Necking checking and control method for melted electrode arc welding
A melting electrode and arc welding technology, which is applied in arc welding equipment, welding equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problem of unstable control system and achieve the effect of stable control system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
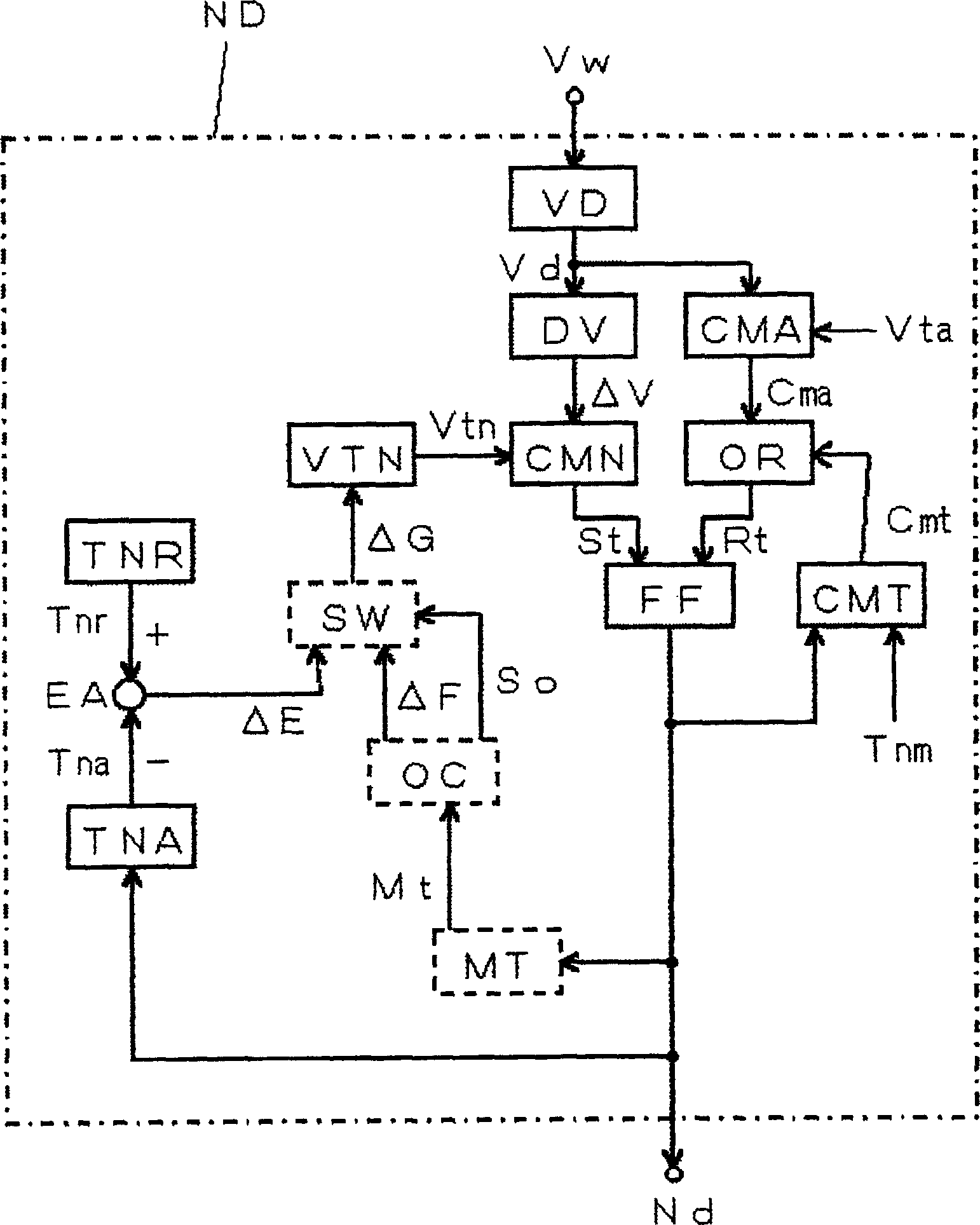
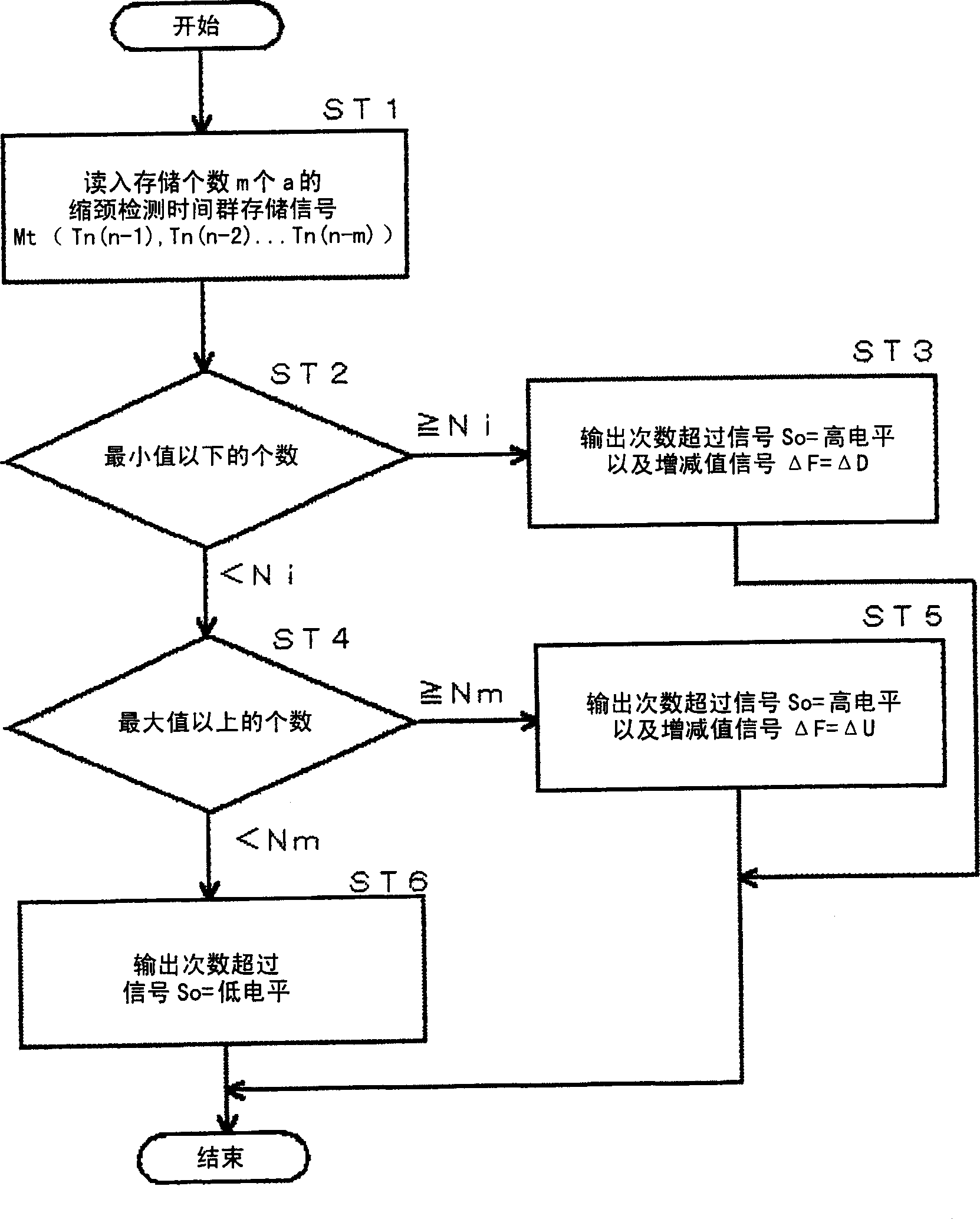
[0039] Embodiment 1 of the present invention is a detection and control method of constriction in molten electrode arc welding, wherein: detecting the constriction detection time in each short circuit, storing a given number m of constriction detection times Tn in the past from the current moment, When the number of stored constriction detection times Tn below the minimum value is greater than or equal to the minimum value, the constriction detection reference value Vtn is reduced by a preset reduction value ΔD, and each stored constriction detection time Tn is not less than the maximum value. When the number of objects is greater than or equal to the maximum value, the constriction detection reference value Vtn is increased by a preset increase value ΔU. Details of Example 1 are described below.
[0040] The block diagram of the welding power source used to implement the detection and control method of the constriction of the molten electrode arc welding in the first embodime...
