Wireless transmission apparatus and peak power suppressing method in multicarrier transmission
A technology of wireless transmission and peak power, applied in multiplexing communication, modulated carrier system, multi-frequency code system, etc., can solve problems such as deterioration, signal distortion, and high peak power, and prevent the decline of transmission efficiency and reduce Effect of peak power and throughput reduction prevention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
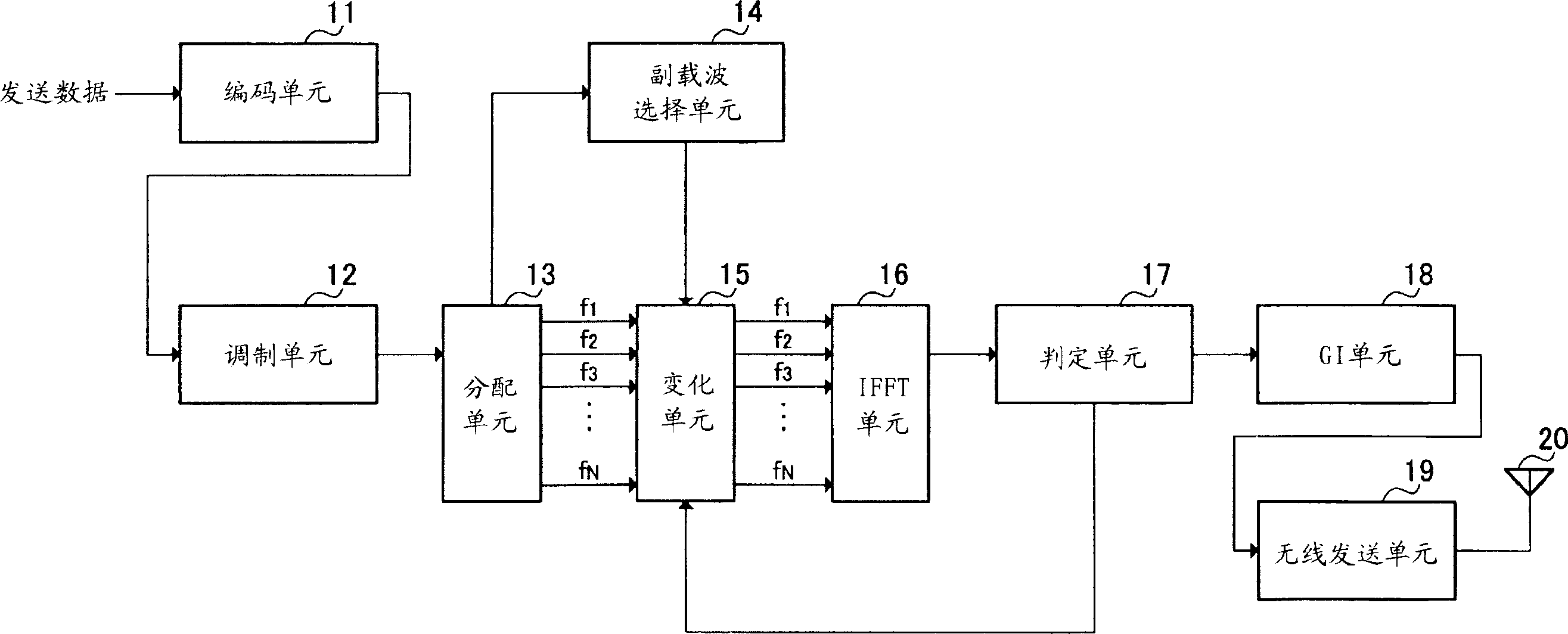
[0041] figure 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the radio transmission apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. figure 1 The shown wireless transmission device includes: a coding unit 11, a modulating unit 12, an allocating unit 13, a subcarrier selecting unit 14, a changing unit 15, an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) unit 16, a judging unit 17, a guard interval ( GI) unit 18 , wireless transmission unit 19 and antenna 20 .
[0042] The coding unit 11 performs error correction coding on the transmission data (bit string).
[0043] The modulation unit 12 modulates data by generating symbols from encoded data and arranging the generated symbols at any one of a plurality of signal points on the I-Q plane. The multiple signal points on the I-Q plane depend on the modulation scheme used by the modulation unit 12 . Details will be described later.
[0044] Distributing unit 13 converts the modulated symbols serially input from modulatin...
example 1
[0061] Variation 1, in such as Figure 7 Change the phase and amplitude of the subcarrier within the range shown. Specifically, the changing unit 15 converts a shown in the following formula (1) k The subcarrier selected by the subcarrier selection unit 14 is multiplied.
