Medical preparations for treatment of alpha-galactosidase A deficiency
A technology of galactose and oligosaccharide, applied in glycosylase, gene therapy, enzyme and other directions, can solve the problem of unsuitable products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0162] Example 1. Preparation and use of constructs designed to deliver and express α-Gal A
[0163] Two expression plasmids, pXAG-16 and pXAG-28, were constructed. These plasmids contain human α-Gal A cDNA encoding 398 amino acids of α-GalA enzyme (without α-Gal A signal peptide), genomic DNA of hGH signal peptide interrupted by the first intron of the human growth hormone (hGH) gene sequence, and hGH gene 3' untranslated sequence (UTS) containing polyadenylation signal. Plasmid pXAG-16 contains the human cytomegalovirus immediate early (CMV IE) promoter and first intron (flanked by non-coding exon sequences), whereas plasmid pXAG-28 consists of the collagen Iα2 promoter and exon 1 driver, it also contains the 5'UTS of the β-actin gene (containing the first intron of the β-actin gene).
[0164] 1.1 Cloning of complete α-Gal A cDNA and construction of α-Gal A expression plasmid pXAG-16
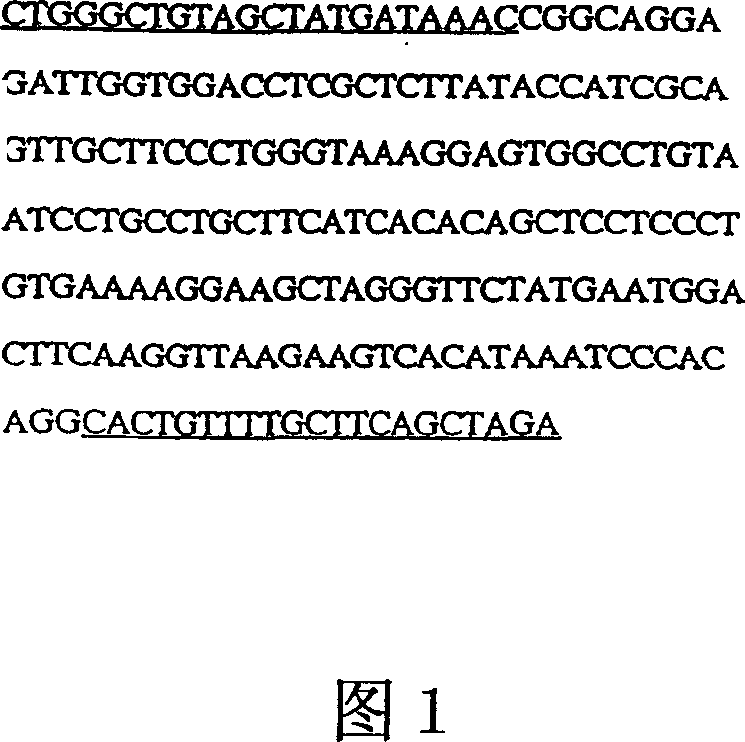
[0165] Cloning of human α-Gal cDNA from a human fibroblast cDNA library was constructed...
Embodiment 2
[0205] Cells were subjected to stepwise methotrexate (MTX) selection. After selection in 0.05 [mu]M MTX, one cell was cloned and subjected to 0.1 [mu]M MTX selection. A pool of cells resistant to 0.1 μMMTX was isolated by this procedure, expanded by culture, and characterized. Example 2. α-Gal A purification
[0206] The following are preferred methods for producing, purifying, and testing α-Gal A. During the purification process, α-Gal A is maintained in a soluble, active, native form. During purification, the protein is not exposed to extremes of pH, organic solvents, or detergents, does not undergo proteolytic cleavage, and does not form aggregates. The purification process was designed not to alter the distribution of α-Gal A glycoforms.
[0207] 2. Purification of 1α-Gal A
[0208] Example 2.1 exemplifies that α-Gal A can be purified to almost homogeneity from the conditioned medium of a human cell line that has been stably transfected to produce the enzyme. From th...
Embodiment 3
[0252] A few cultured human cell lines are known to express the mannose receptor. However, a murine macrophage-like cell line (J774.E) that carries mannose receptors but little, if any, M6P receptors, can be used to determine whether the purified α-Gal A of the present invention is internalized via mannose receptors . Diment et al., J. Leukocyte Biol. 42:485-490, (1987). J774.E cells were cultured overnight in the presence of 10,000 U / mL α-Gal A. Selected samples also contained 2 mM M6P, while others contained 100 mg / mL mannose. Cells were washed and harvested as described above, and each sample was assayed for total protein and [alpha]-Gal A activity. M6P did not inhibit α-Gal A uptake by these cells, whereas mannose reduced α-Gal A accumulation levels by 75%. Thus, in cell types expressing this particular cell surface receptor, [alpha]-Gal A of the present invention can be internalized by the mannose receptor. Example 3. Pharmaceutical formulations
[0253] Preparation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com