Refrigeration cycle device for vehicle
a technology for refrigeration cycle devices and vehicles, which is applied in refrigeration components, transportation and packaging, light and heating equipment, etc., to achieve the effect of suppressing the increase of refrigerant pressur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
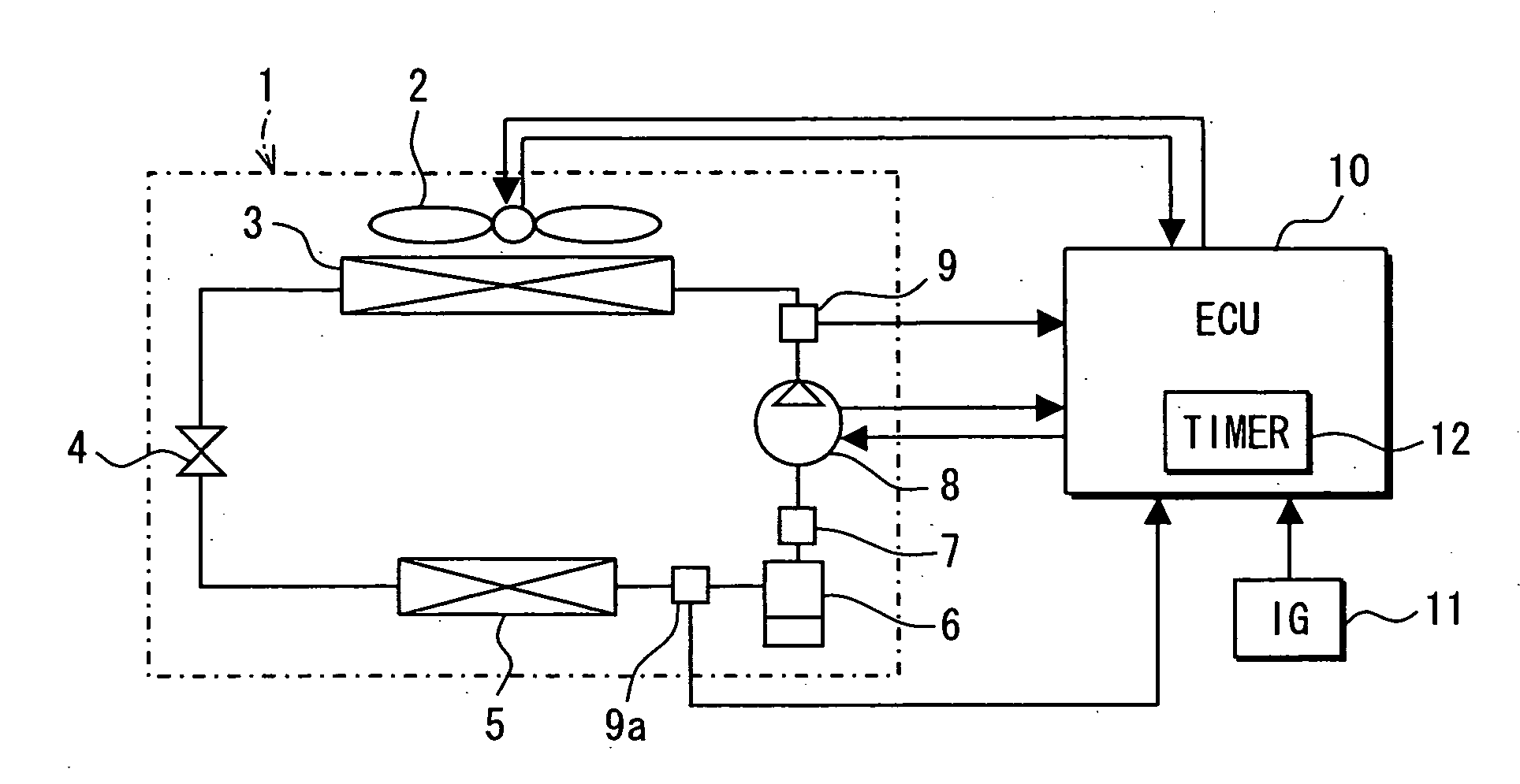
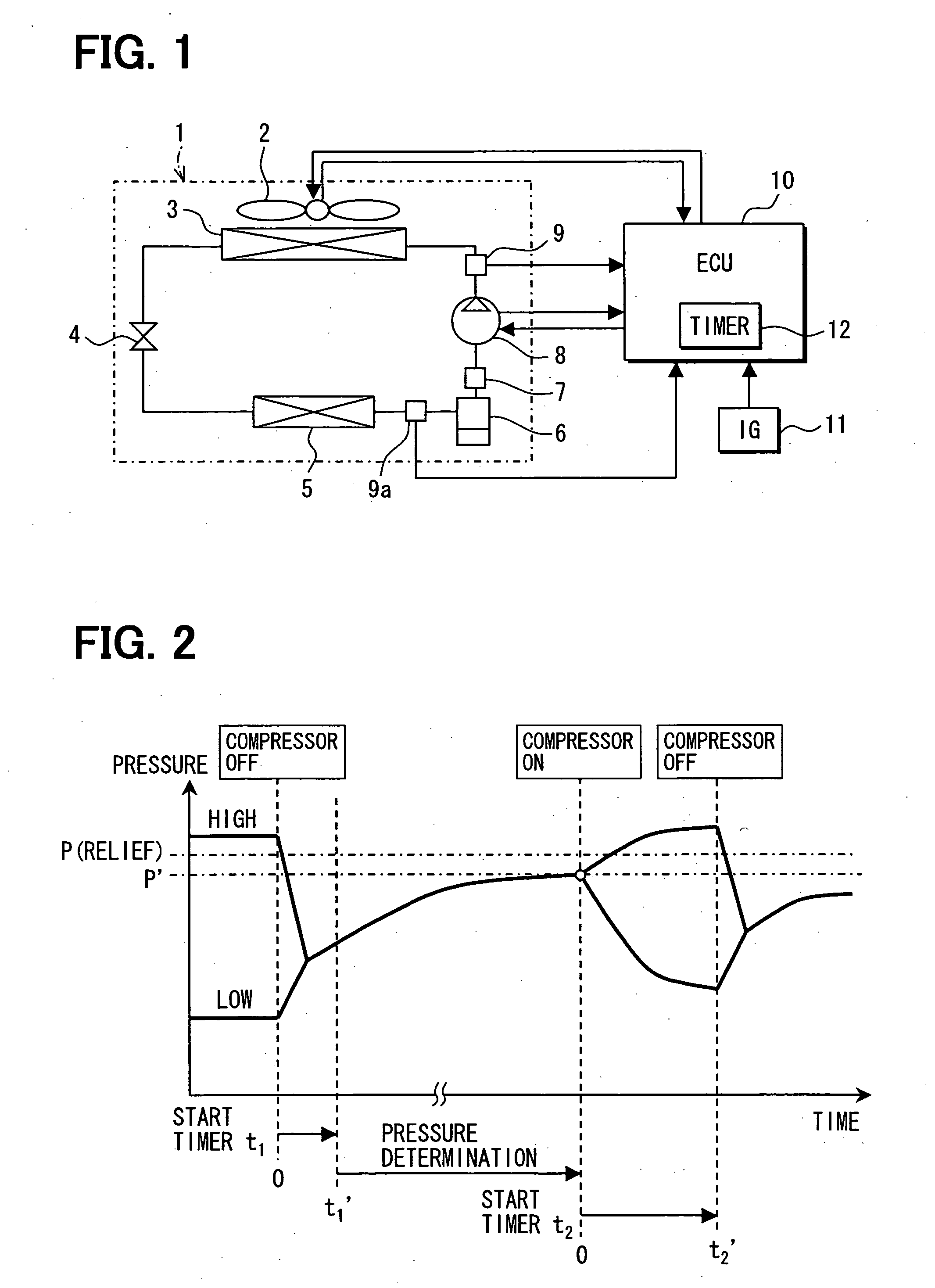
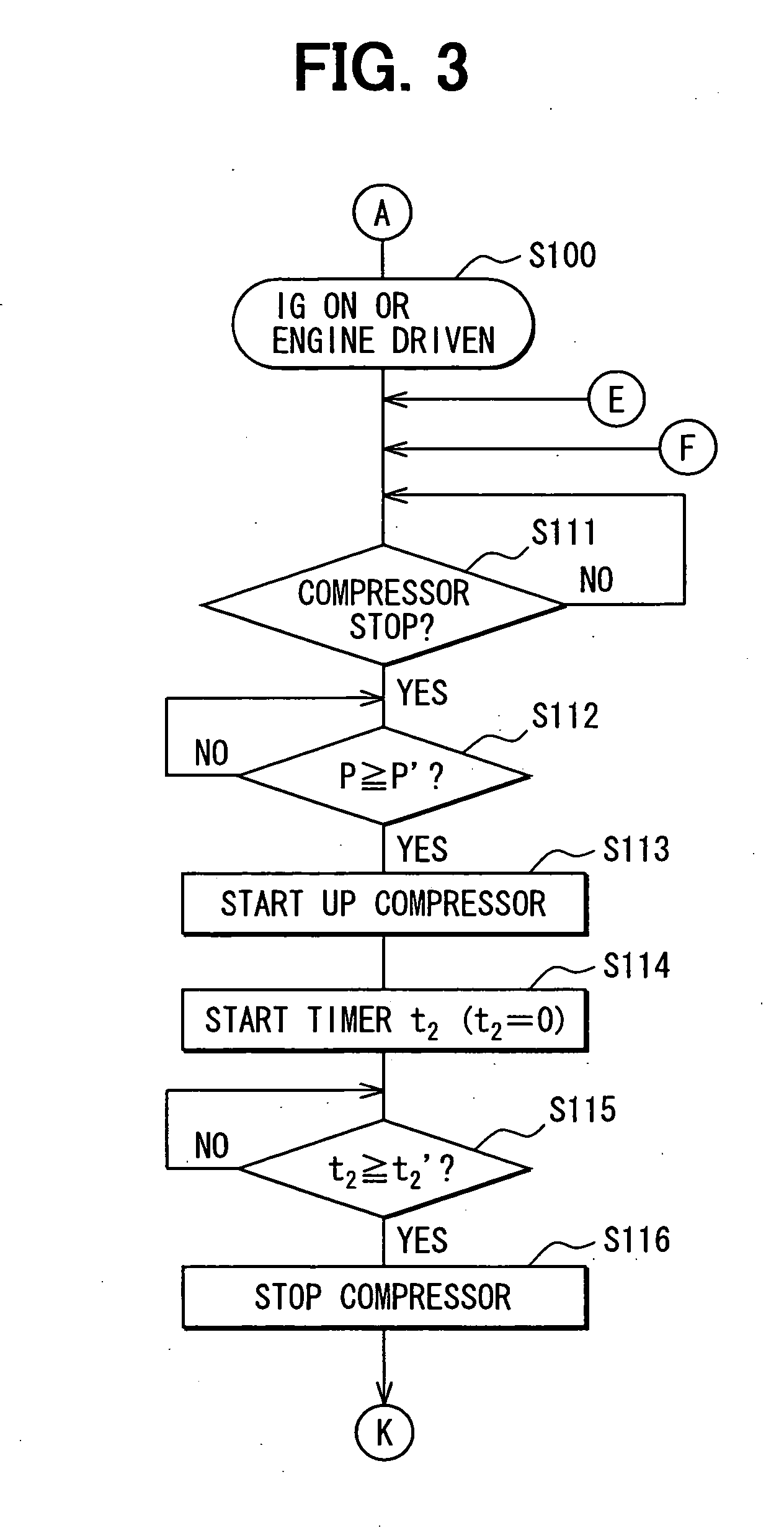
[0053] A refrigeration cycle device for a vehicle according to a first embodiment carries out inherent control to reduce refrigerant pressure in a refrigerant cycle using refrigerant containing carbon dioxide (CO2) as a main component so that parts in the refrigerant cycle can be prevented from being damaged due to increase of the refrigerant pressure. Particularly, the refrigeration cycle device for a vehicle is peculiar and different from a stationary refrigeration cycle device in that the increase of the refrigerant pressure is greatly affected by heat occurring when a vehicle engine is driven unlike.
