Data converting circuit and display apparatus using the same
A technology for converting circuits and data, applied in color signal processing circuits, static indicators, cathode ray tube indicators, etc., can solve problems such as large chip size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
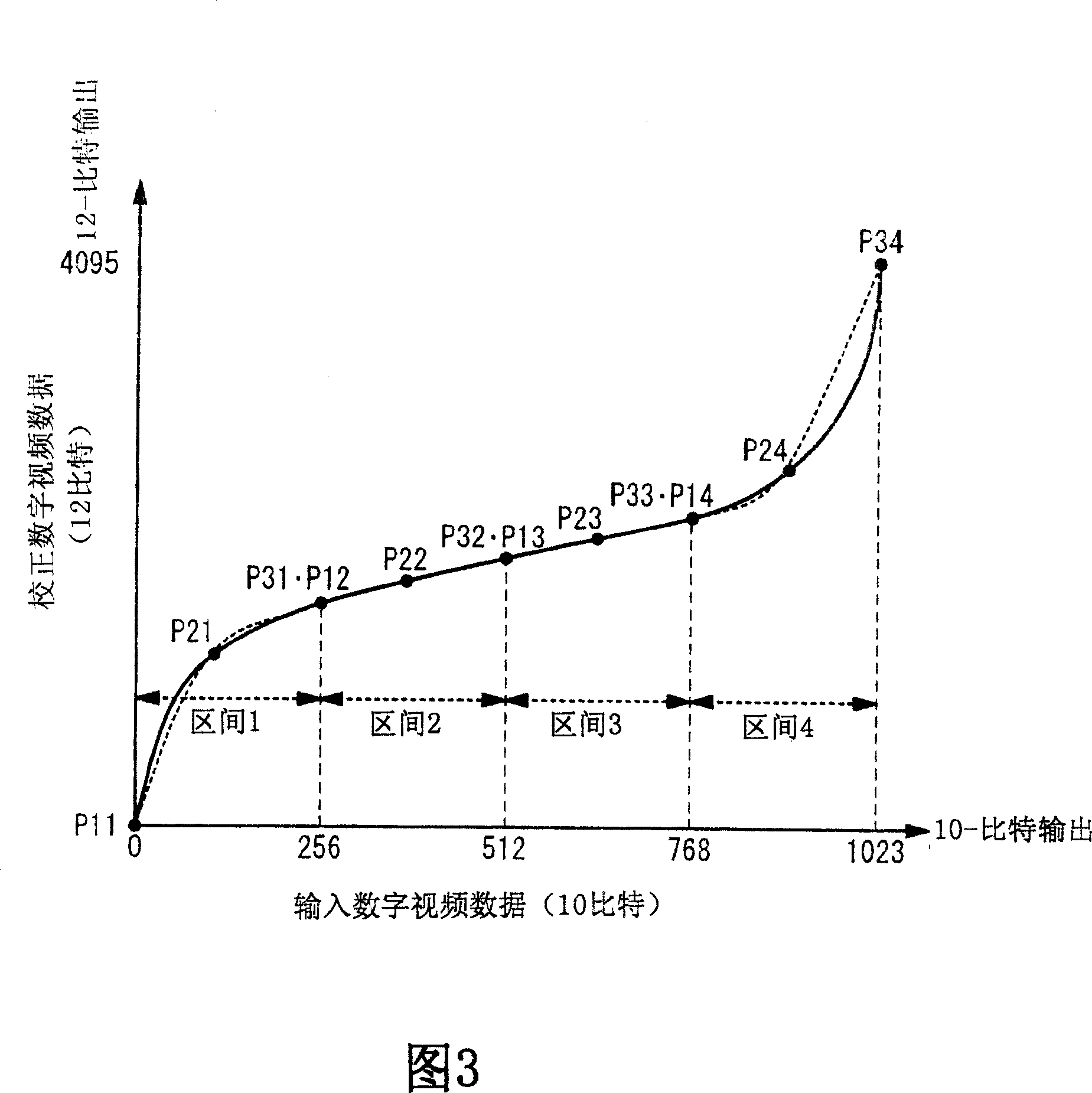
[0058] In the data conversion circuit according to the first embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 3 , approximation calculation of 4 divisions is performed by using a quadratic curve. The pixel data of the input digital video data has 10 bits, and the pixel data of the corrected digital video data after conversion has 12 bits. In general, when performing approximate calculations using an nth-order equation (n is an integer of 1 or more), it is necessary to set (n+1) control points on the curve. Therefore, in the case of a quadratic curve, 3 control points need to be set on the curve for each interval. These 3 control points are usually the start point P1, the curve passing point P2 at the center of the calculation interval, and the end point P3. As shown in FIGS. 4A and 4B , since the control points P1 , P2 , P3 are set to true values (with 12 bits each), the original curve can be approximately represented. However, due to the approximate calculation, ther...
no. 2 example
[0076] A data conversion circuit according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described below. In the second embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 12, similarly to the first embodiment, the section is divided into 4 sections. However, the second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that a linear equation (approximately a straight line) is used. In the case of a straight line approximation, for each interval, two control points on the curve are required. As shown in FIGS. 13A and 13B , start point 1 and end point 2 are used as the two control points. Since the control points P1 and P2 are set to true values (with 12 bits each), the original curve becomes approximately a straight line. In the case of a straight line approximation, the relationship between the error and the input digital video data is always as shown in FIG. 14 . This example is characterized in that the calculation error is 0 at the points P1 and P2, and the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com