Method of preserving early embryos of experimental animals by vitrification
a technology of experimental animals and early embryos, which is applied in the field of vitrification of mammalian early embryos or es cells, can solve the problems of poor retrieval rate, difficult to solve problems, and cell culture usually involves the risk of a mutation of traits, and achieves high cell survival rates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preservation of Rat 2Cell-Stage Embryos by Vitrification
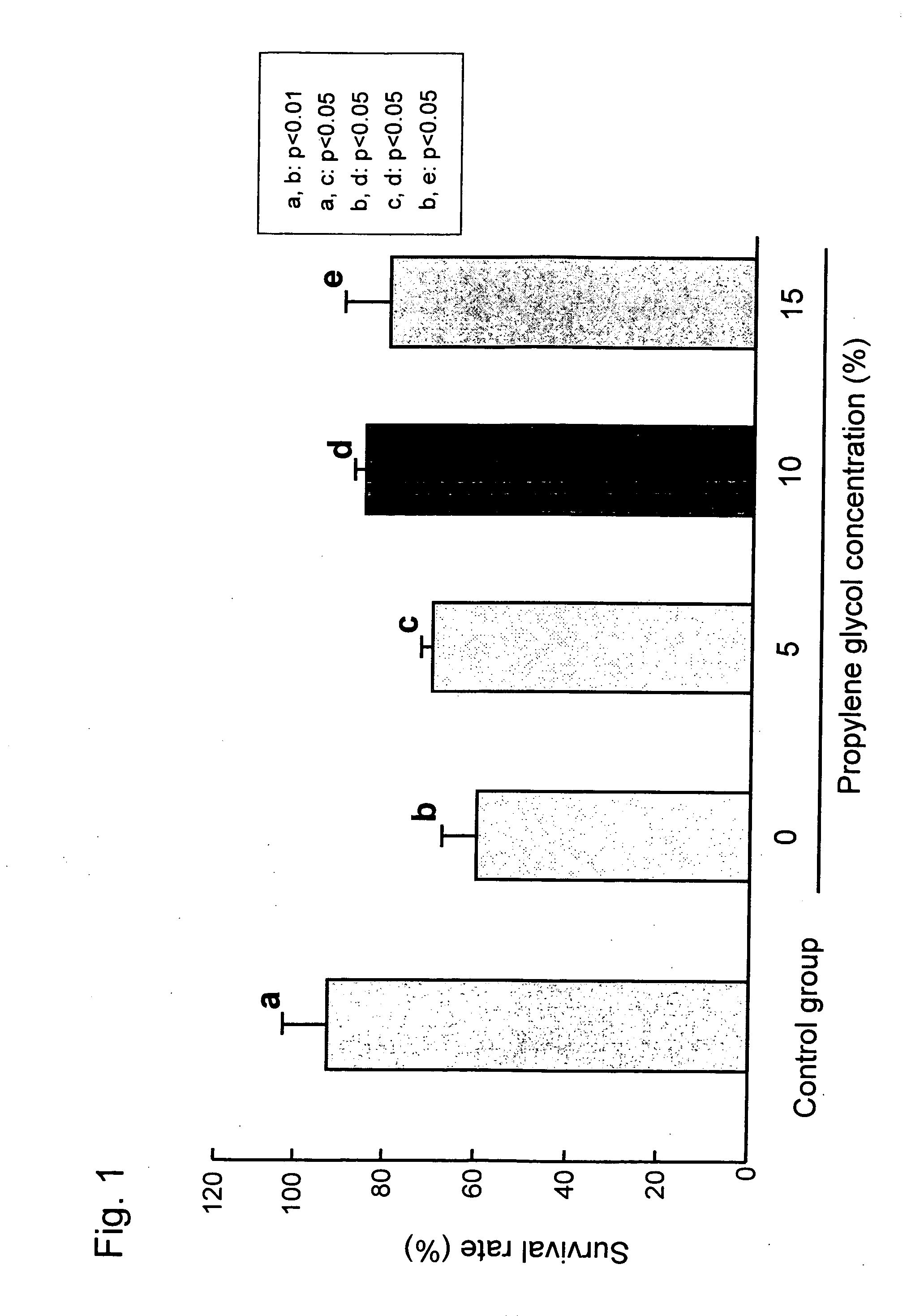
[0045] Rat 2cell-stage embryos were used. Brl Han:Wist@Jcl (GALAS) rats were employed. 8-12-week-old female rats and 12-24-week-old male rats were employed. As test embryos, 2cell-stage embryos obtained from female rats that had been subjected to superovulation followed by natural mating were employed. Specifically, 150 IU / kg of PMGS was injected intraperitoneally into female rats and 75 IU / kg of hCG was injected intraperitoneally 48 hours thereafter. Rats were subjected to mating immediately after the injection of hCG, smears were sampled the following morning, and the estrous cycle and sperm impregnation were confirmed. The 2cell-stage embryos were sampled from female rats having positive smears via perfusion of the oviducts 45 hours after the injection of hCG. The sampled embryos were cultured at 37° C. in 5% CO2 and 95% air for approximately 1 hour and then subjected to the test.
