Permanent magnet type rotating electric machine capable of suppressing deformation of rotor core
A technology of rotating electrical machines and permanent magnets, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, magnetic circuit, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of unable to maintain the strength of the bridge and affect the reliability of rotating electrical machines, so as to ensure reliability and suppress Effects that deform and increase degrees of freedom
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
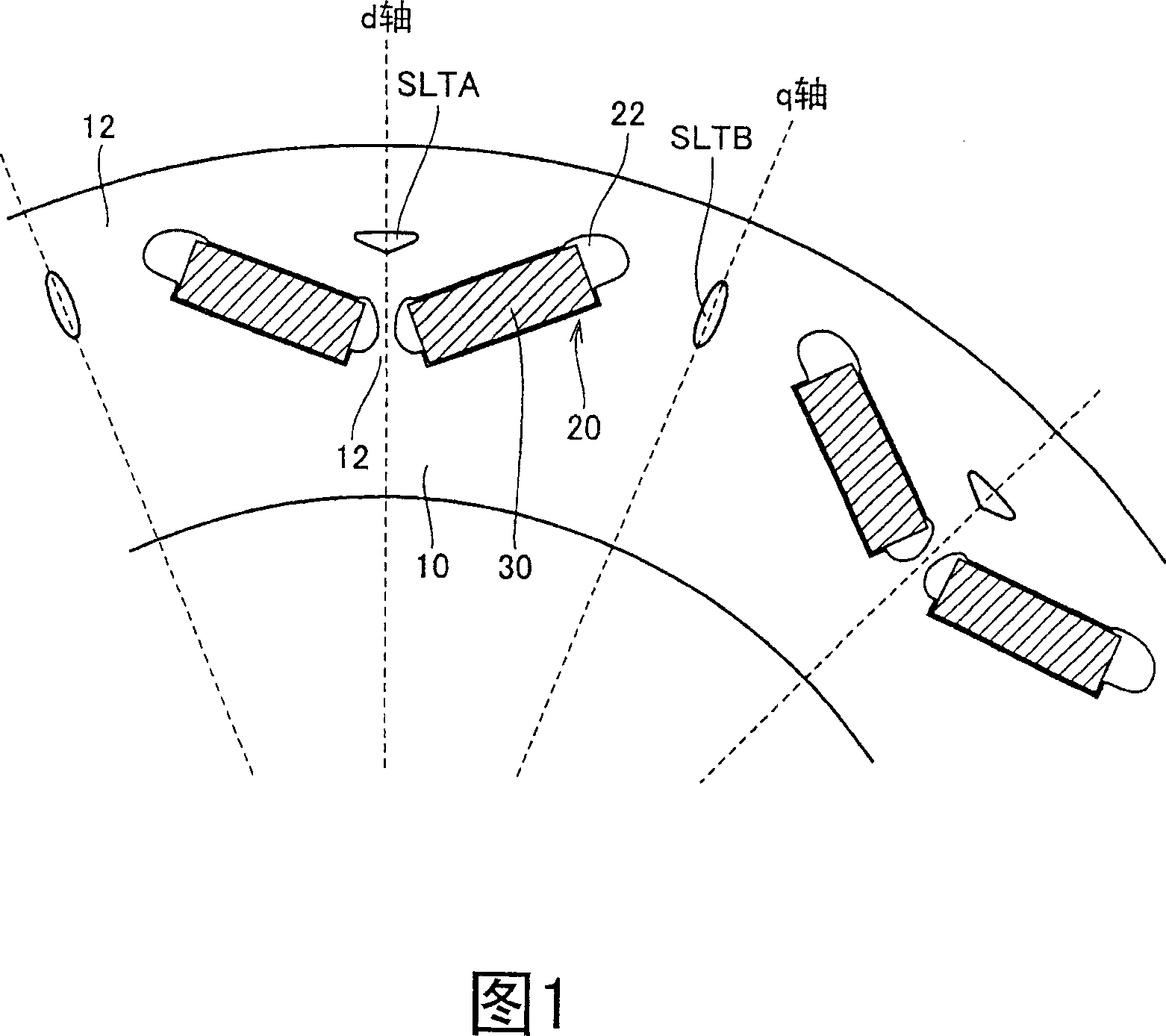
[0041] FIG. 1 is a diagram for describing the structure of a rotor in a permanent magnet type rotating electric machine according to a first embodiment of the present invention. Fig. 1 is an enlarged view of a rotor viewed from the direction of the rotation axis.
