IL-12 an adjuvant for bordetella pertussis vaccines
a vaccine and adjuvant technology, applied in the field of vaccines against bordetella species, can solve the problems of human infant morbidity, mortality, whooping cough, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the protective
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Analysis of Cytokine Production
[0046] Mice. Female BALB / c mice were bred and maintained under the guidelines of the Irish Department of Health. All mice were 8 to 12 weeks old at the initiation of this and the following experiments.
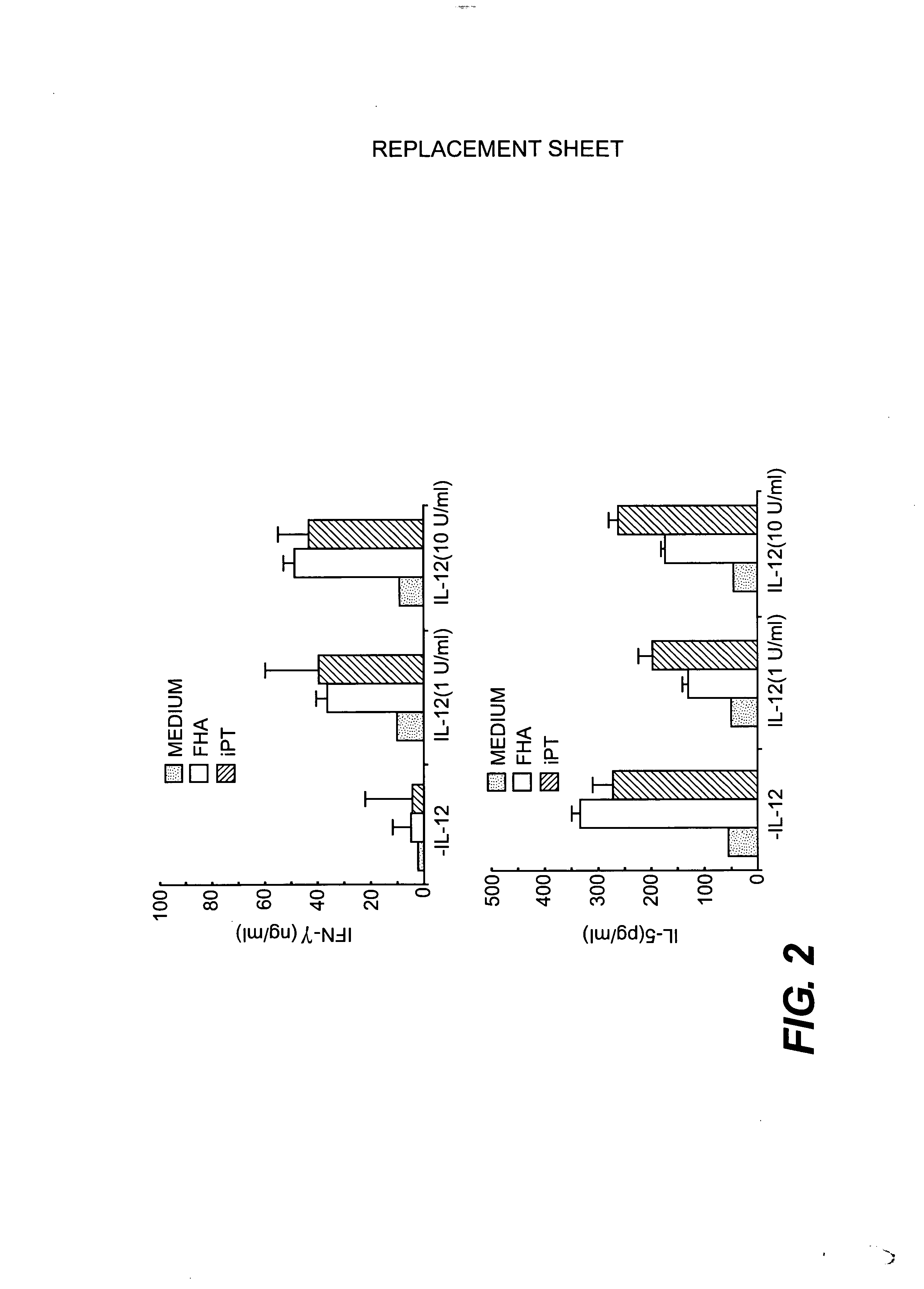
[0047] Cytokine Production. T cell cytokine production was assessed using spleen cells from mice stimulated with B. pertussis antigens in vitro. Spleen cells (2×106 / ml) from immunized or naive control mice were cultured with antigens or with medium alone (background control), and supernatants were removed after 24 hours to determine IL-2 production and after 72 hours to determine the concentrations of IFN-γ, IL4, and IL-5. IL-2 release was assessed by the ability of culture supernatants to support the proliferation of the IL-2-dependent CTLL-2 cell line. The concentrations of murine IL-4, IL-5, and IFN-γ were determined by specific immunoassays using commercially available antibodies (PharMingen, San Diego, Calif., USA) as previously described (B. P. Ma...
