Pack of wipes with enhanced dispensing
a technology of enhanced dispensing and wipes, which is applied in the direction of article separation, thin material handling, packaging, etc., can solve the problems of user difficulty in reaching and dispense of first wipe of the stack, and the exposed leading portion of the wipe can be difficult to grip, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing dry-out, high adhesion and high friction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
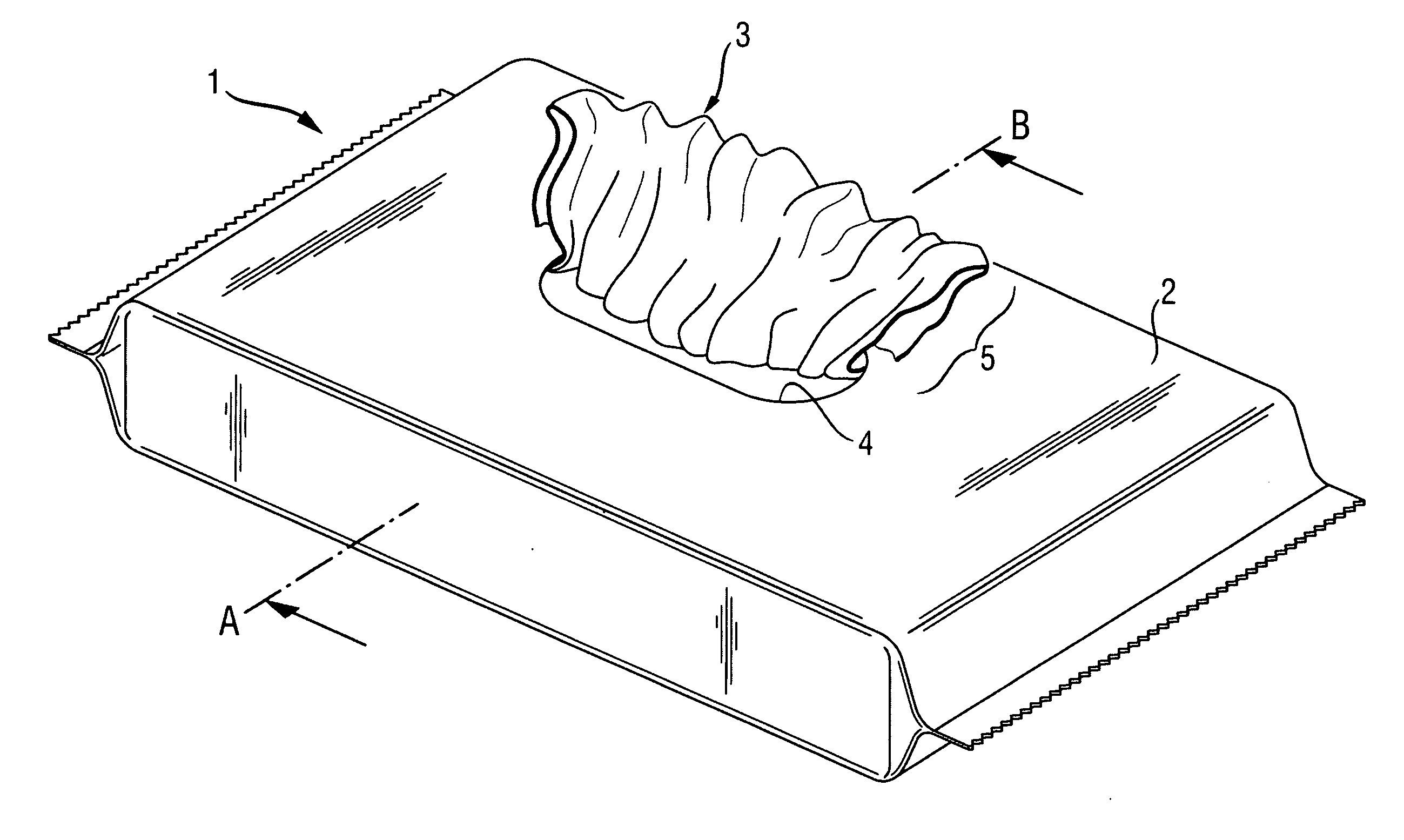
