Nuclein acid fixing method and method for producing biosensor by said method
A technology of biosensors and immobilization methods, applied in the field of nucleic acid immobilization, can solve the problems of long film formation time, difficulty in nucleic acid density, and density changes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086]
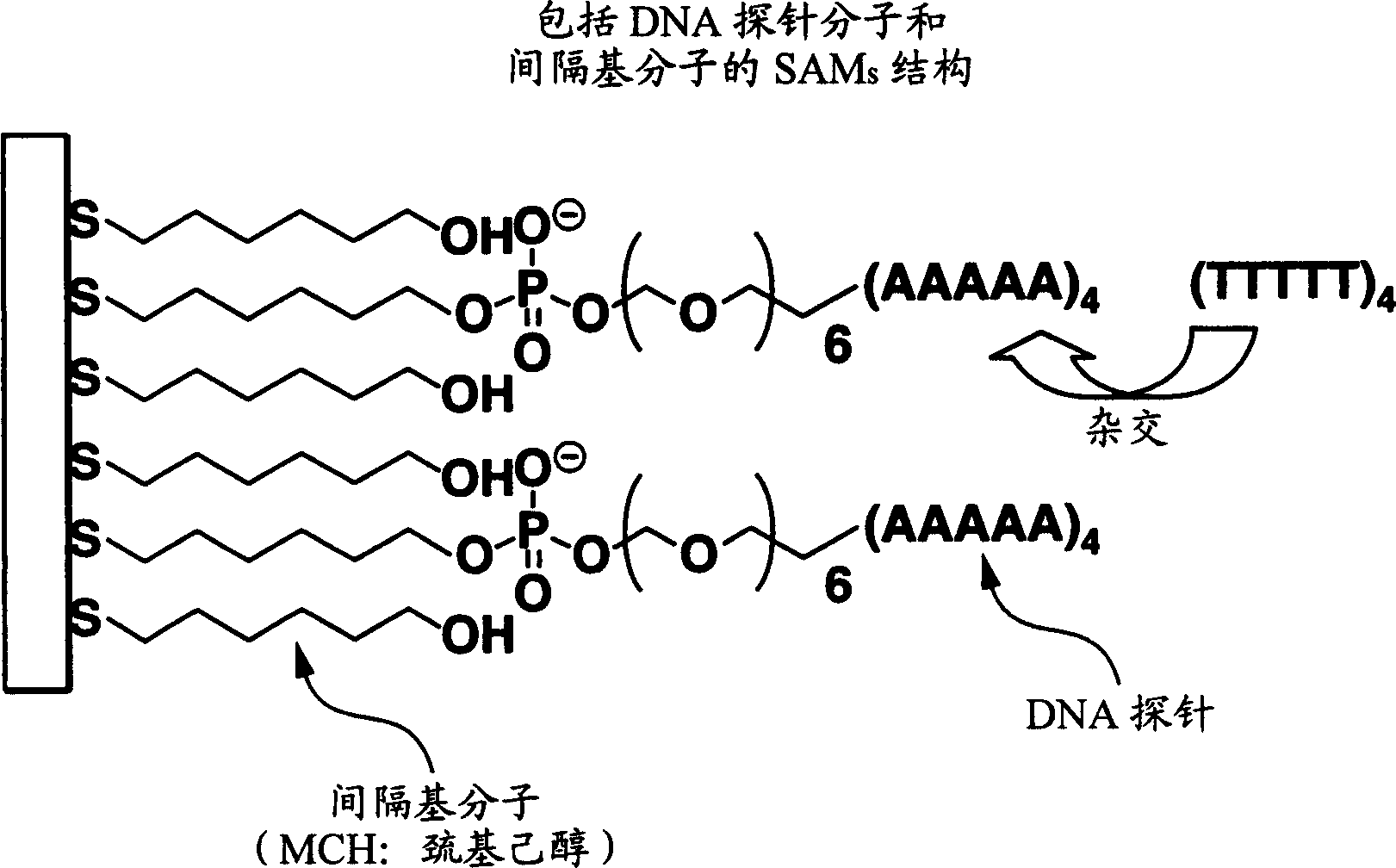
[0087] (1) Nucleic acid probes: nucleic acid probes for adsorption on solid substrates can be purchased from the formula (dA)20-(CH 2 -O-CH 2 ) n PO 4 -(CH 2 ) 6 Nucleic acid probe represented by -SH. Here, dA refers to deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate.
[0088] (2) Spacer molecule: The spacer molecule can be purchased as 6-mercapto-1-hexanol (MCH).
[0089] (3) Preparation of buffer: prepare PBS buffer (50mM KPO 4 , 5mM EDTA, 1M NaCl, pH7.0). Nucleic acid probes and spacer molecules were dissolved in this PBS buffer, and two solutions of 1 μM and 10 μM were used, respectively.
[0090] (4) Preparation of solid substrate: According to this manufacturing method, a glass substrate with a gold thin film on the surface is prepared as a solid substrate.