[0046] The P10 solution, which comprises th...
example 2
Preservation of Marmoset ES Cells by Vitrification
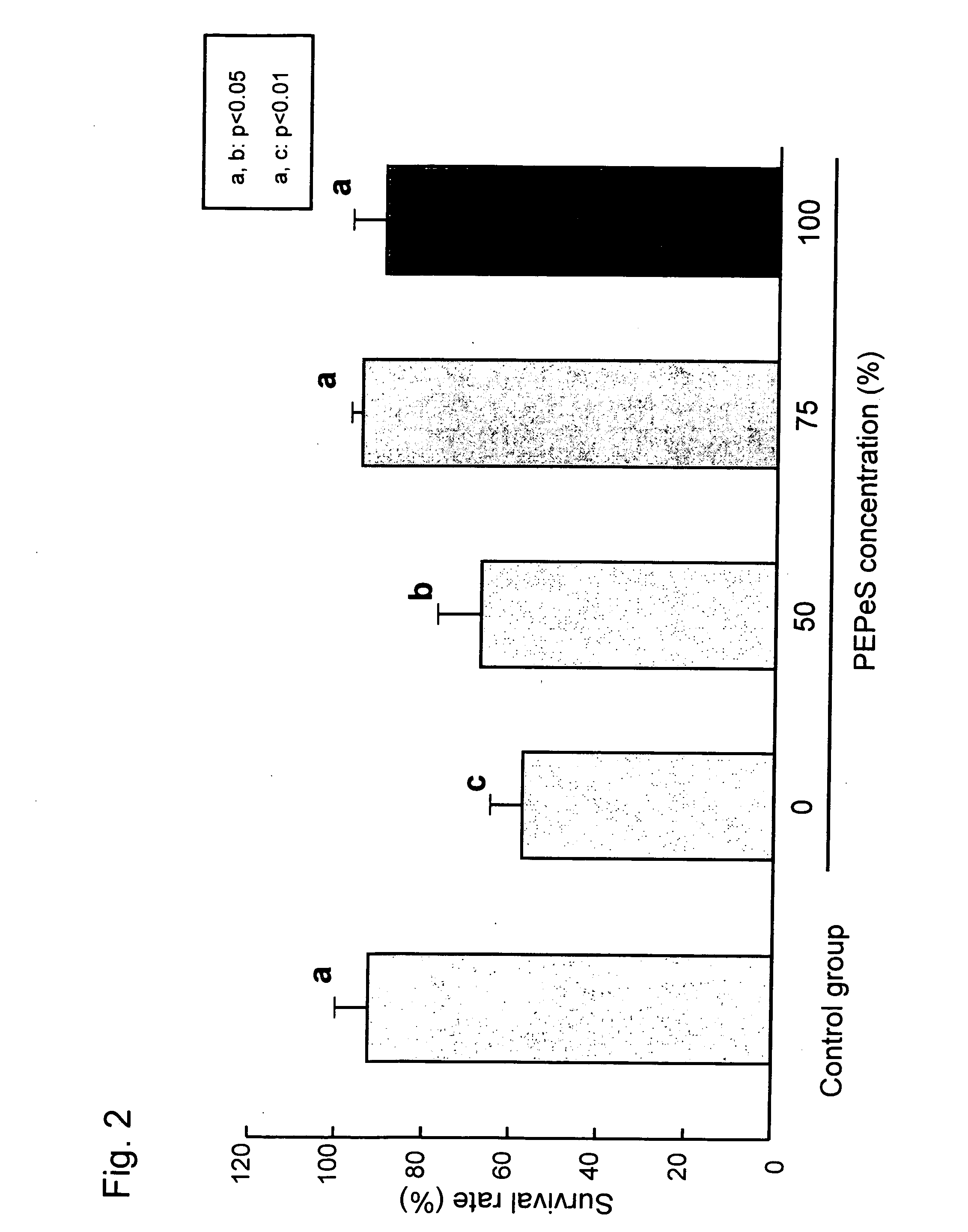
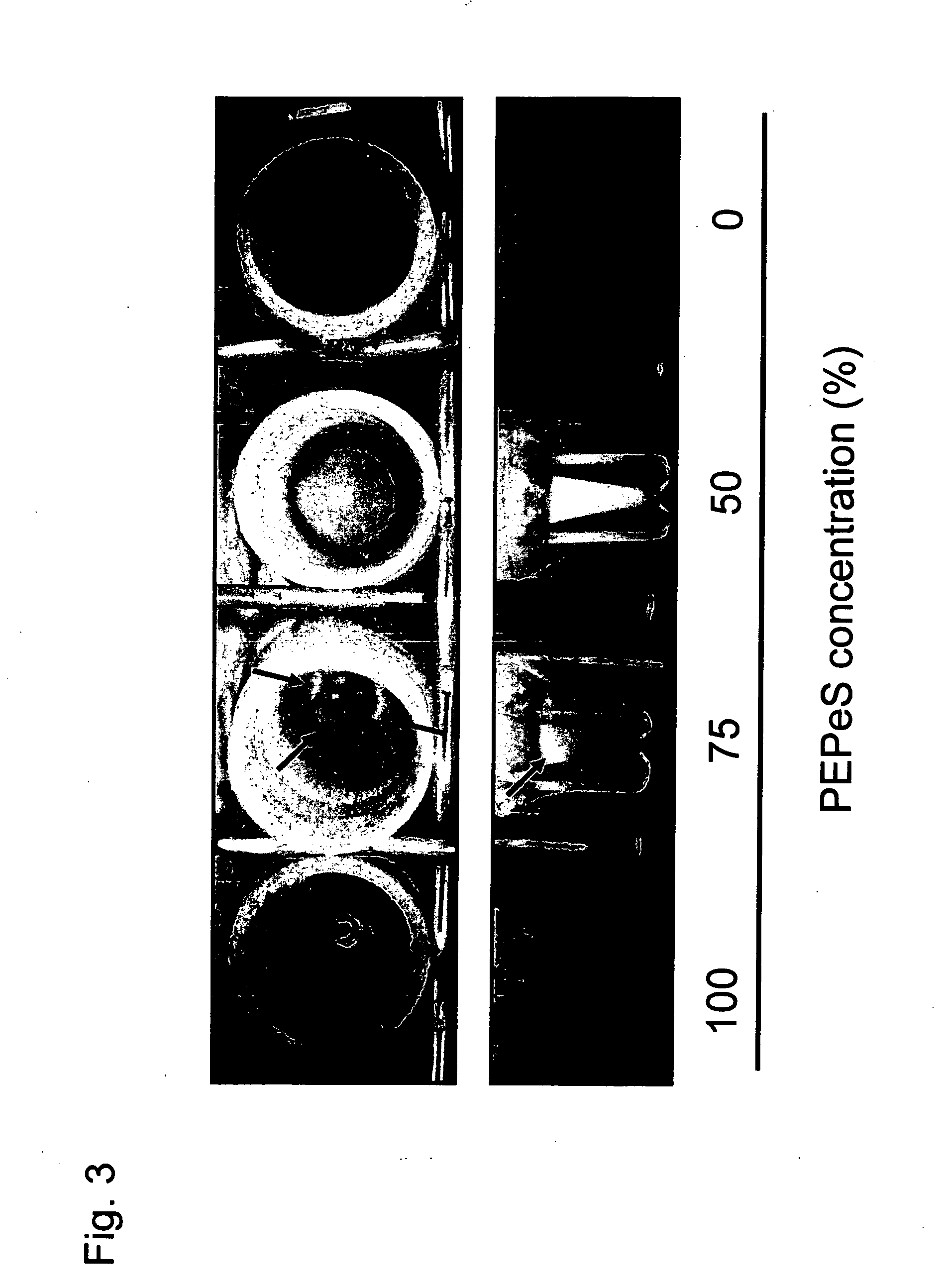
[0056] As marmoset ES cells, two cell lines, i.e., No. 40 and No. 20, which were established by the Central Institute for Experimental Animals (Japan), were employed (Sasaki E. et al., 2005, Establishment of Novel Embryonic Stem Cell Lines Derived from the Common Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus), Stem Cells. (in press)). The cell clumps seperated via trypsin treatment were recovered with an egg-sampling pipette and used in the preservation experiment.
[0057] In the method of preservation by vitrification according to the present invention, the P10 pretreatment solution comprising PB13 and 10% propylene glycol and the PEPeS solution comprising PB1, 10% propylene glycol, 30% ethylene glycol, 20% Percoll®, and 0.3 M sucrose were used. In thaw, the SPB1 solution comprising PB1 and 0.3 M sucrose was used.
[0058] In preservation of the control embryos by vitrification (Fujioka T. et al., Int. J. Dev. Biol. 48: 1149-1154), a DAP213 solution c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com