[0042] Referring to FIG. 1 , the rotor includes a rotor core 10 disposed at an outer periphery of a rotating shaft, not shown, and a permanent magnet 30 disposed at the rotor core 10 .
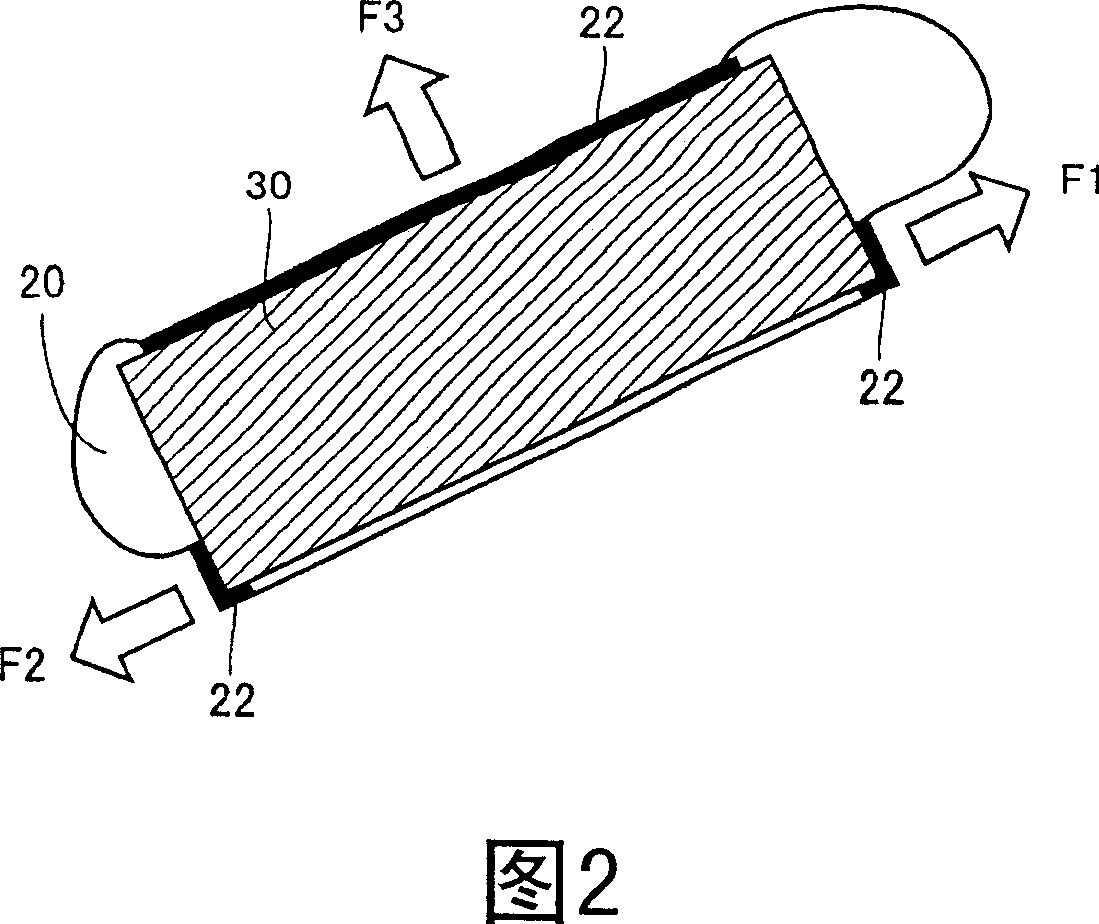
[0043] The rotor core 10 is formed of, for example, a plurality of electromagnet pieces stacked in the rotation axis direction of the rotor. The openings 20 are provided in plural numbers along the circumferential direction of the rotor core 10 . When the electromagnet plates are punched to obtain thin plates forming the rotor core 10, the openings 20 are simultaneously punched and formed parallel to the rotation axis as the thin plates are stacked.
