Distributed hash table in opposite account
A distributed hash table and distributed hash technology, applied in the field of resource location technology, can solve problems such as lack of resources, poor network scalability, and slow query response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
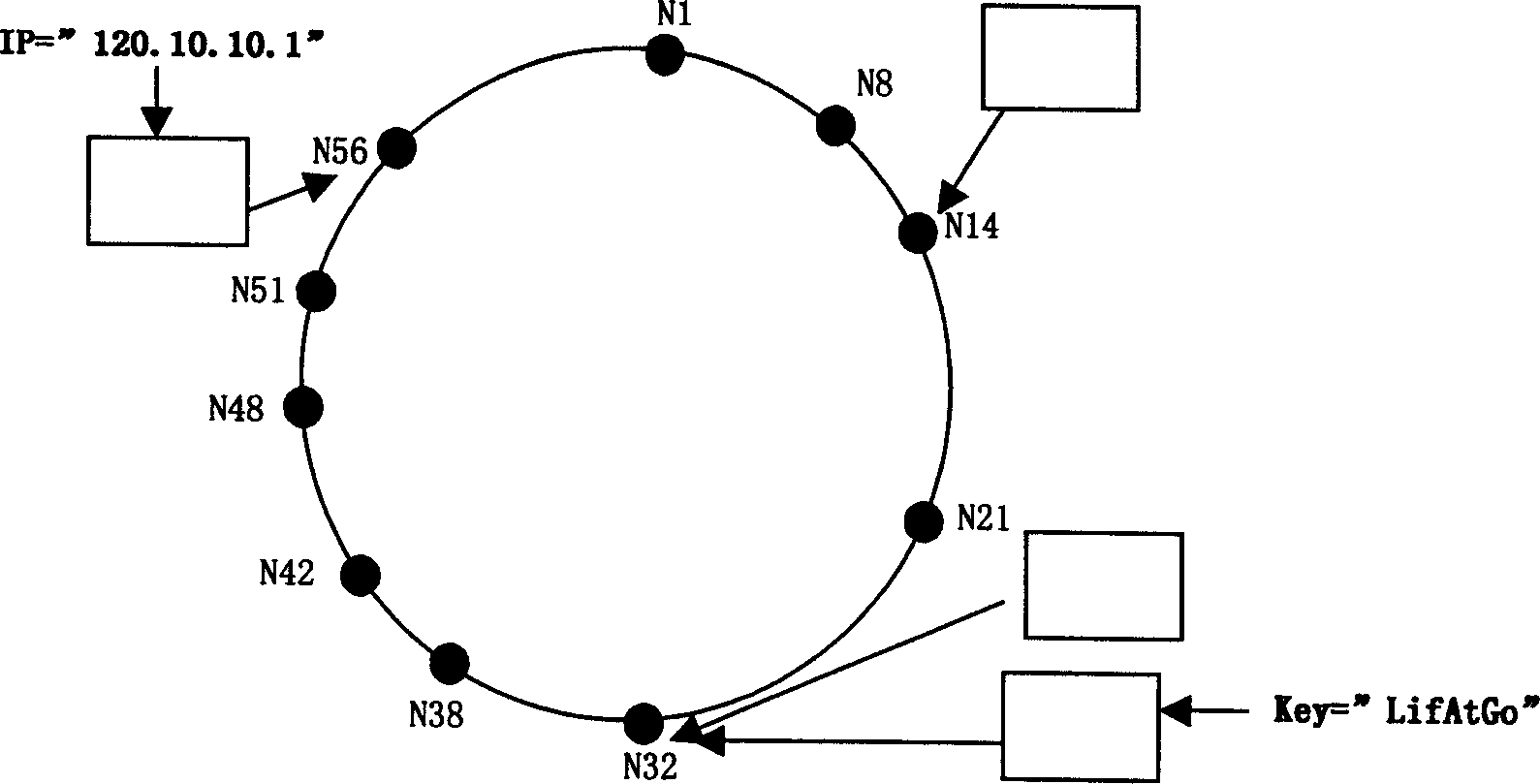
[0049] figure 1 is an example map of consistent hashing. Among them, those starting with N represent node identifiers, and those starting with K represent resource key identifiers. For example, the node with the IP address of 120.10.10.1 in the figure gets the identifier K54 after SHA1 hashing, which is stored in its successor node identifier N56; and the identifier after the hash of the keyword "LifAtGo" is K30, which is stored in Its successor node identifier N32.