Embodiment 2
[0092]
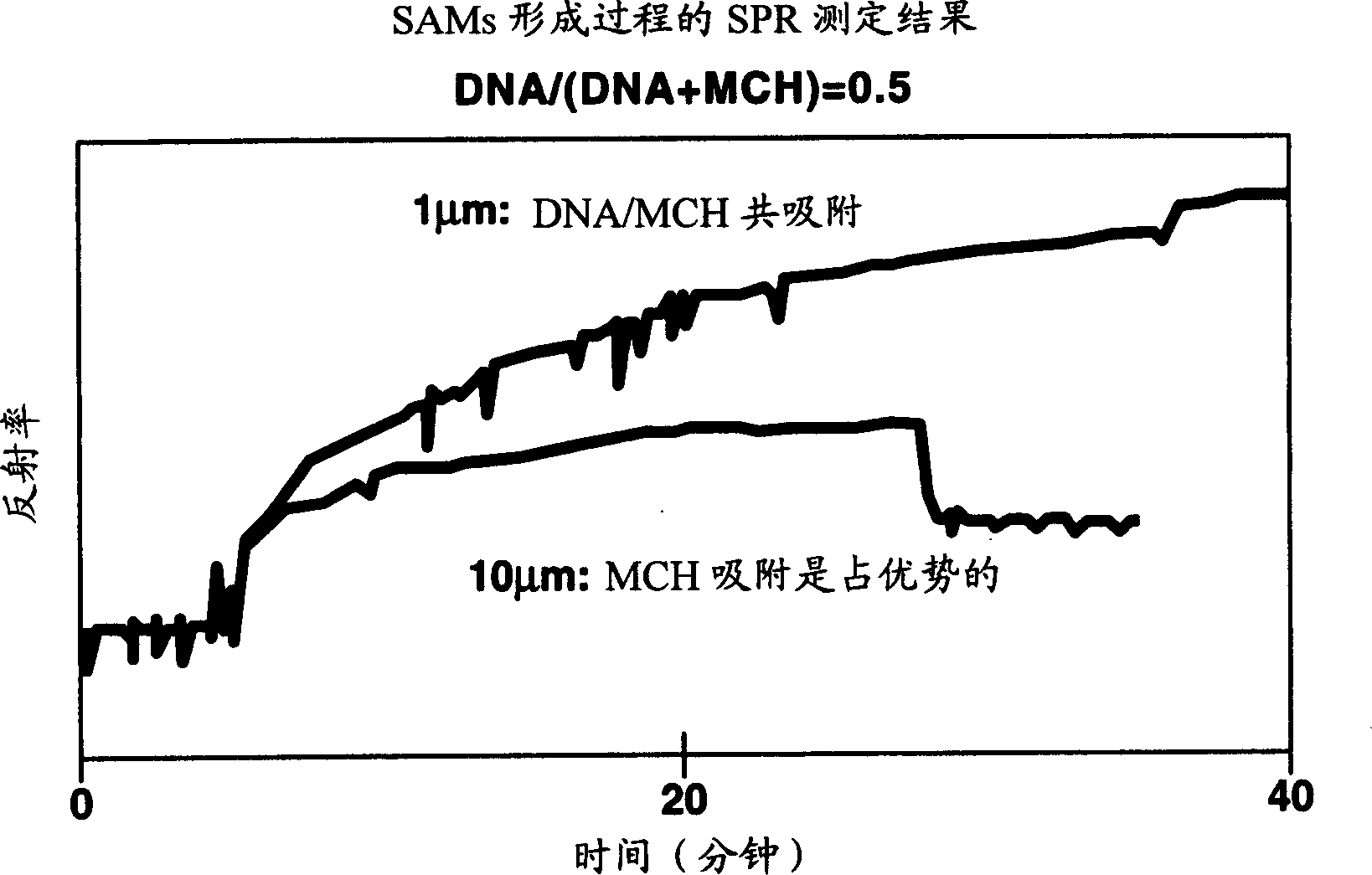
[0093] (1) Co-adsorption: Prepare a mixed solution by mixing the nucleic acid probe solution prepared in Example 1 and the spacer molecule solution (respectively 1 μM and 10 μM), and the ratio of nucleic acid / MCH=25 / 75, Three ratios of 50 / 50 and 75 / 25, 1 μM nucleic acid probe solution and 1 μM spacer molecule solution were mixed, and 10 μM probe solution was mixed with 10 μM spacer molecule solution to prepare a mixed solution. Dip the solid substrate with a clean surface into the mixed solution and incubate for 1-3 hours. The reflected light intensity of the substrate was measured by the SPR method with the viewing angle fixed.
[0094] (2) Results:
[0095] figure 2 Shown is the result of evaluating the adsorption process of the nucleic acid probe by the amount of change in reflected light measured by SPR. Changes in the intensity of reflected light are associated with changes in the refractive index and, furthermore, with increases and decreases in film thick...
