Digital map position information communication method, program for executing the same, program product therefor, system therefor, and apparatus therefor
A technology for location information and digital maps, applied in traffic control systems, traffic control systems for road vehicles, maps/plans/charts, etc., to solve problems such as frequent errors and ineffective means
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
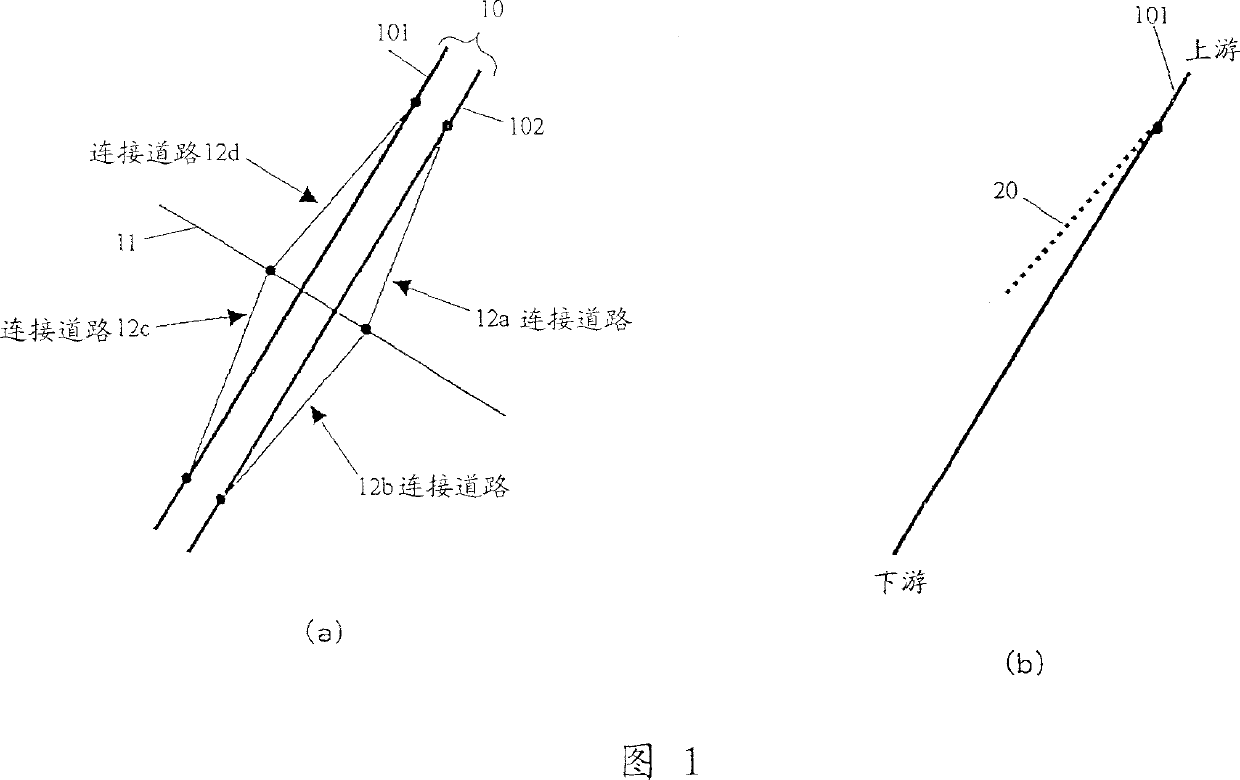
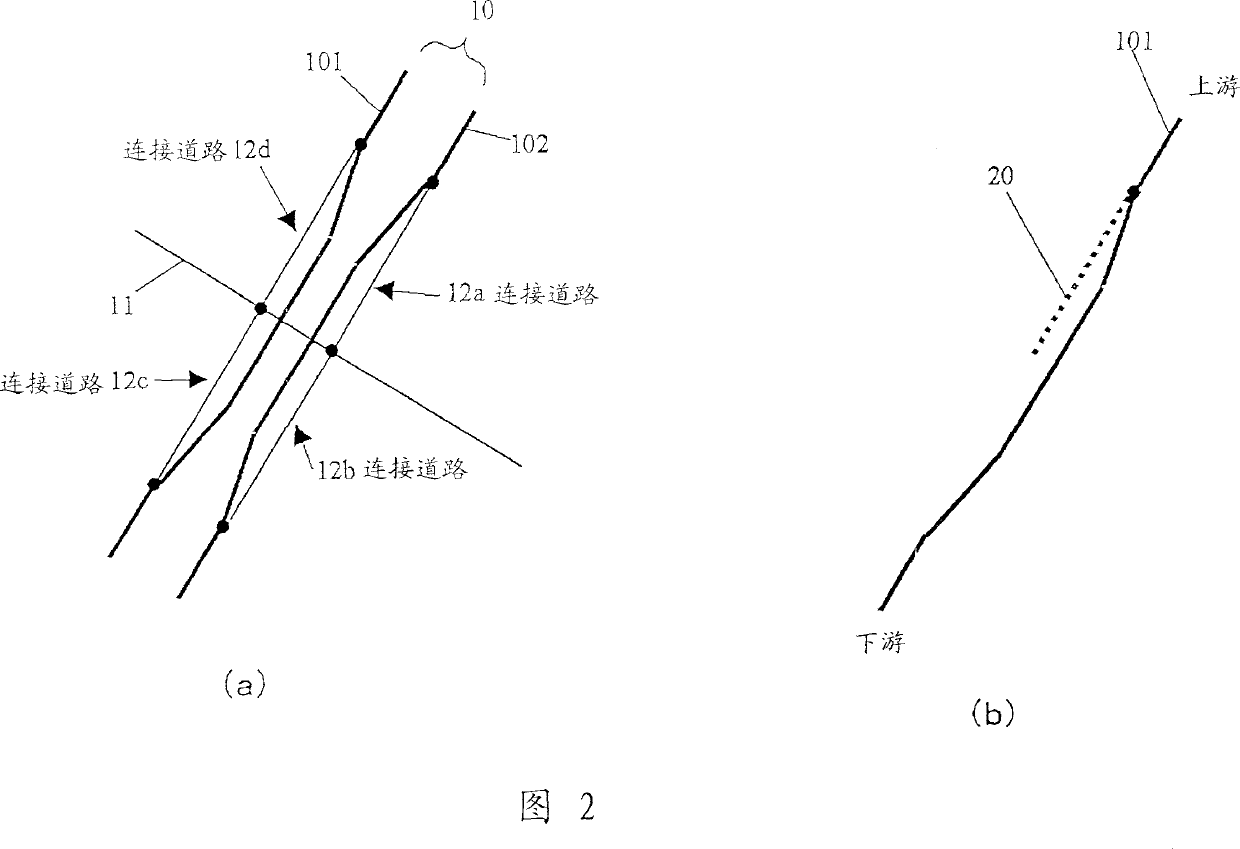
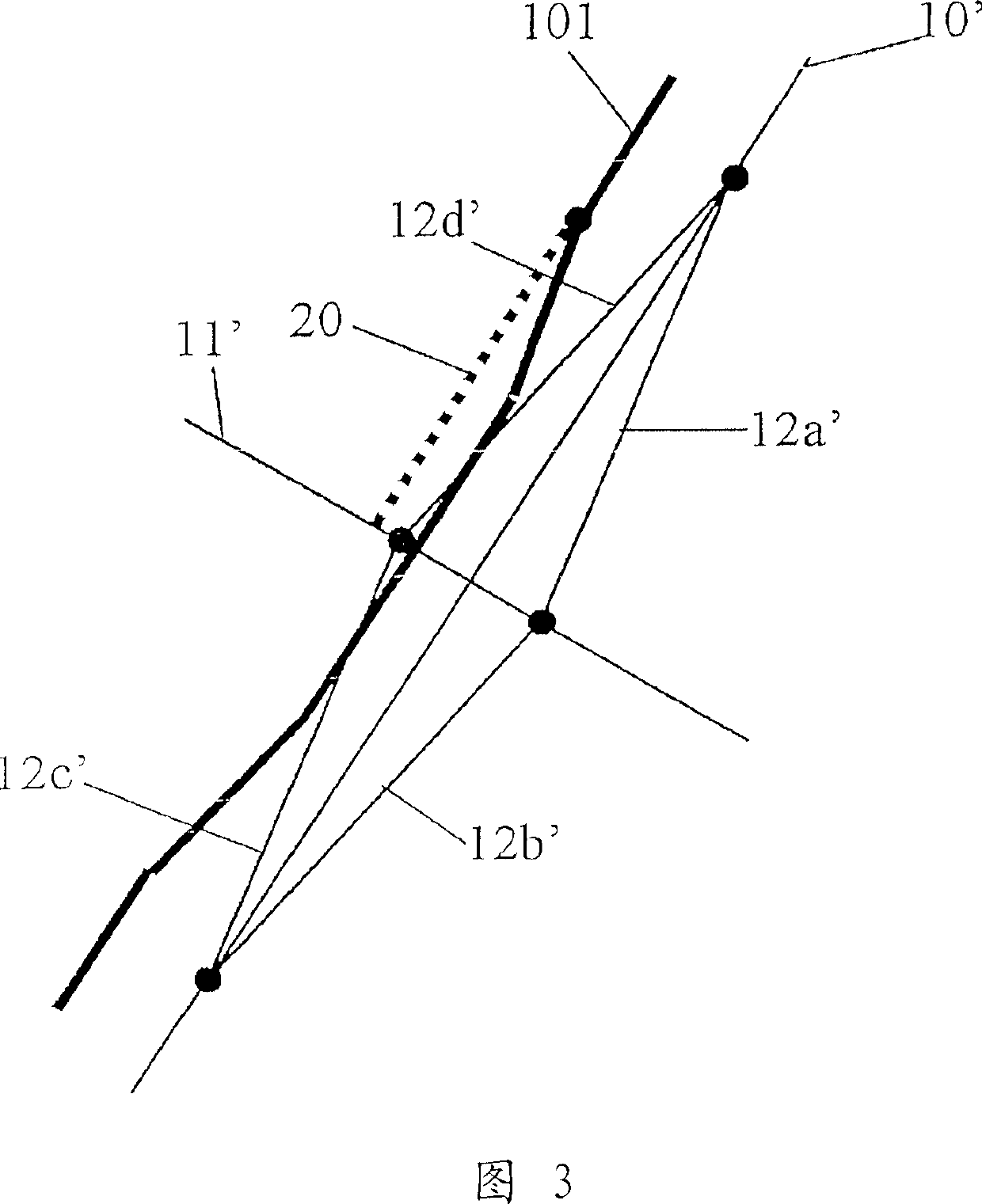
[0086] In the location information transmission method of the embodiment of the present invention, the transmitting side not only transmits the road shape data of the target road which is prone to spot recognition errors, but also the branch part of the road which is separated from the target road at a predetermined angle. Alternatively, shape data of a portion intersecting the target road (these two points will be collectively referred to as "branch") is transmitted as auxiliary information or reference information. In short, "branches" are roads (or connecting roads) connected to roads (ie, object roads) of the main object to be