Automatic power control in uncoordinated frequency-hopping radio systems
A technology of power control and transmission power control, which is applied in the direction of transmission control/equalization, power management, transmission system, etc., and can solve problems such as unstable power adjustment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
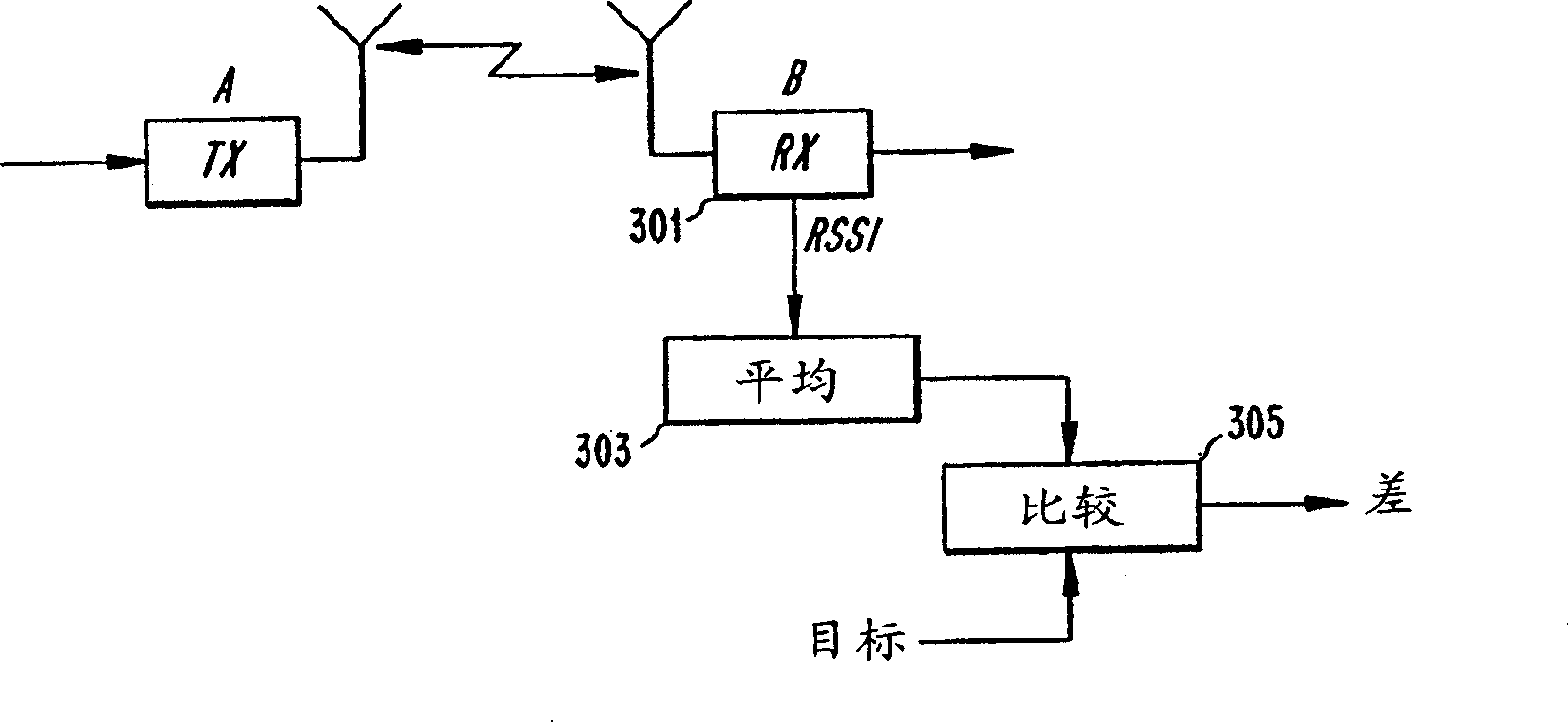
[0030] The various features of the invention will now be described with reference to the drawings, in which like parts are identified by like reference characters.
