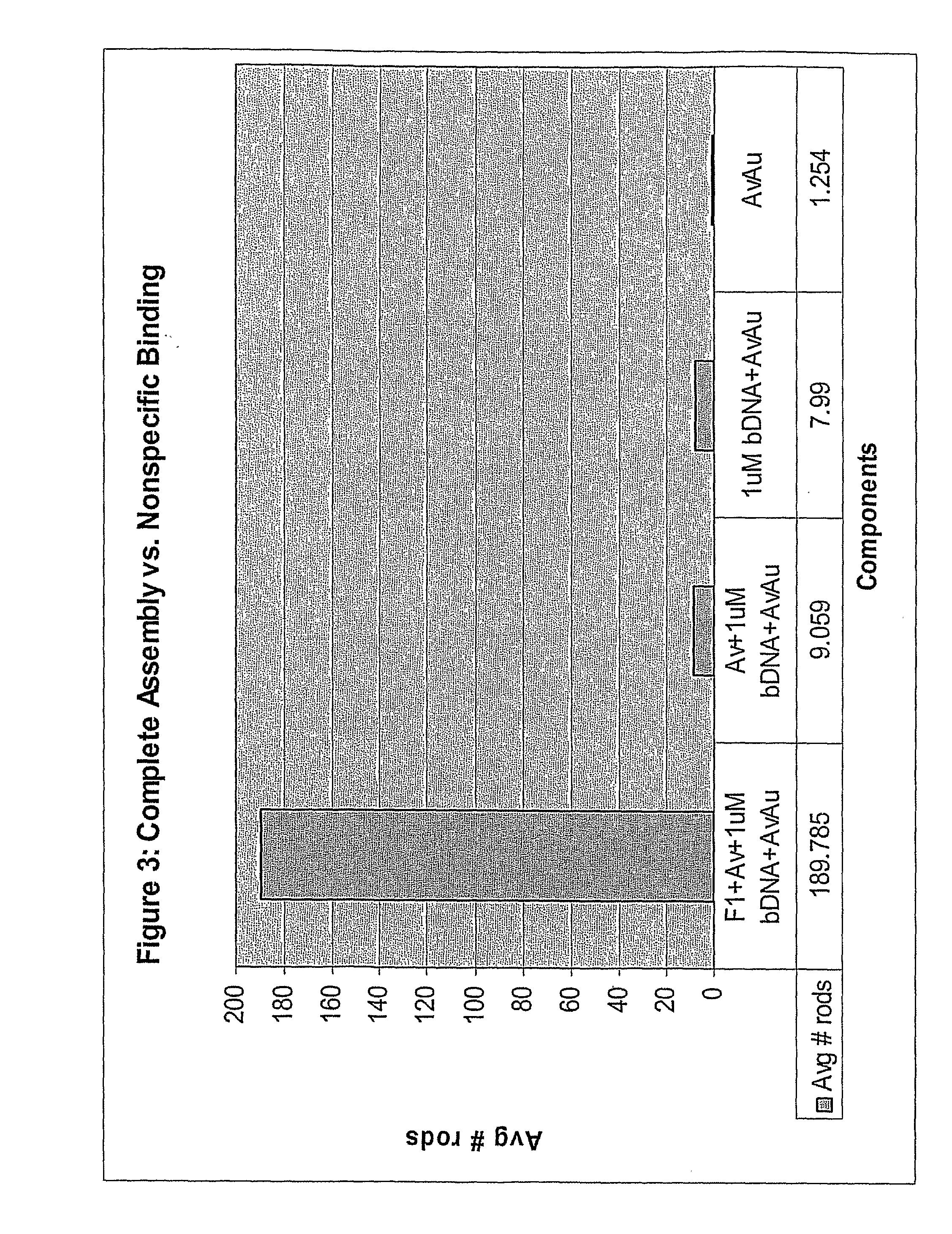
[0068]Four components of a molecular semaphore device were prepared separately: (1) a DNA bridge made from the target DNA; (2) modified F1-ATPase; (3) nickel-coated coverslips; and (4) coated nanorods. After these components were prepared, they were assembled into the device. Rotation of the nanorod attached to the device was observed if the DNA bridge was present to enable assembly of the device.
1. LCR Procedure to Prepare the DNA Bridge.
[0069]All oligonucleotides were synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), including those with biotin labels. The target DNA used in this example was F1 plasmid DNA (GenBank accession no. J01594). The two probes used were.
5′-CTTGCCGAAGGCATGAAAGTTAAGTG (Probe 1);andTACTGGCCGTATCCTGGAAGTTCCG-3′ (Probe 2).
[0070]These sequences are complimentary to the target in the following order:
CTTGCCGAAGGCATGAAAGTTAAGTGTACTGGCCGTATCCTGGAAGTTCCG.
[0071]The 5′ end of probe 1 contained covalently bound biotin. The 3′ end of the probe 2 contained covalently bou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength range | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com