Display device and manufacturing method thereof
A display device and one-sided technology, applied in static indicators, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large working voltage, inability to move particles, and increased working voltage, etc., to achieve good display and achieve the effect of displaying spots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
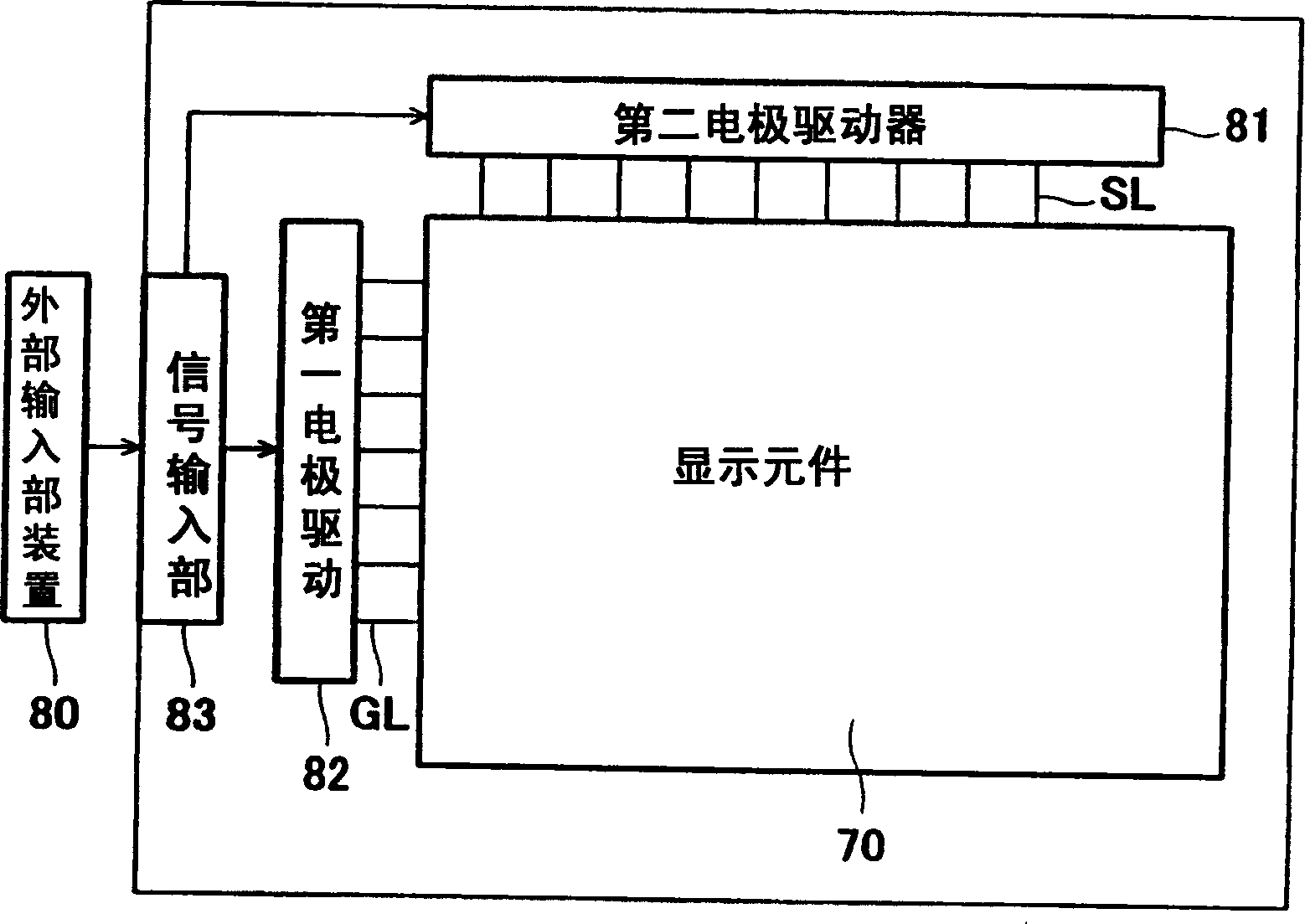
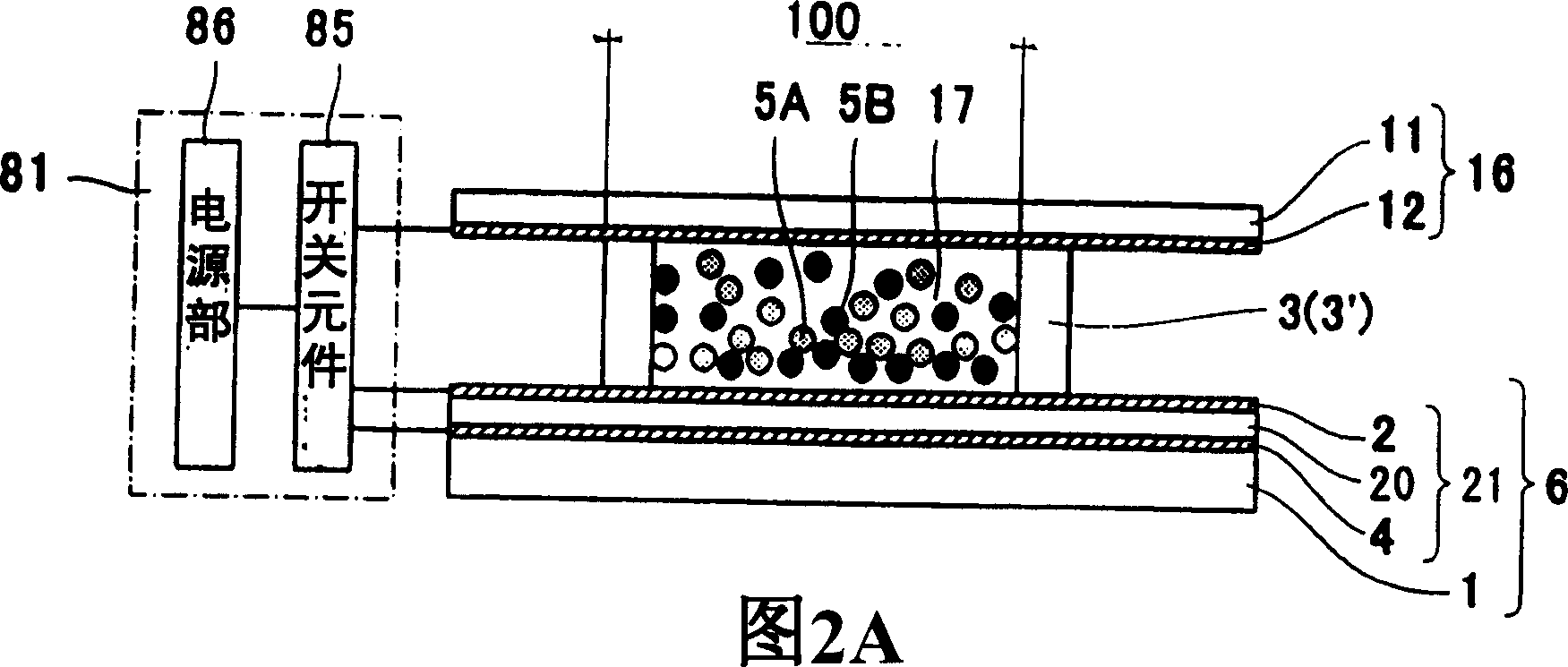
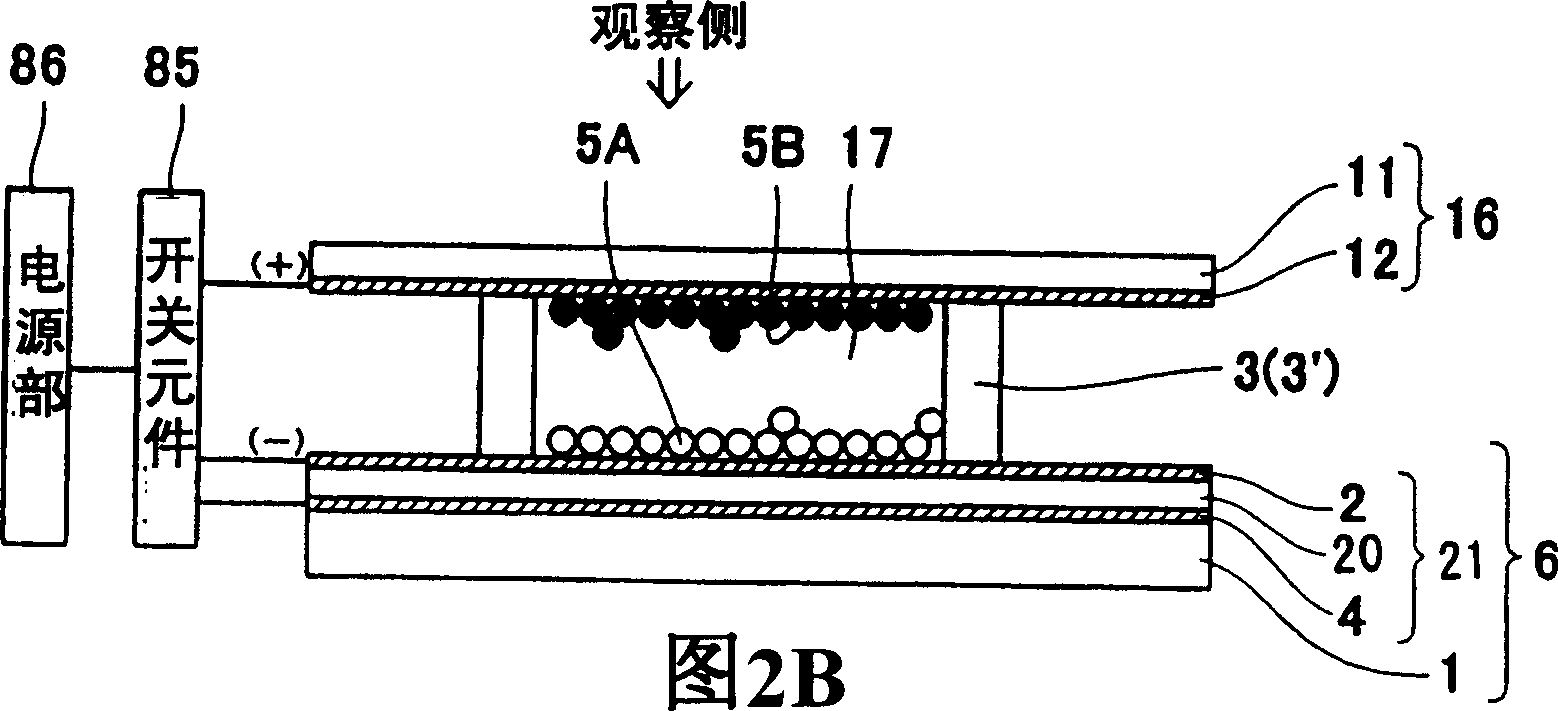
[0108] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the display device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In addition, Figures 2A-2C are diagrams showing the configuration figure 1 A schematic diagram of a pixel structure of a display element of a display device, showing a cross section perpendicular to the display surface (hereinafter referred to as a vertical cross section).
[0109] Such as figure 1 As shown in FIGS. 2A-2C , the display device is composed of a display element 70 whose display portion is a display panel. As shown in FIGS. 2A-2C , the display element 70 has a lower substrate 6 and an upper substrate 16, and the two substrates 6, 16 are