Embodiment 3
[0098]
[0099] (1) The preparation of nucleic acid probes, spacer molecules, buffers, and solid substrates is as follows
[0100] The record of embodiment 1.
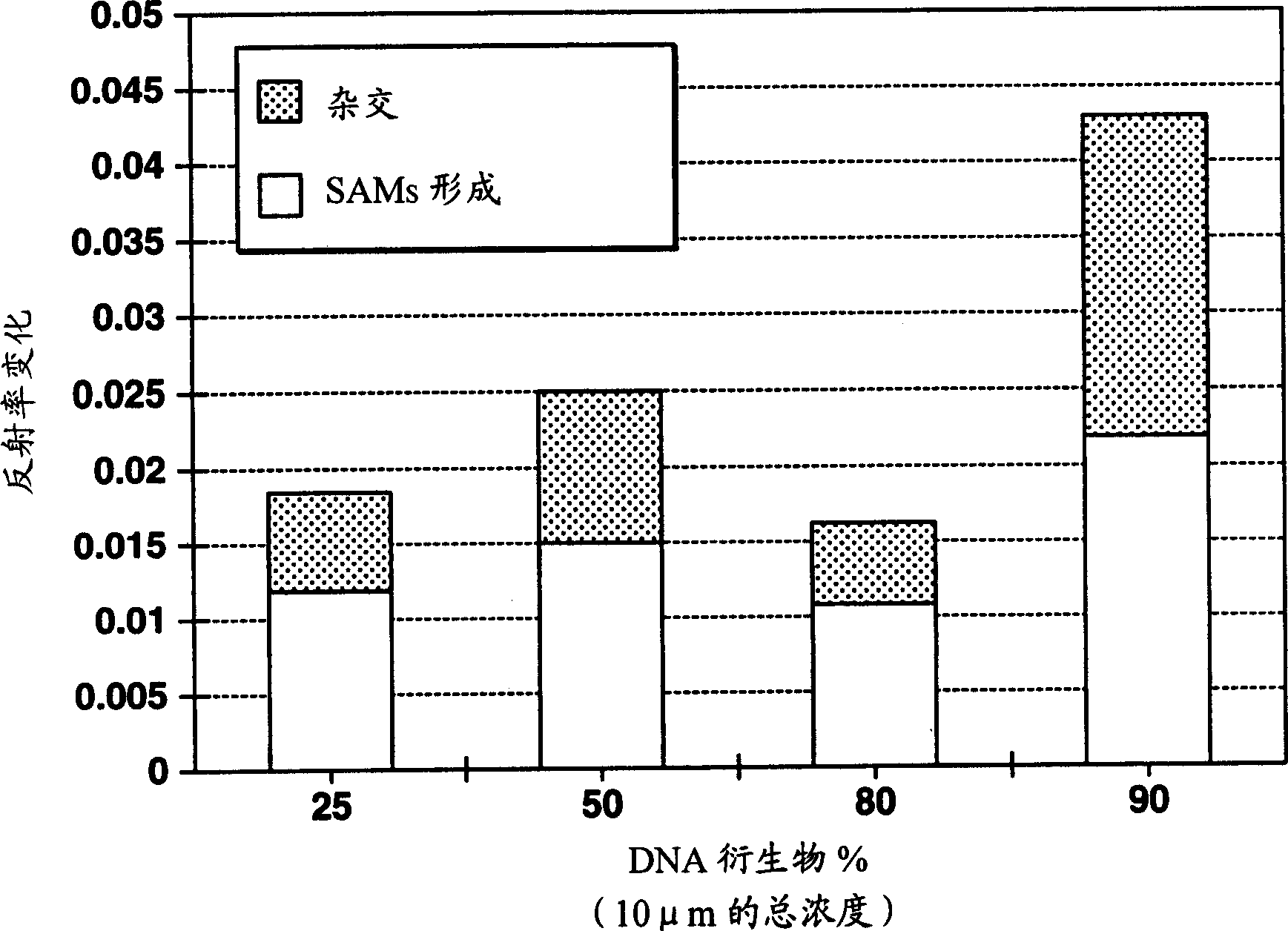
[0101] (2) Co-adsorption: the nucleic acid probe solution prepared in Example 1 and the spacer molecule solution (respectively 10 μM) were mixed in molar % ratio with nucleic acid / MCH=25 / 75, 50 / 50, 80 / 20, 90 / 10 The four ratios were mixed to prepare a mixed solution. Dip the solid substrate with a clean surface into the mixed solution and incubate for 1-3 hours.
[0102] (3) Hybridization reaction: The complementary DNA (target DNA molecule: dT20) was dissolved in PBS buffer at a DNA concentration of 1 μM, and the DNA solution was brought into contact with the co-adsorbed membrane substrate prepared in (2) above to cause a hybridization reaction.
[0103] (4) Results:
[0104] image 3 Shown are the results of evaluating the degree of adsorption of nucleic acid probes and the level of hybridization using the amoun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com