Novel nucleotide and amino acid sequences, and assays and methods of use thereof for diagnosis of prostate cancer
a technology of amino acid sequences and nucleotides, applied in the field of new nucleotide and amino acid sequences, assays and methods of use thereof, can solve the problems of background art not teaching or suggesting markers, and achieve the effect of overcompensating deficiencies and high degree of differential detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
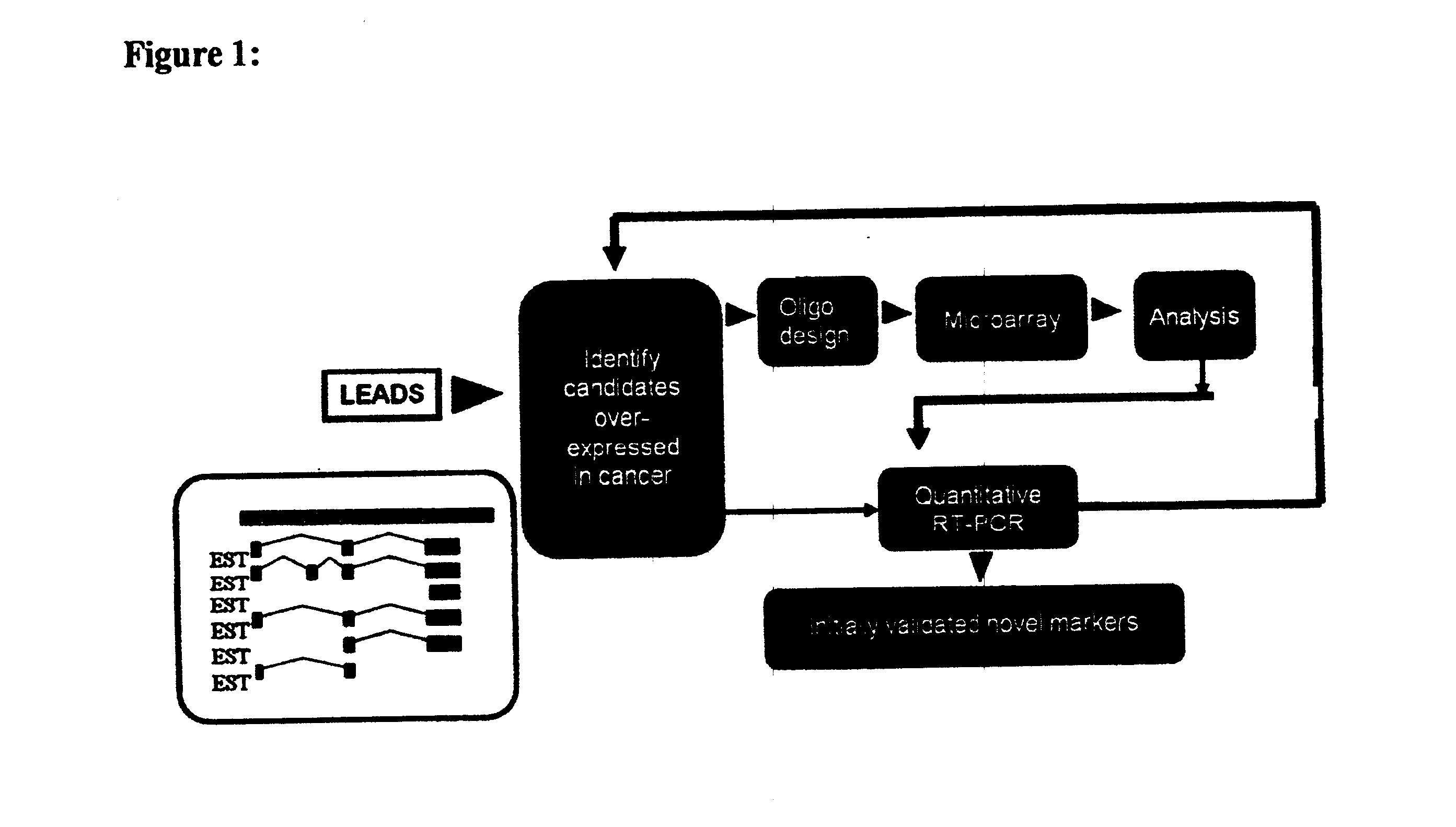
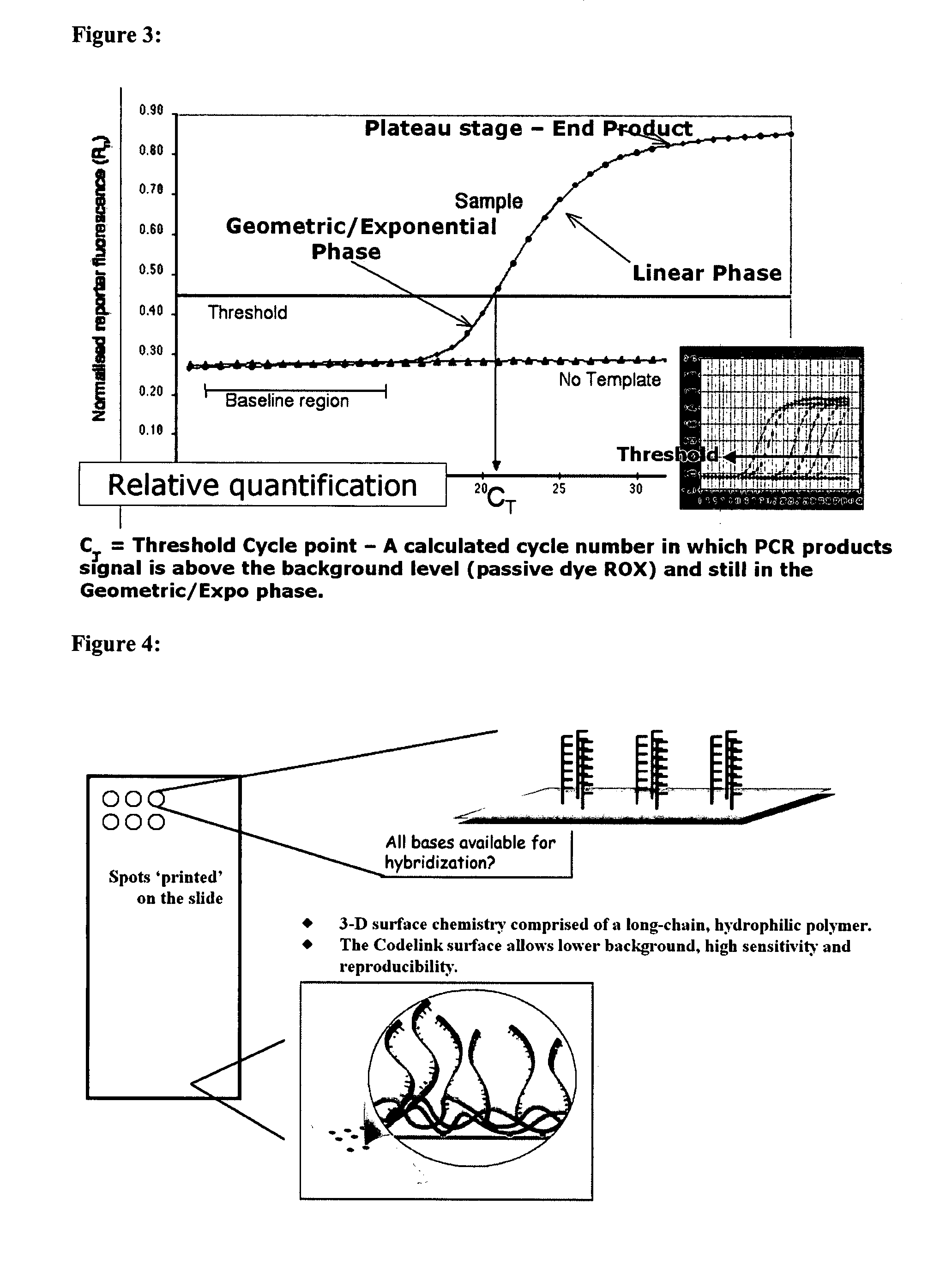
Identification of Differentially Expressed Gene Products
[0352] In order to distinguish between differentially expressed gene products and constitutively expressed genes (i.e., house keeping genes) an algorithm based on an analysis of frequencies was configured. A specific algorithm for identification of transcripts over expressed in cancer is described hereinbelow.
[0353] Dry Analysis
[0354] Library Annotation—Est Libraries are Manually Classified According to:
[0355] (i) Tissue origin
[0356] (ii) Biological source—Examples of frequently used biological sources for construction of EST libraries include cancer cell-lines; normal tissues; cancer tissues; fetal tissues; and others such as normal cell lines and pools of normal cell-lines, cancer cell-lines and combinations thereof. A specific description of abbreviations used below with regard to these tissues / cell lines etc is given above.
[0357] (iii) Protocol of library construction—various methods are known in the art for...
example 2
Identification of Genes Over Expressed in Cancer
[0362] Two different scoring algorithms were developed.
[0363] Libraries score—candidate sequences which are supported by a number of cancer libraries, are more likely to serve as specific and effective diagnostic markers.