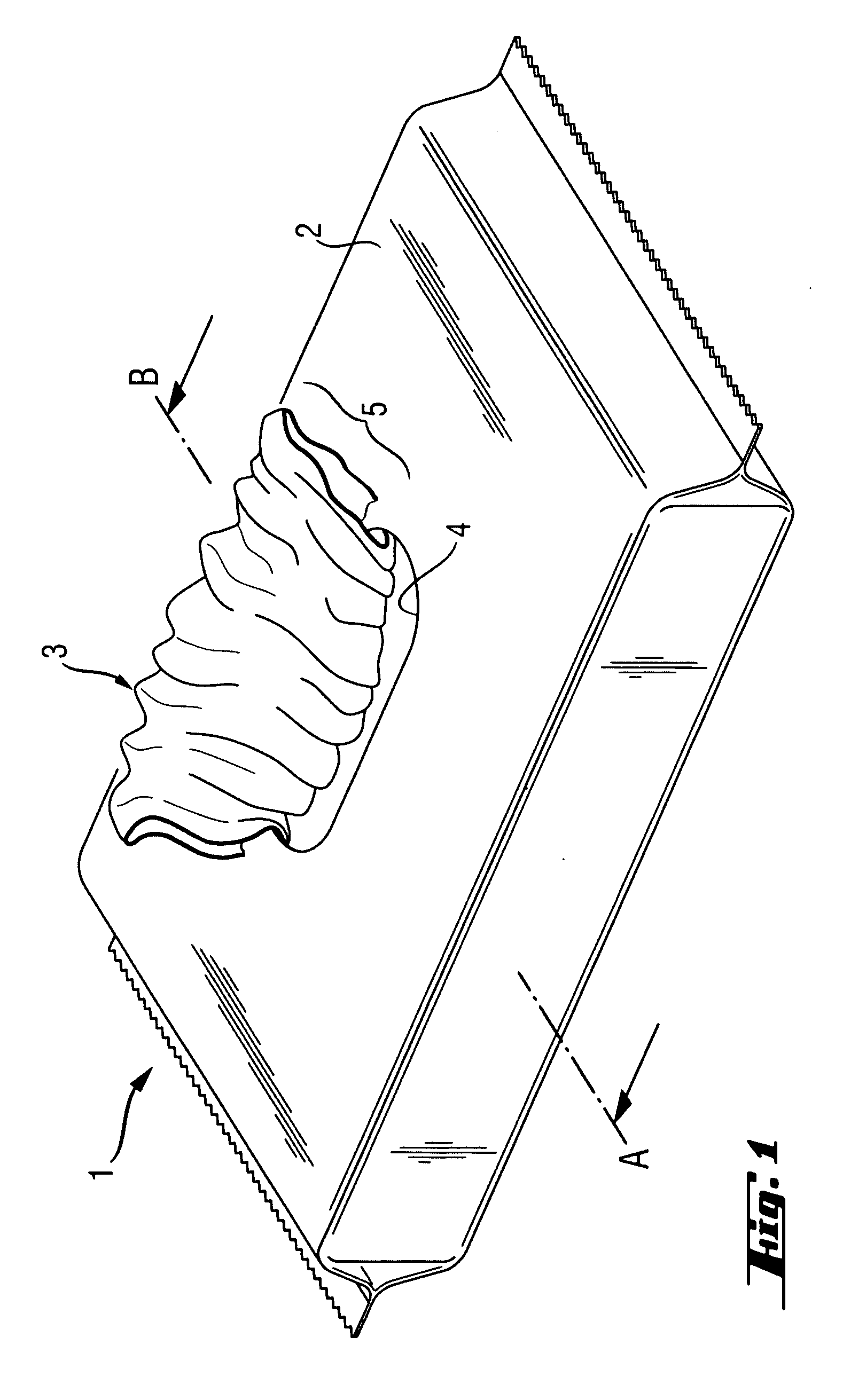
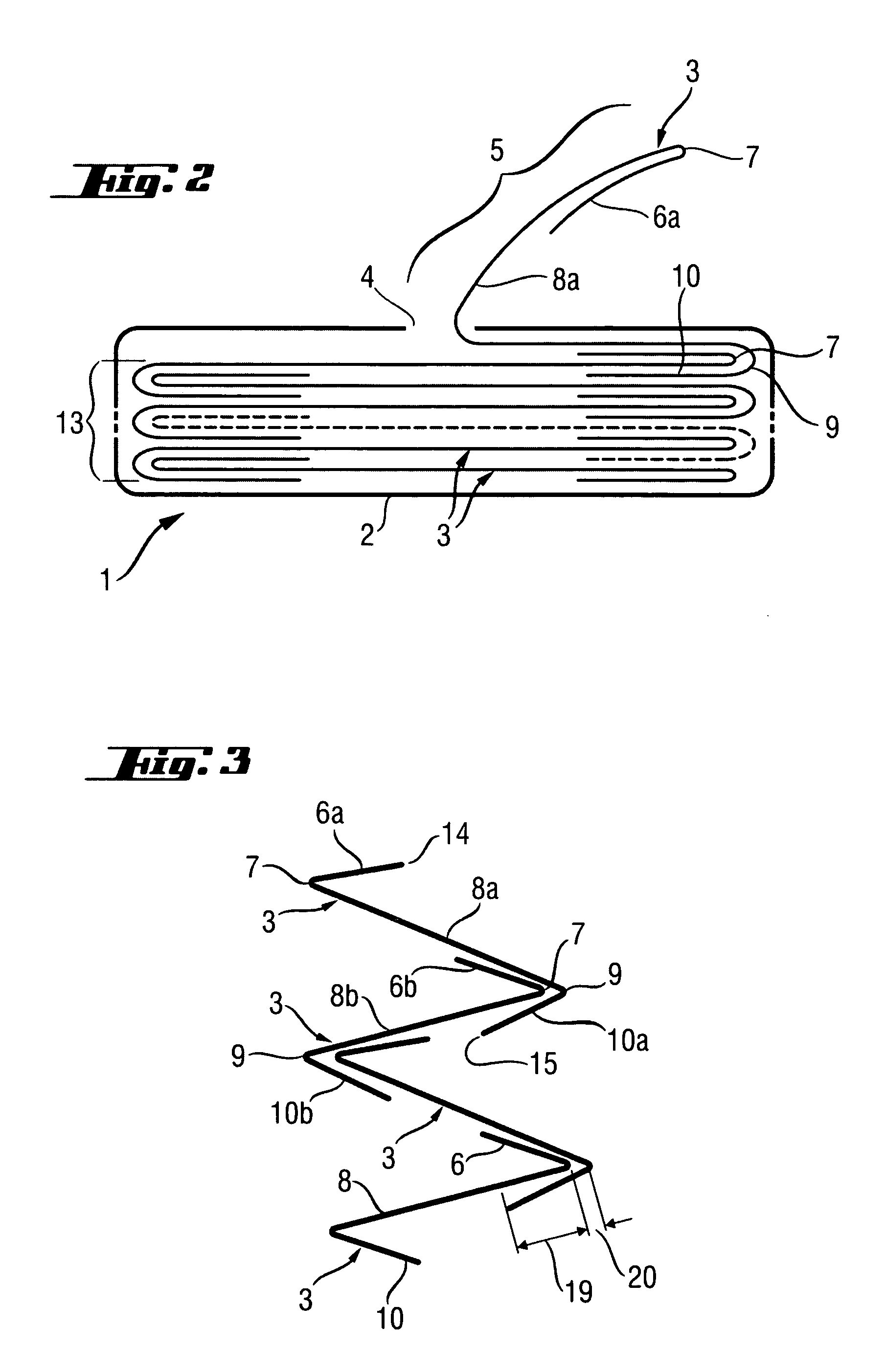
[0020] Generally, wipes are articles comprising a substantially flat substrate. Conventionally wipes are articles used for cleaning, treating and / or and removing residues from surfaces. The surfaces may include hard surfaces (such as the surface of a piece of furniture or a floor) or soft surfaces, including parts of a human body. Certain wipes include baby, children and adult wipes conventionally used for cleaning the anal area of adults or children. Yet, other wipes includes articles for cleaning floors, kitchen surfaces, windows or office surfaces. Other typical wipes include tissues (e.g. facing cleansing tissues), paper handkerchiefs (to clean the nasal area of the human body), kitchen towels and toilet papers. The substrate of the wipes is usually soft and flexible. The substrate can include synthetic fibers, natural fibers or mixtures thereof. Most common body cleaning wipes are made of a polyethylene / polypropylene substrate. The wipes are generally impregnated with a composi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com