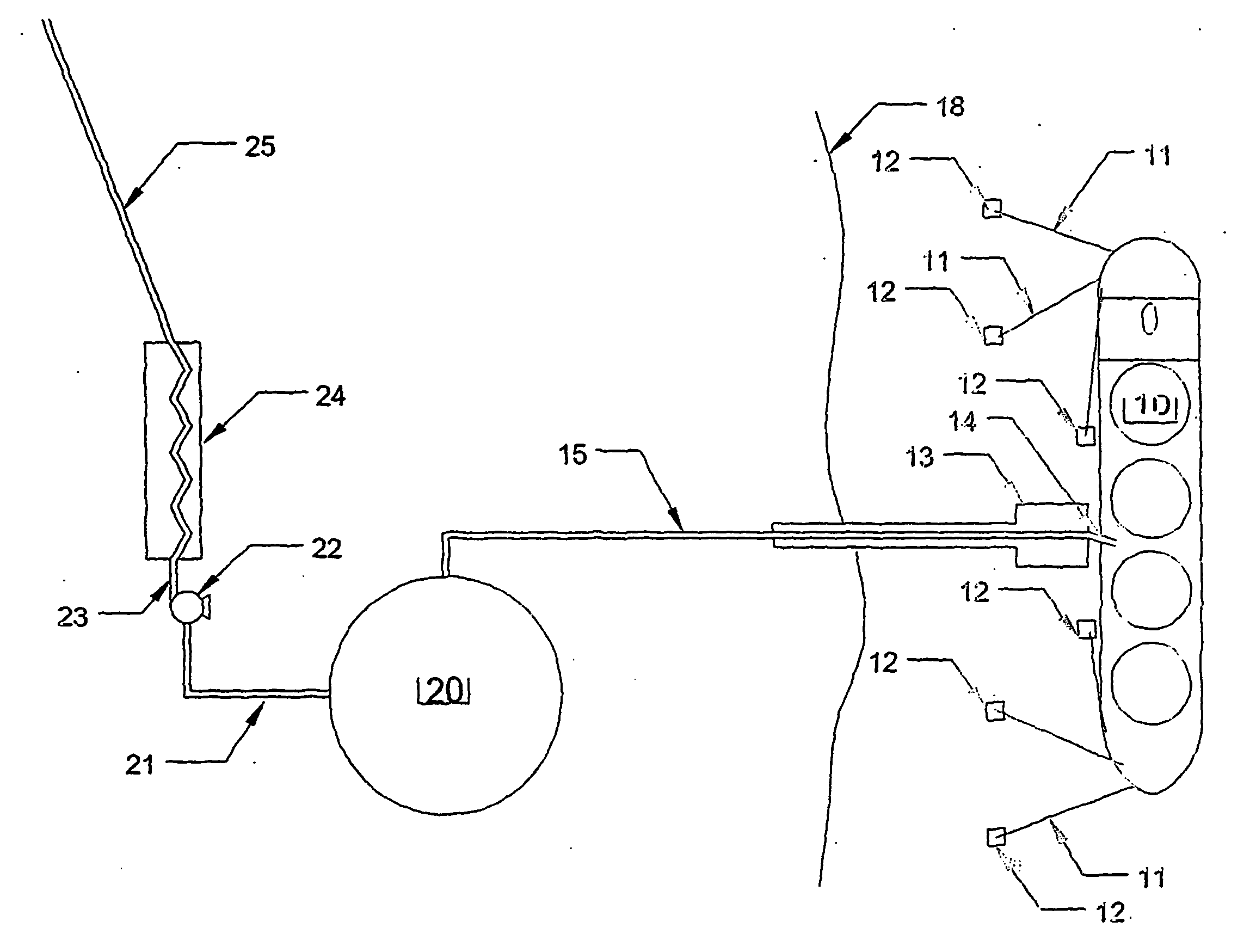
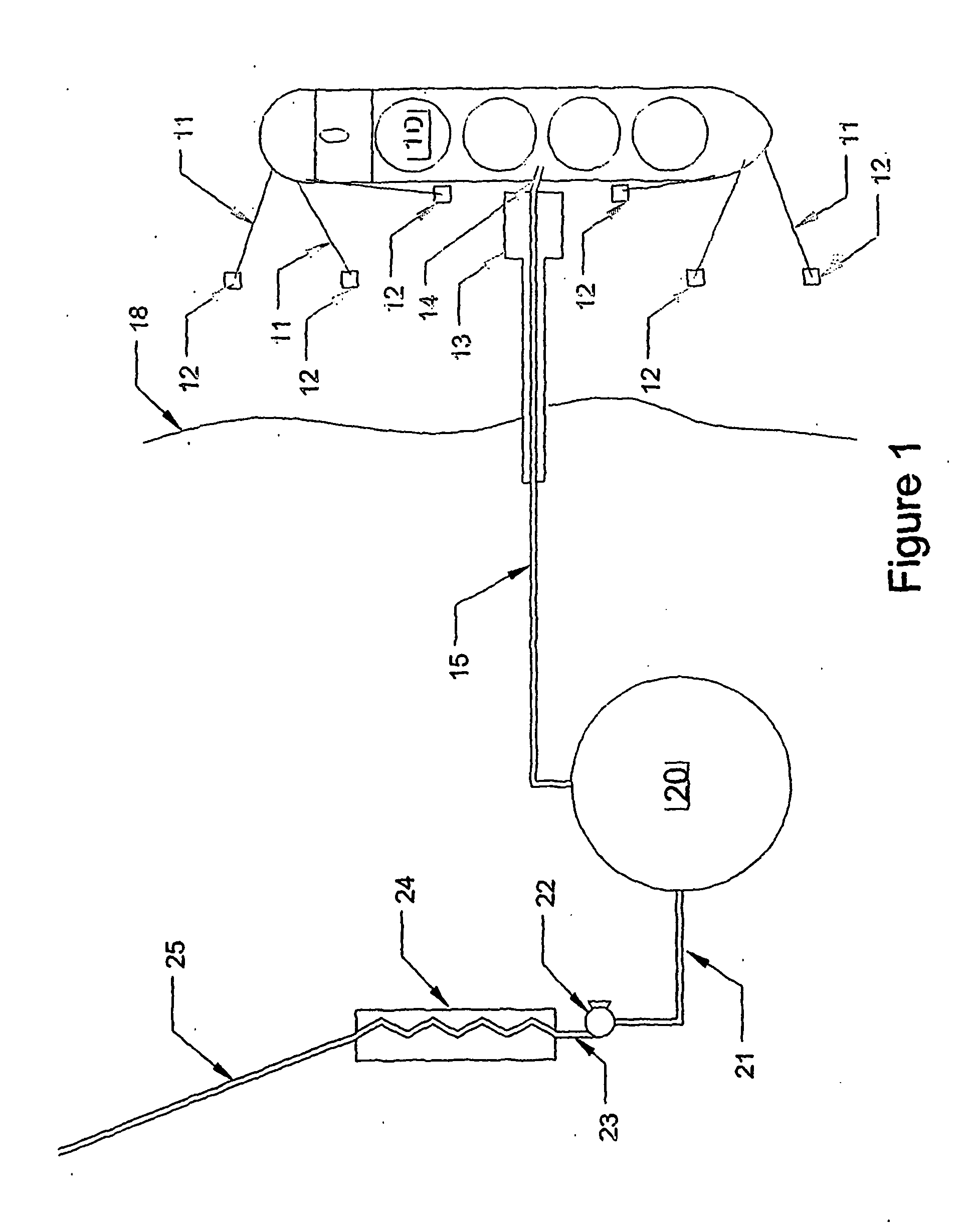
Discharge of liquified natural gas at offshore mooring facilities
a technology of liquified natural gas and offshore mooring, which is applied in the direction of transportation and packaging, special-purpose vessels, passenger handling apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of corresponding costs and costly to equip each vessel with this capability, and achieve the effect of efficient and inexpensive heating of the lng
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0061]FIG. 8 illustrates the invention. In this embodiment, the heat exchanger pipe 80 is buried below the seabed to protect it from fishing gear and anchors. A typical burial depth would be 1 meter. Using typical values for the thermal conductivity of frozen soils the heat influx into a 500 mm pipe may be 1.7 kW / m at the upstream end. Assuming a transfer rate of 1000 tonnes / H which corresponds to 278 kg / sec the total heating requirement is 278*600=167,000 kW.
[0062] Pipe 80 serves in this case the dual role of heat exchanger pipe and delivery pipe to shore. Pipe 80 is shown on FIG. 8 to cross the shore line 81 and connect to a conventional heater 82. Heater 82 will heat the gas to near ambient and convey the gas to overland delivery pipeline 25. If pipe 80 is 20 km long, then the pipe can deliver 20,000*1.7=34,000 kW of heating. This is only 20% of the total heating requirement of 168,000 kW, however, taking a throughput of 24,000 tonnes / day and assuming the values cited previously ...
first embodiment
[0063] In the invention, vessels trying to anchor above the heat exchanger 43 as shown in FIG. 5 may damage or even rupture the pipe with potential catastrophic consequences. Likewise fishing vessels fishing with fishing gear dragged on or near the seabed may damage the heat exchanger 43 shown in FIG. 5.
third embodiment
[0064]FIG. 9 is a plan view of the invention that avoids the dangers from anchors and fishing gear by protecting the heat exchanger 90 by structures that make the navigation above the heat exchanger by all but very small vessels impossible. In this embodiment, the heat exchanger 90 is contained within a protective structure 91 comprising a series of vertical piles 92 spaced sufficiently close that vessels cannot pass.
[0065] In FIG. 9 the LNG delivery tanker 10 is moored some distance from heat exchanger 90. The LNG is transferred by a riser 40 to sub-sea pipeline end manifold 41, which is in fluid connection with sub-sea pipeline 100. The sub-sea pipeline 100 is in fluid connection with a pumping assembly 96 that is located on a platform 95, which is adjacent to the protective enclosure 91. The sub-sea pipeline 100 need be long enough that a safe distance be provided between tanker 10 and enclosure 90 and at the same time short enough that the enclosed volume of gas can be absorbed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com