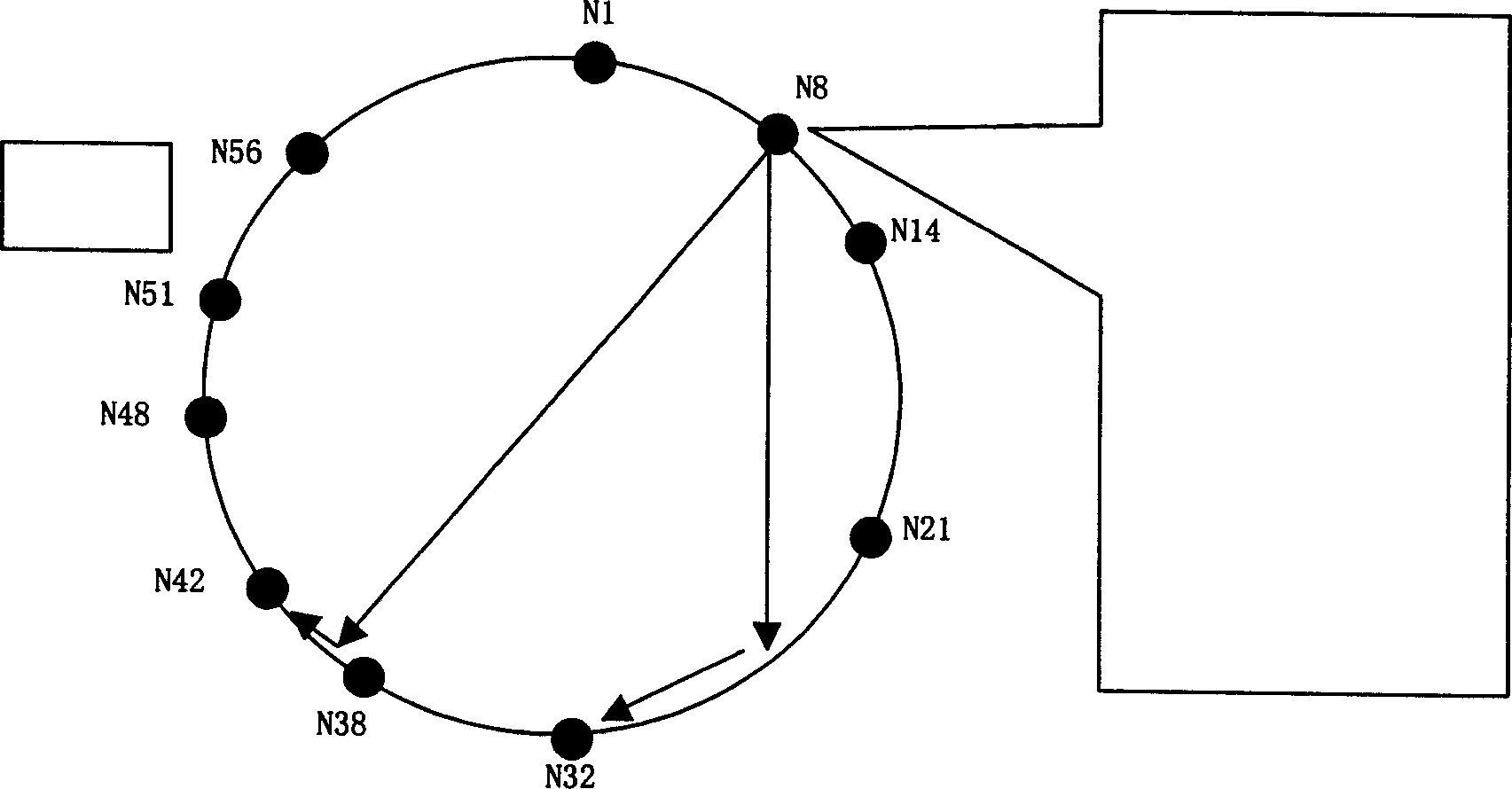
[0050] figure 2 BChord data organization instance. Among them, those starting with N represent node identifiers, and those starting with K represent resource key identifiers. Each node only needs to maintain a routing table consisting of at most m entries, which is called a finger table. If the N8 node can query information through N(8+16), that is, the N24 operation, but there is no N24 node, so the N8 node can query the information of the successor node N32 of N24 through the N(8+16) operation. Similarly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com