DNA fingerprinting using allelic specific oligonucleotide reversed dot blot (ASO-RDB) flow through hybridization process and device
a technology of reversed dot blot and allelic specific oligonucleotide, which is applied in the field of dna fingerprinting, can solve the problems of compromising the accuracy of paternity and kinship analyses, and achieve the effect of reducing the difficulty of obtaining adequate discriminating power, compromising the accuracy of paternity and kinship analyses, and being a good alternative for human identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
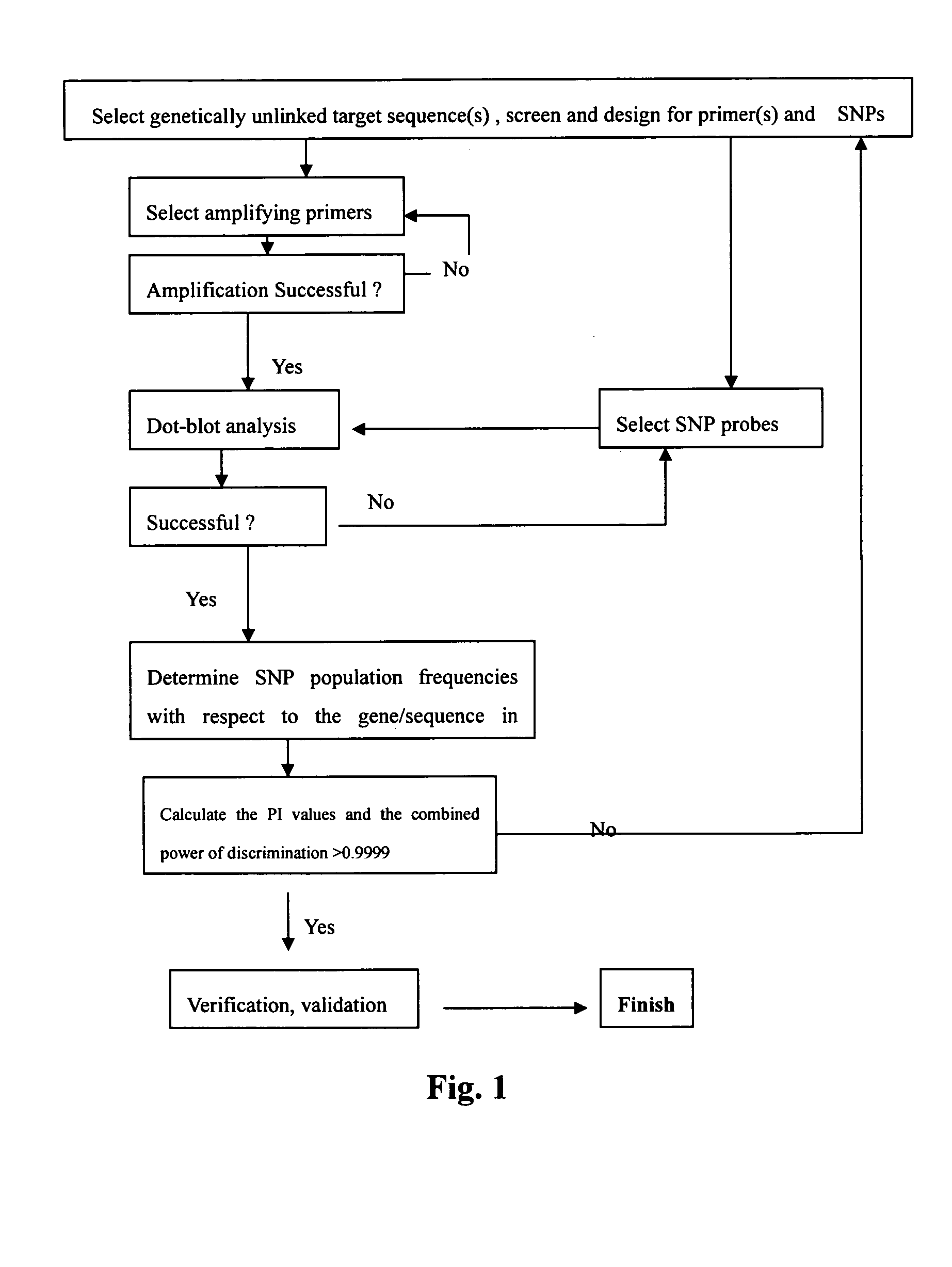
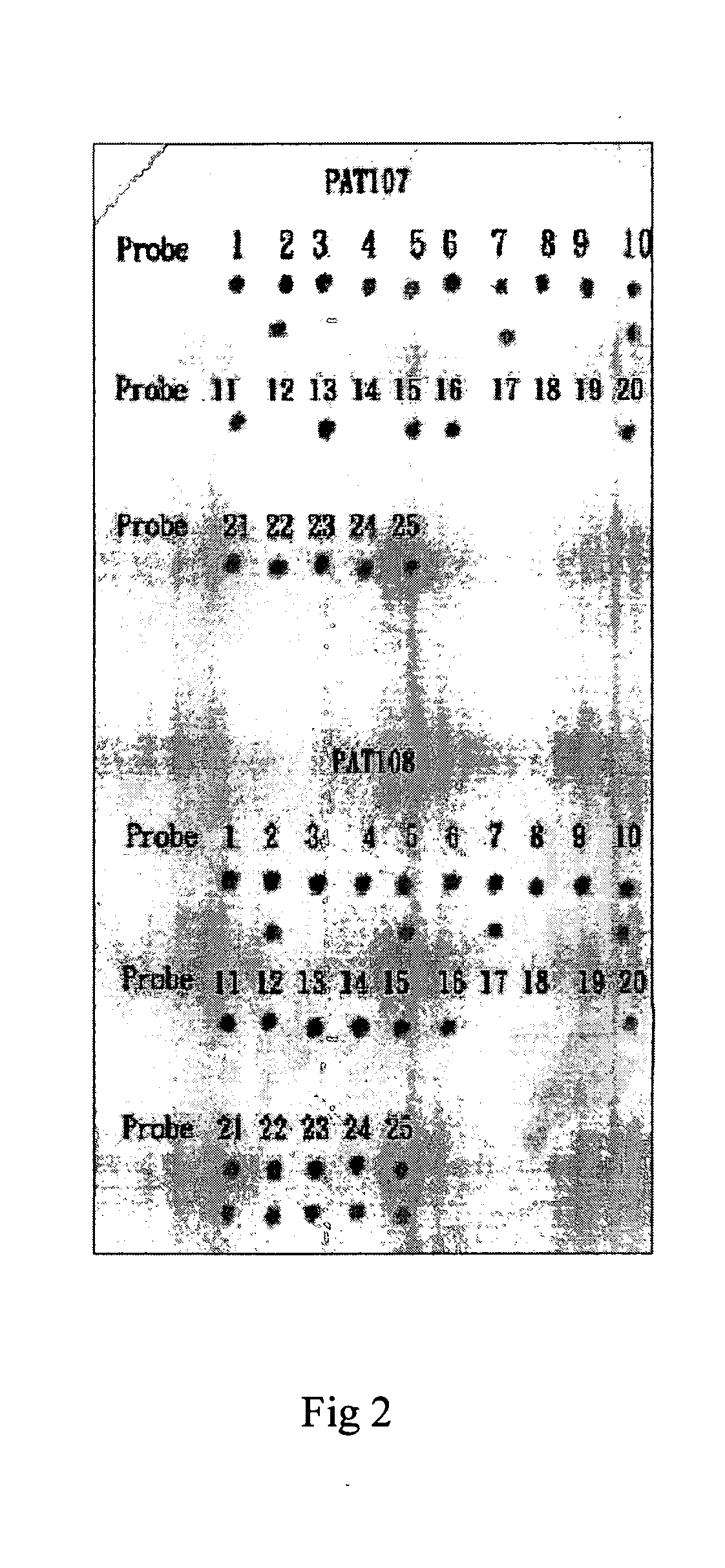
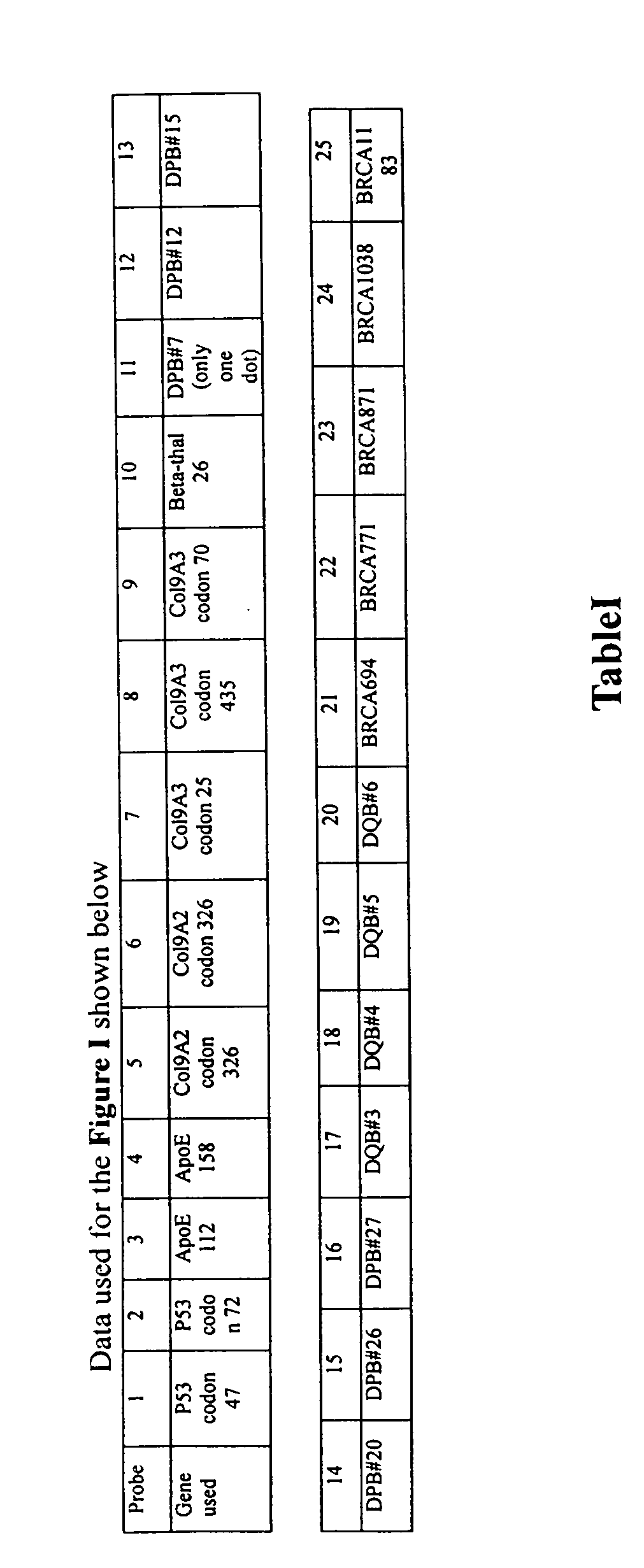
[0021] We have sequenced eight gene clusters and 55 segment sequenced with 50 to 400 individual samples for determining the SNP sites. FIG. 2 showed one of the panels we used for such fingerprinting each of which has been compared with the STR Profiler Plus fingerprinting kit from Applied Biosystems Inc for identification. Table I showed the loci used for such determination in the FIGURE I. Other probes and primers for other candidate genes / sequences are being tested. Genes partially tested include Globin genes for Thalassemia, BRCAs, ApoE, Collagens, p53, G6PD deficiency alleles and HLA DP, DQ and DR. In principle, any known SNPs of any organisms with adequate data to perform genetic analysis can be tested or detected by the Flow-through Hybridization Method.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com