example 2
Macrophage Secrete IL-12 in Response to Bordetella Antigens
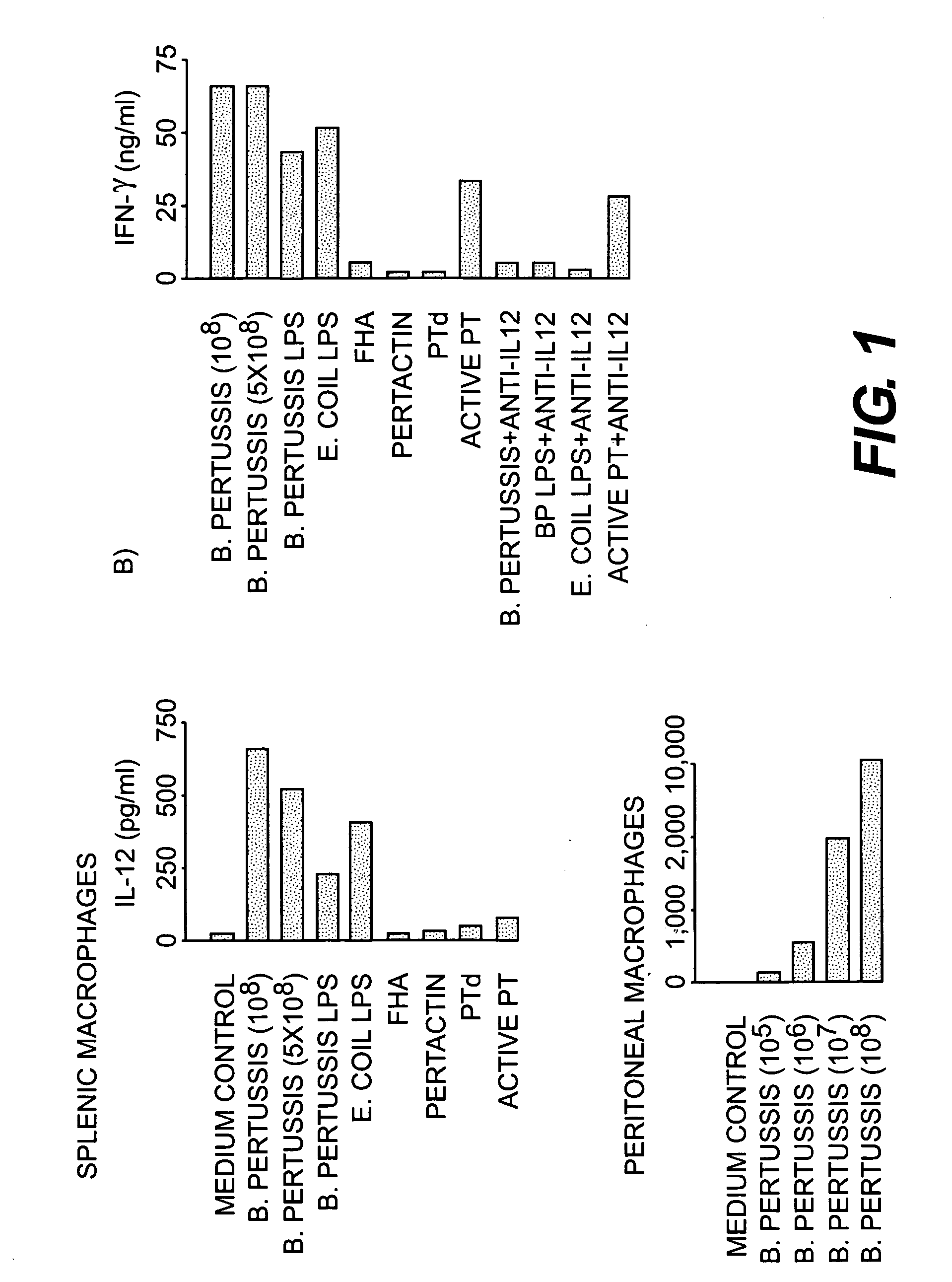
[0049] This experiment tested the ability of killed whole B. pertussis and B. pertussis components to stimulate the production of IL-12 by murine macrophages.
[0050] Macrophages. Murine peritoneal macrophages were obtained from naive animals by plastic adherence of cells obtained by peritoneal lavage. Splenic macrophages were prepared by plastic adherence and alveolar macrophages were isolated by bronchoalveolar lavage as previously described (K. Redhead, A. Barnard, J. Watkins, and K. H. G. Mills, 1993, Infect. Immun. 61: 3190-3198). The murine macrophage cell line J774 was also used in studies of IL-12 production. Macrophages were infected with viable phase I B. pertussis at a bacteria to macrophage ratio of 5:1 for two hours before extensive washing. Extracellular bacteria were killed by treatment with polymyxin B sulphate (100 μg / ml) for 40 minutes followed by further washing. This treatment reduces the number of extrac...
example 3
IL-12 Stimulates Immune Cell Proliferation in Response to B. pertussis Antigens
[0056] We tested the ability of IL-12 to modulate immune responses to B. pertussis antigens in vivo by immunization of mice with FHA and PTd in the presence or absence of alum. Spleen cells from immunized or control mice were tested for in vitro proliferation against heat-killed B. pertussis (106 / ml), heat-inactivated PT (1.0 μg / ml), FHA (1.0 μg / ml), and pertactin (1.0 μg / ml) as previously described (K. H. G. Mills, A. Barnard, J. Watkins, and K. Redhead, 1993, Infect. Immun. 61: 399-410) and incorporated herein by reference. Results were calculated as mean counts per minute (CPM) of [3H]thymidine incorporation for triplicate cultures for groups of four to six mice. Stimulation indices were calculated by dividing the proliferative response to the antigens by the response of control cultures, where cells were stimulated with medium alone.
[0057] Recombinant murine IL-12 was kindly provided by Stanley Wolf...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com