Embodiment 2
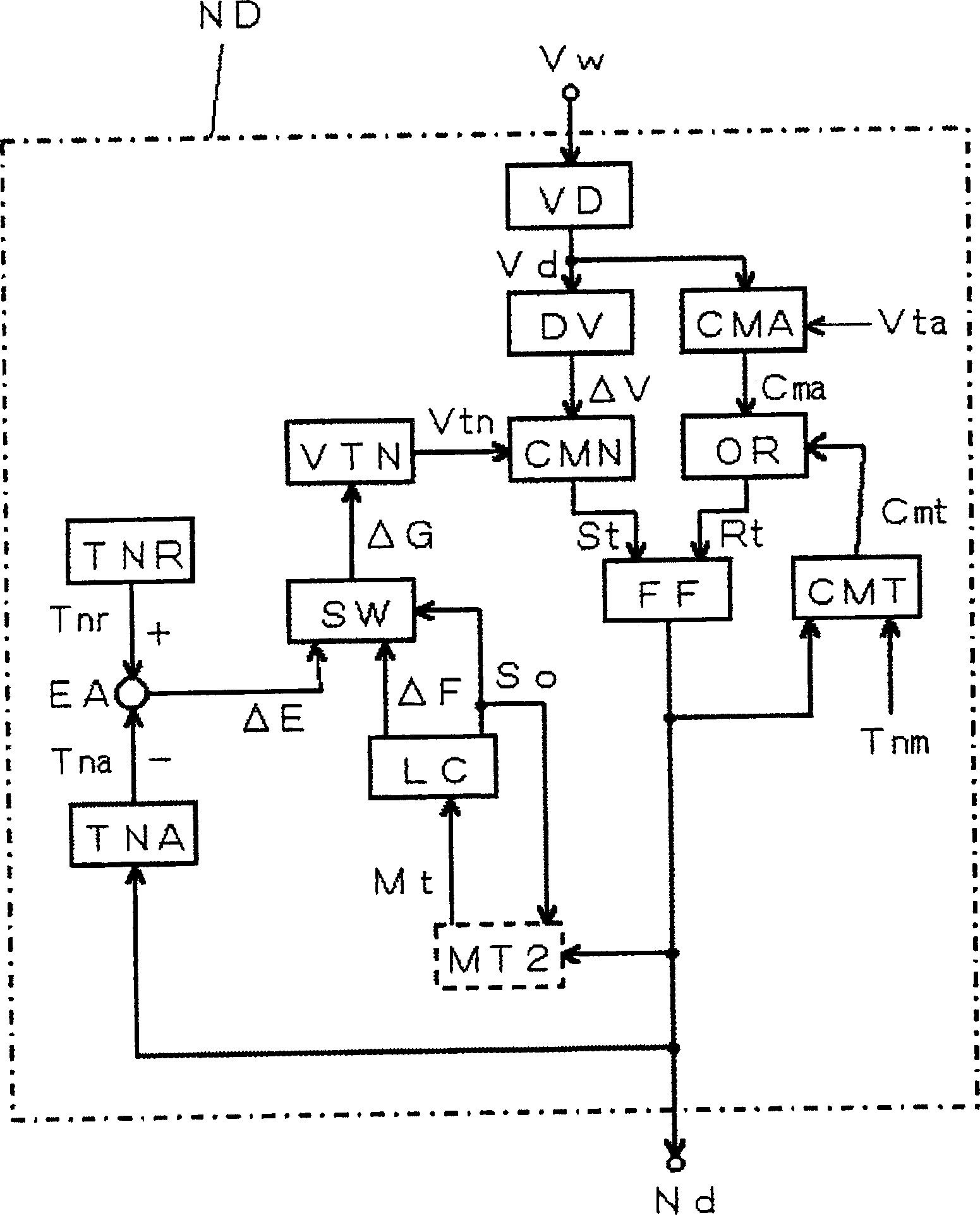
[0047] The block diagram of the welding power source used to implement the detection and control method of the constriction of the molten electrode arc welding according to the second embodiment of the present invention is described in the above-mentioned Figure 5 , so that the necking detection control circuit ND is image 3 The block diagram shown. exist image 3 , for the above figure 1 The same blocks are given the same symbols, and their descriptions are omitted. The following instructions are compatible with figure 1 The different blocks are indicated by dotted lines.
[0048] The second constriction detection time group storage circuit MT2 takes the constriction detection signal nd as an input, detects the constriction detection time of each short circuit, stores constriction detection time groups with a given storage number m in the past from the current moment, and outputs the constriction detection time group. The neck detection time group stores the signal M...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com