Method for classifying and identifying insect utilizing molecule searching table
A key and insect technology, applied in the field of classification and identification of insects using a molecular key, can solve the problems that eggs, larvae and pupa cannot be identified, and achieve a broad application prospect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] Preparation of gene chip
[0026] Various types of probes are solidified on the surface of a solid-phase chip carrier (such as an aldehydic glass sheet) by using a spotting instrument, and a chip with a probe matrix is obtained through hydration, fixation and film washing. In addition to general probes and specific probes, probes usually include positioning probes, positive control probes, negative control probes and blank controls. Except for positioning probes, other types of probes usually have 3 repetitions on the probe matrix to ensure the repeatability and stability of the experimental results.
[0027] Hybridization of PCR products with probes
[0028] Add one or more PCR products with fluorescent markers obtained by PCR amplification of universal primers, add an appropriate amount of hybridization buffer, mix, denature at 95°C, add the solid-phase chip carrier with probes, at a certain temperature (40°C-60°C) hybridize for 1-3 hours or more, wash the slices ...
example 1
[0040] Example 1 Molecular Identification of Insect Species Biochip
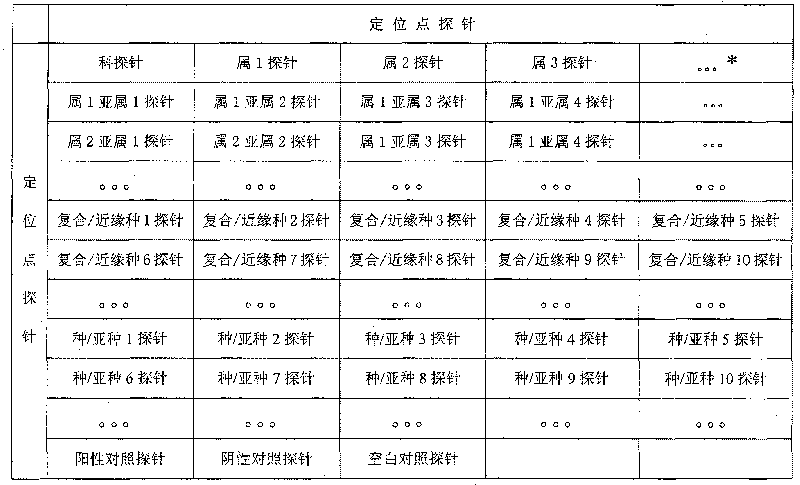
[0041] Using the principles of molecular identification of insects, an unknown insect can be classified into smaller taxa using a different set of probes. Table 1 lists the molecular identification probe arrangement list of a gene chip for insect species. The probes on the list include family general probes, genus general probes, subgenus general probes, compound species / relative species specific probes and Species / subspecies-specific probes and locus probes, positive control probes, negative control probes, and blank control probes. That is, except for the anchor point probe, the rest of the probes were repeated three times.
[0042] Table 1 Schematic list of molecular identification probes for insect gene chips
[0043]
[0044] * Indicates more subgenus, compound / relative probes or species / subspecies probes
[0045] Extract DNA from the insect to be identified, perform PCR amplification with univer...
example 2
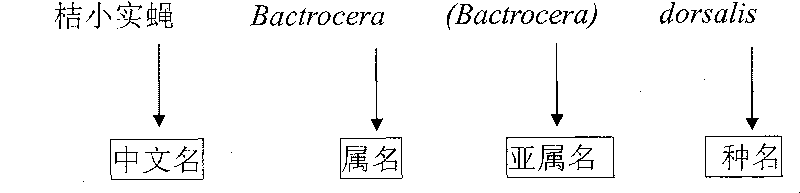
[0048] Example 2 Biochip Rapidly Differentiates Bacteralis Dorsalis Compound Species and Molecular Key
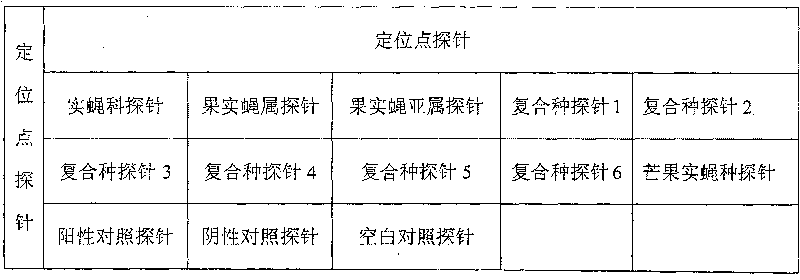
[0049] Bactrocera dorsalis is a kind of Diptera (Diptera), Tephritidae (Tephritidae), Bactrocera (Bactrocera), fruit fly subgenus (Bactrocera) insects. There are as many as 75 species of Bactrocera dorsalis compound species, and it is difficult to distinguish between species. The biochip can quickly distinguish five compound species of Bactrocera dorsalis by setting 1 general probe of Tephritidae, 1 general probe of genus, 1 general probe of subgenus and 6 specific probes of compound species on the chip substrate. According to the principle of insect molecular identification in Example 1, the biochip identification probes for Bactrocera dorsalis complex species are arranged as shown in Table 3, and the complex species are distinguished from each other by a molecular key after chip hybridization. The sequences of the probes in Table 3 are shown in Table 4, Table 5 and the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com