[0054] In order to solve the problem under such a peculiar condition, the vehicle refrigeration cycle device of this embodiment is controlled in consideration of the effect of heat occurring when the vehicle travels. Particularly, one factor causing the increase of the refrigerant pressure in the refrigerant cycle which is applied to the vehicle environment is as follows. That is, w...
second embodiment
[0124] This embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that temperature data are used for the condition detection based on the condition detecting unit. In the supercritical refrigerant cycle, when refrigerant is sealed at some cycle sealing density, if the cycle average temperature at that time is increased, the sealed refrigerant falls into the supercritical state, and the pressure is determined by the temperature at that time. Therefore, according to this embodiment, the refrigerant detection is detected by detecting the refrigerant temperature.
[0125] Next, the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 8 to 17. The same constituent elements as the first embodiment are represented by the same reference numerals.
[0126]FIG. 8 is a diagram showing the construction of a refrigeration cycle device for a vehicle according to the second embodiment. As shown in FIG. 8, the refrigerant cycle 20 includes a compressor 8, a discharge temperature sensor 13 serving...
third embodiment
[0182] In the third embodiment, under the state that the ignition (IG) switch is set to OFF, the compressor or the cooling fan is started up at the condition detection time, and then the stop control is carried out as in the case of FIGS. 3, 5 and 12. The different point of the third embodiment from the first and second embodiments resides in that an electrically-driven compressor and an electrically-driven cooling fan is controlled in place of the compressor 8 and the cooling fan 2 to keep the refrigerant pressure proper. The third embodiment will be described hereunder with reference to FIGS. 18 to 21.
[0183]FIG. 18 is a control flowchart showing the processing of reducing the refrigerant pressure by controlling the electrically-driven compressor on the basis of the detection value of the refrigerant pressure when the ignition (IG) switch is set to OFF.
[0184] In this control flow shown in FIG. 18, first, when the ignition (IG) switch is set to OFF (step S170), it is determined wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com