Vascular closure methods and apparatuses
a technology of vascular closure and vascular valve, which is applied in the field of vascular closure methods and apparatuses, can solve the problems of high rate of post-puncture hemorrhage, large number of steps, and considerable complications, and achieve the effects of preventing intravascular preventing the migration of the device, and keeping tension on the wound
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example embodiments
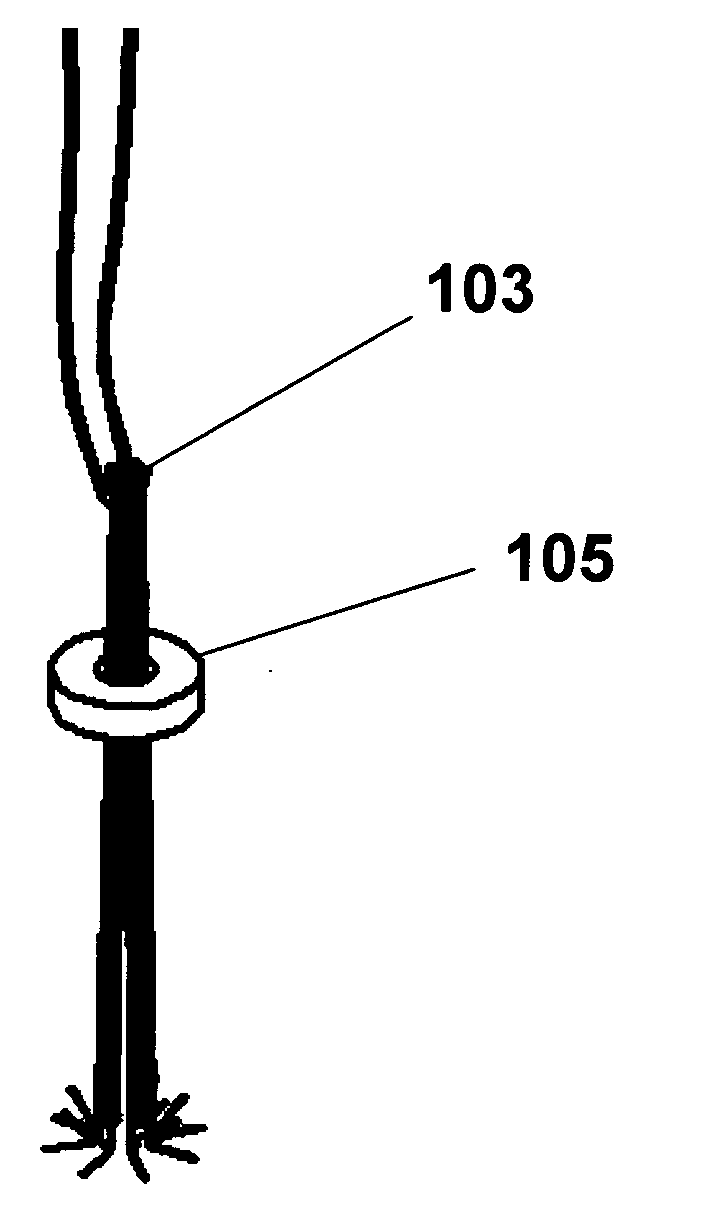
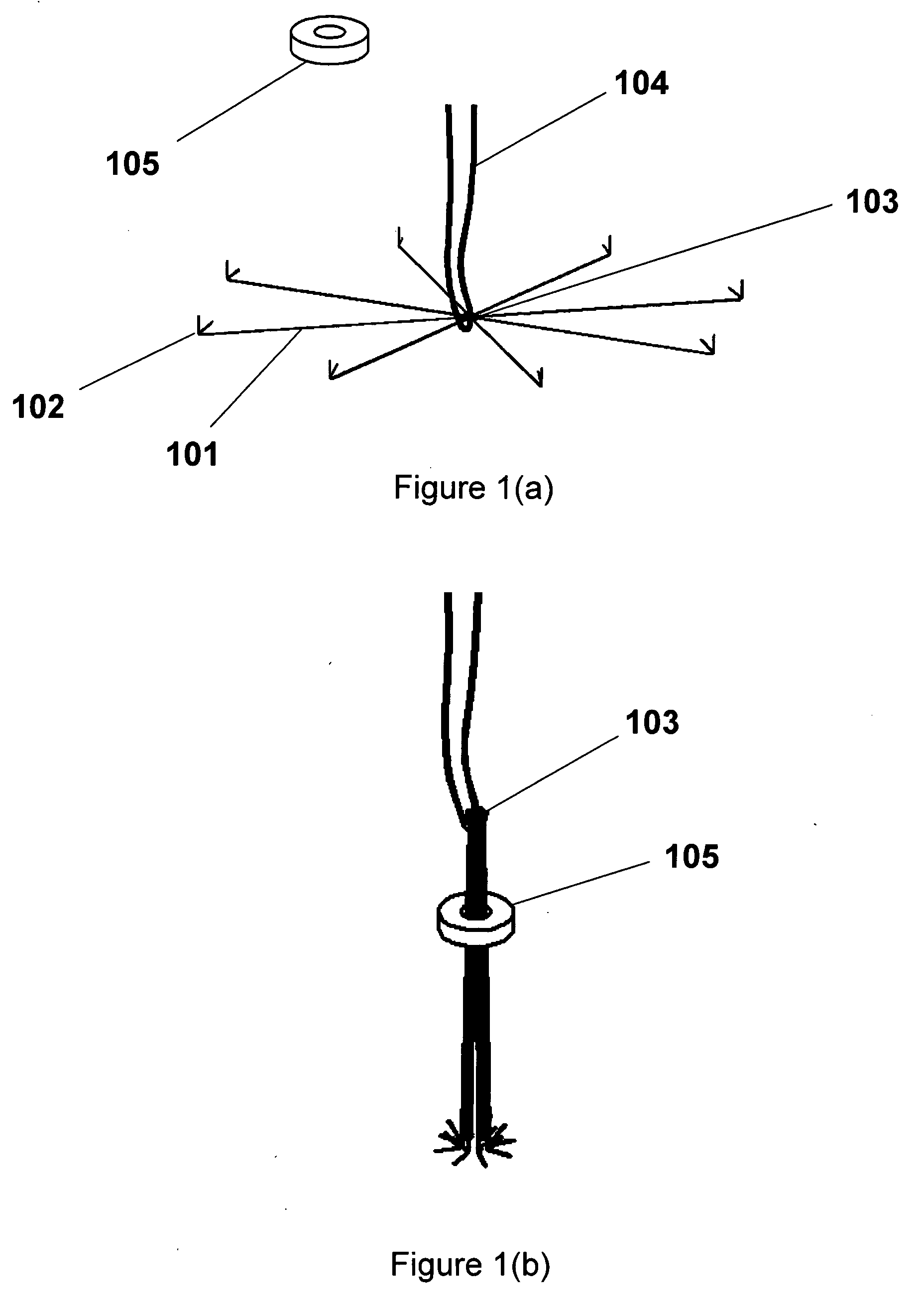