transferred. At the time of point recognition, the receiving side refers to the branch shape and specifies the target road. "Spot recognition" defines an action of pointing out the position of an object road on a digital map or recognizing a corresponding road on a digital map. This also includes the concepts of so-called "map matching" and "pattern...
no. 2 example
[0145] Hereinafter, a second embodiment of the present invention is explained in conjunction with another method for determining an evaluation value representing the similarity between an object road candidate and a branch candidate (ie, an auxiliary candidate, which will be omitted below) and an original shape.
[0146] In this method:
[0147] (1) As shown in Fig. 17 (a), the coordinates of the point that advances Ln along the object road of the original shape from the branch point On of the branch are represented by Pn(Xn, Yn), and are represented by Qn(Vn, Wn) Indicates the coordinates of the point that progressed Ln along the branch of the original shape. In addition, the coordinates of a point advancing Ln along the target road candidate k are represented by Pkn(Xkn, Ykn), and the coordinates of a point advancing Ln along the branch candidate are represented by Qkn(Vkn, Wkn);
[0148] (2) The angle θn of Pn→On→Qn (with positive and negative signs) and the angle θkn of P...
no. 3 example
[0155] The third embodiment of the present invention will be described in connection with another method of calculating the comprehensive evaluation value of the target road candidate.
[0156] In this method:
[0157] (1) As shown in Fig. 18(a), calculate the intersection point Pn between a circle whose branch point is the center O and whose radius is Rn and the object road, and the distance between the circle and the branch in the original shape intersection point Qn;
[0158] (2) Calculate the vector of pn→Qn. This vector may be represented by relative coordinates ΔXn and ΔYn, as shown in the first embodiment, or it may be represented by the angle θn between Pn→O→Qn and Rn;
[0159] (3) As shown in FIGS. 18(b) and 18(c), starting from the intersection point Pkn between a circle with the branch point of the branch candidate as the center O and radius Rn and the target road candidate k, and using Vector Pn→Qn, set Qkn′;
[0160] (4) According to the road network other tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com