[0062] 【Formula 1】
[0063] a k =p·e jθ ...(1)
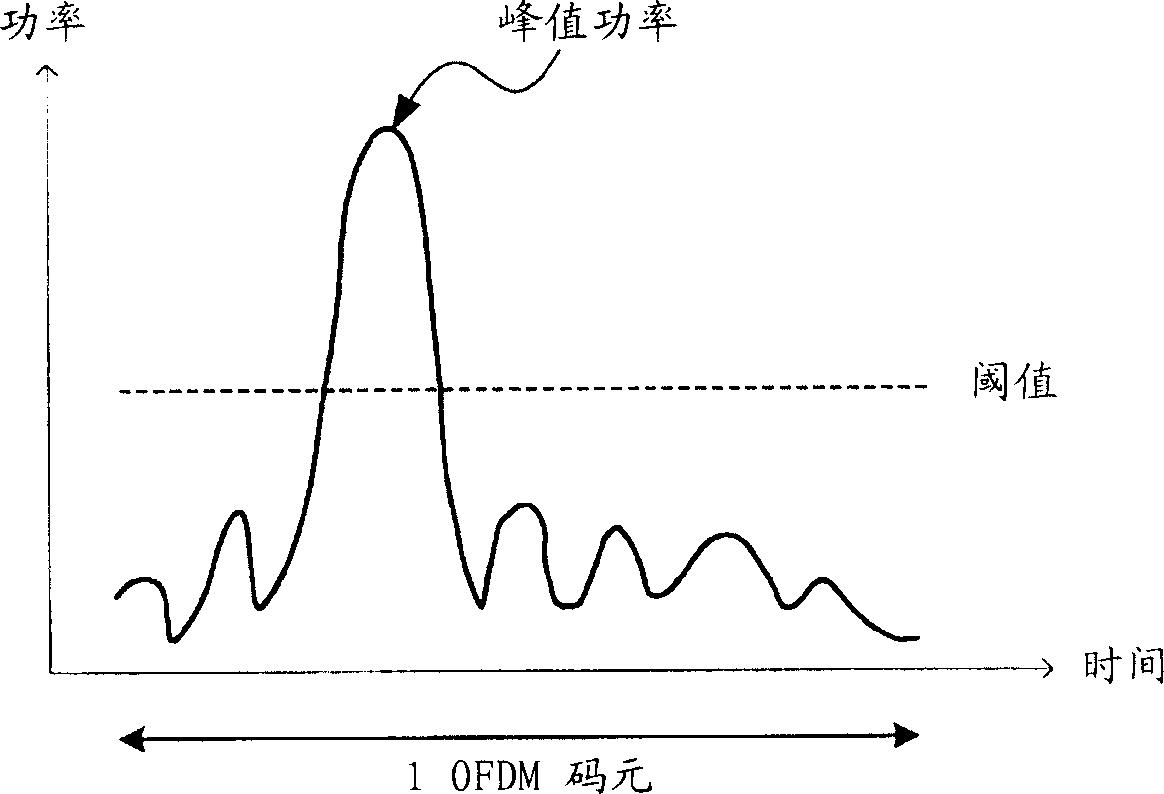
[0064] Wherein, p is a variable 0<p<1 for changing the amplitude, and θ is a variable π / 4<θ<π / 4 for changing the phase, both of which are random variables for each subcarrier. Also, k is 1, 2..., N (N is the total number of subcarriers included in one OFDM symbol). In this way, when θ is randomly changed to change the phase of each subcarrier, the phases of each subcarrier can be made out of synchronization, and as a result, the peak power of the OFDM symbol can be suppressed. In addition, since p is 0<p<1, the change range is the range inside the amplitude increase / decrease boundary line (a part of a circle with a radius of 1). Compared with the su...
example 4
[0070] Variation 4, in such as Figure 10 Change the phase and amplitude of the subcarrier within the range of variation shown (within the range in which the circle in Variation 3 is changed to an ellipse). In Variation 4, as in Variation 3, since the variation range is larger on the inside than outside of the amplitude increase / decrease boundary, the transmission power of the OFDM symbol decreases in terms of probability.
[0071] (Variation 5)
[0072] Variation 5, in Figure 11 Change the phase of the subcarrier within the range shown (on the boundary line between amplitude increase and decrease). That is, instead of changing the amplitude, only the phase. Specifically, the changing unit 15 converts a shown in the following formula (2) k The subcarrier selected by the subcarrier selection unit 14 is multiplied.
[0073] [Formula 2]
[0074] a k =e jθ ...(2)
[0075]Wherein, θ is π / 4<θ<π / 4, and is a random variable of each subcarrier. In this modification examp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com