supported by a spacer 3' and are arranged facing each other with a predetermined gap therebetween. Thus, a space 17 is formed between the two substrates 6 , 16 . Since the space 17 is divided by the partition 3', the partition 3' is referred to as the partition wall 3 herein. Each area of the spac...
Embodiment approach 2
[0155] image 3 It is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the structure of a pixel constituting a display element of a display device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, the display element of this embodiment has the same structure as that of the display element of Embodiment 1, but the difference is that the black particles 5B have conductivity and are formed on the first and second electrodes 2, 12 as a charge transport layer. The electron transport layer 7.
[0156] In Embodiment 1, the case where all the colored particles have insulating properties was described, but if at least one of them is insulating, one of them may be conductive. When the colored particles are conductive, it is necessary to form a thin film or an insulating film containing a charge transport material on the surfaces of the first and second electrodes 2 and 12 that are in contact with the particles. Details are described below.
[0157] For example, ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0162] Figure 4 It is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the structure of a pixel constituting a display element of a display device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Such as Figure 4 As shown, in the display element of the present embodiment, the partition wall 3 functions as the vibration generating portion 21 .
[0163] When making the display element of the present embodiment, for example, use two glass substrates as the first and second substrates 1, 11, and form an ITO film on the surface of each glass substrate respectively, as the first and second electrodes 2, 12, At the same time, polycarbonate films are respectively formed on the ITO films as insulating films 22 . Thus, the upper substrate 16 and the lower substrate 6 are produced.
[0164] Next, on the surface of the prepared lower substrate 6 or upper substrate 16, a sheet-shaped piezoelectric body 20 (hereinafter referred to as a piezoelectric sheet 20) whose front and back surfaces a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com