[0044]As shown in FIG. 1 , the openings 20 are arranged at the outer peripheral ...
no. 2 example
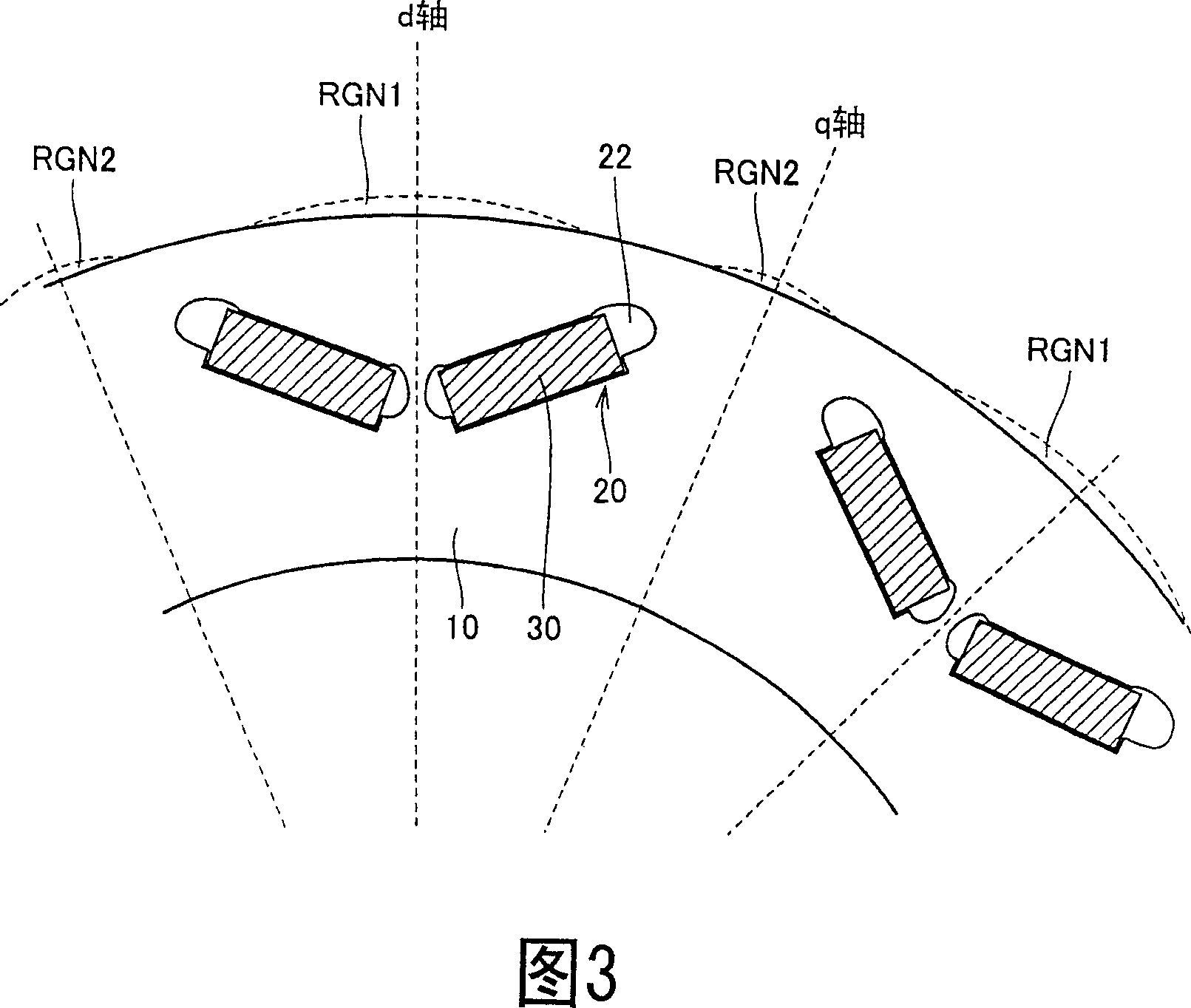
[0089] Fig. 8 is a diagram for describing the structure of a rotor in a permanent magnet type rotating electric machine according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0090] Referring to FIG. 8 , the rotor core 10c includes a plurality of openings 20 and caulking members 40A and 40B. The rotor core 10c in FIG. 8 corresponds to the rotor core 10 in FIG. 1, and the slits SLTA, SLTB thereof are replaced by riveting members 40A and 40B.
[0091] Specifically, as shown in FIG. 9 , each of the caulking members 40A and 40B has a caulking portion protruding in the rotation axis direction and a slit SLTE provided continuously to the caulking portion. When the electromagnetic steel sheet is punched to obtain thin plates forming the rotor core 10 , the caulking portion and the slit SLTE are simultaneously formed and formed parallel to the rotation axis as the thin plates are stacked. By riveting the stacked electromagnetic steel sheets, adjacent electromagnetic steel sheet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com