[0364] The basic algorithm—for each cluster the number of cancer and normal libraries contributing sequences to the cluster was counted. Fisher exact test was used to check if cancer libraries are significantly over-represented in the cluster as compared to the total number of cancer and normal libraries.
[0365] Library counting: Small libraries (e.g., less than 1000 sequences) were excluded from consideration unless they participate in the cluster. For this reason, the total number of libraries is actually adjusted for each cluster.
[0366] Clones no. score—Generally, when the number of ESTs is much higher in the cancer libraries relative to the normal libraries it might indicate actual over-expression.
[0367] The a...
example 3
Identification of Tissue Specific Genes
[0383] For detection of tissue specific clusters, tissue libraries / sequences were compared to the total number of libraries / sequences in cluster. Similar statistical tools to those described in above were employed to identify tissue specific genes. Tissue abbreviations are the same as for cancerous tissues, but are indicated with the header “normal tissue”.
[0384] The algorithm—for each tested tissue T and for each tested cluster the following were examined:
[0385] 1. Each cluster includes at least 2 libraries from the tissue T. At least 3 clones (weighed—as described above) from tissue T in the cluster; and
[0386] 2. Clones from the tissue T are at least 40% from all the clones participating in the tested cluster
[0387] Fisher exact test P-values were computed both for library and weighted clone counts to check that the counts are statistically significant.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com