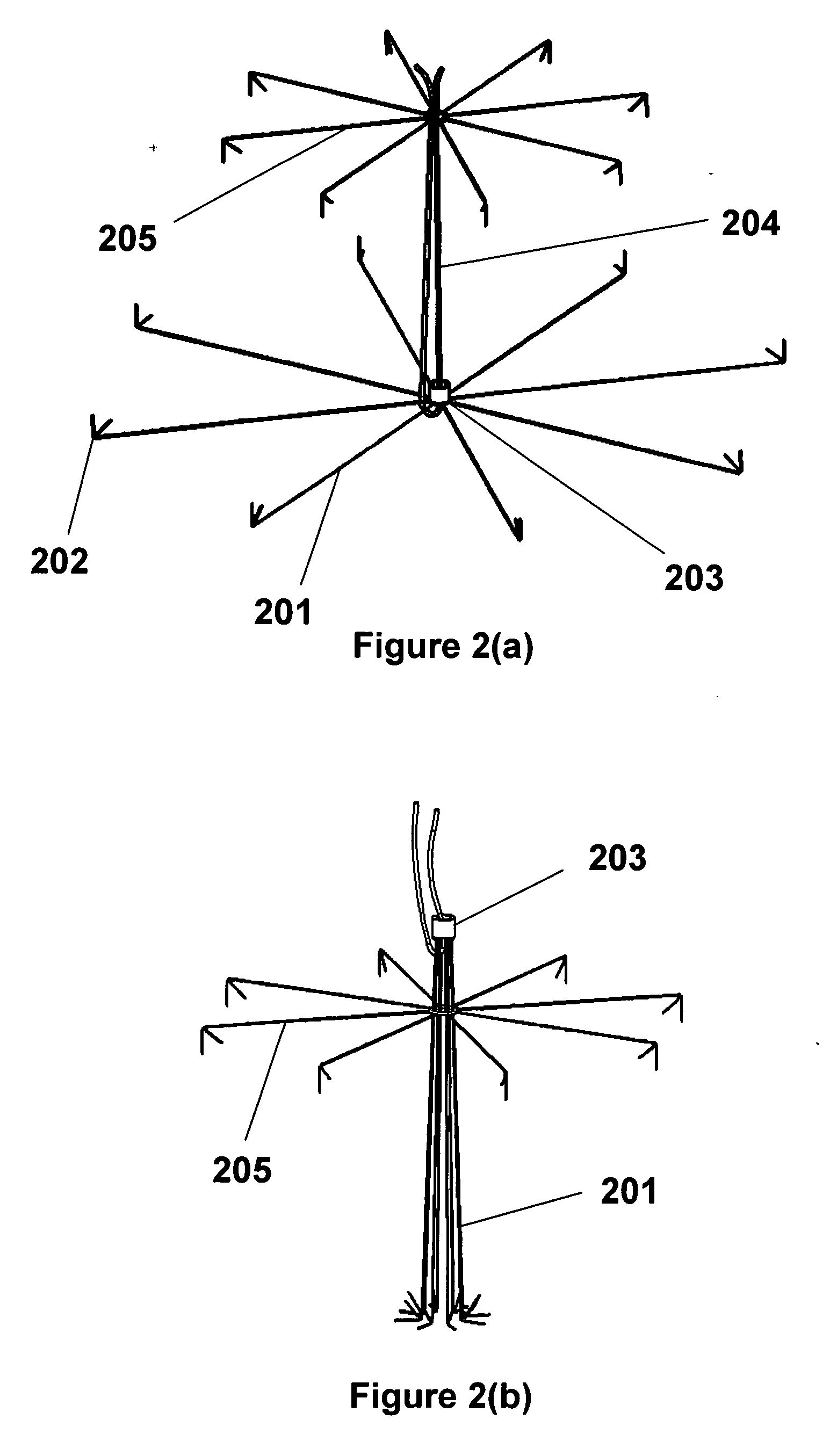
[0045] The present invention can comprise a device to close puncture wounds caused by catheter procedures and especially angiography comprised of an expandable umbrella-like device that in the compressed state resides in a sheath, and after being expelled from the sheath assumes a planar or conical or other shape, engages vessel wall by means of tissue hooks or penetrators, is collapsed, analogous to umbrella tines, and brings the edges of the vessel wound or puncture into apposition. The device can have a retaining locking device that prevents the umbrella-like structure from reopening. This locking can be achieved by mechanical means including deformable enlargements on the members, dentates, male-female connectors, peg and hole, or other directional mating / locking devices on the members and retaining locking device. This locking device can have a washer like appearance, but can also take a number of different forms, including an inverted umbrella device made of metal, plastic, co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com