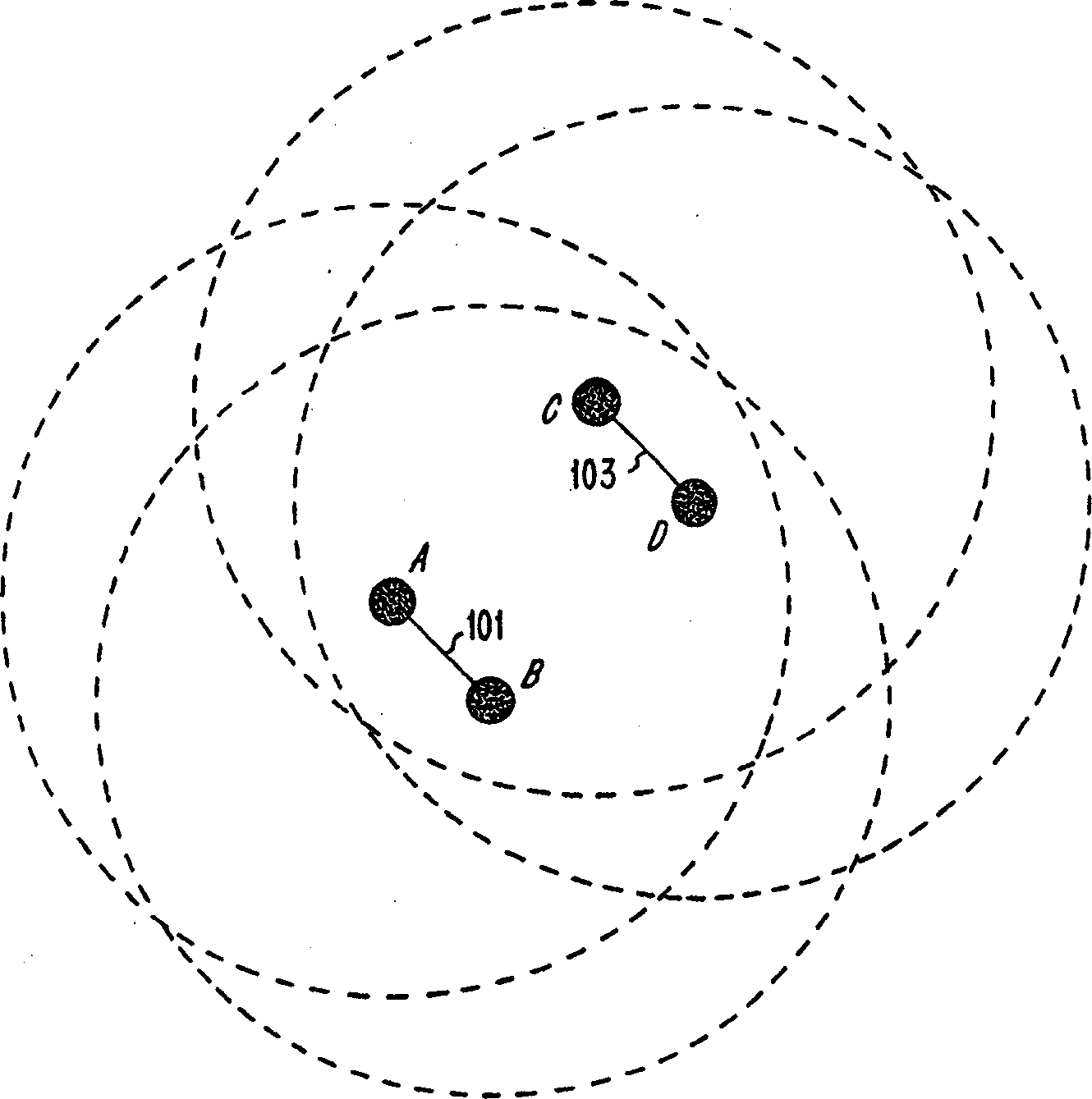
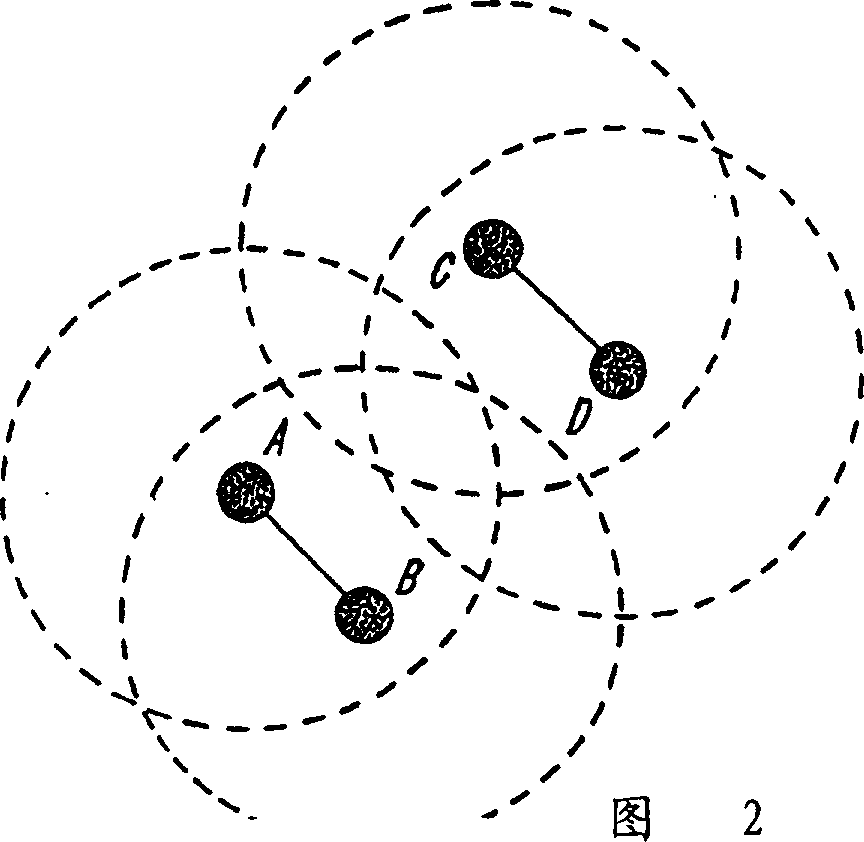
[0031] figure 1Two independent frequency hopping (FH) radio links 101 and 103 are illustrated that are closely spaced from each other. Exemplary applications employing these links are described in U.S. Patent Application Nos. 08 / 932911 (Haartsen), filed September 17, 1997, and U.S. Patent Application Nos. 08 / 932,244, filed September 17, 1997 (Haartsen). system, the contents of these two patent applications are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety. The coverage area of each radio unit is illustrated with a dotted circle. Units A and B communicate according to one FH scheme, and units C and D communicate according to another FH scheme. The two radio links 101 and 103 are not coordinated and occasionally use the same frequency hopping channel. In this case, depending on the relative distance betwe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com