Constant-tension buffering mechanism based on hinge zero-stiffness spring
A cushioning mechanism and zero-stiffness technology, applied in springs/shock absorbers, low internal friction springs, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in adjustment, poor zero-stiffness characteristics, and weak load-carrying capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
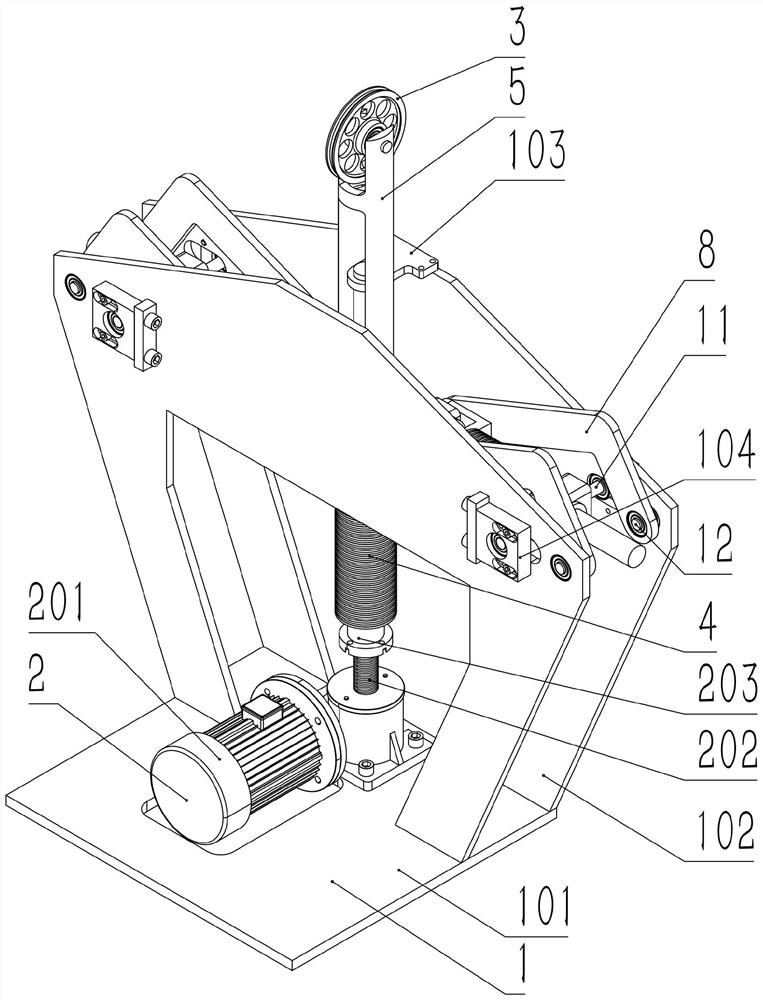
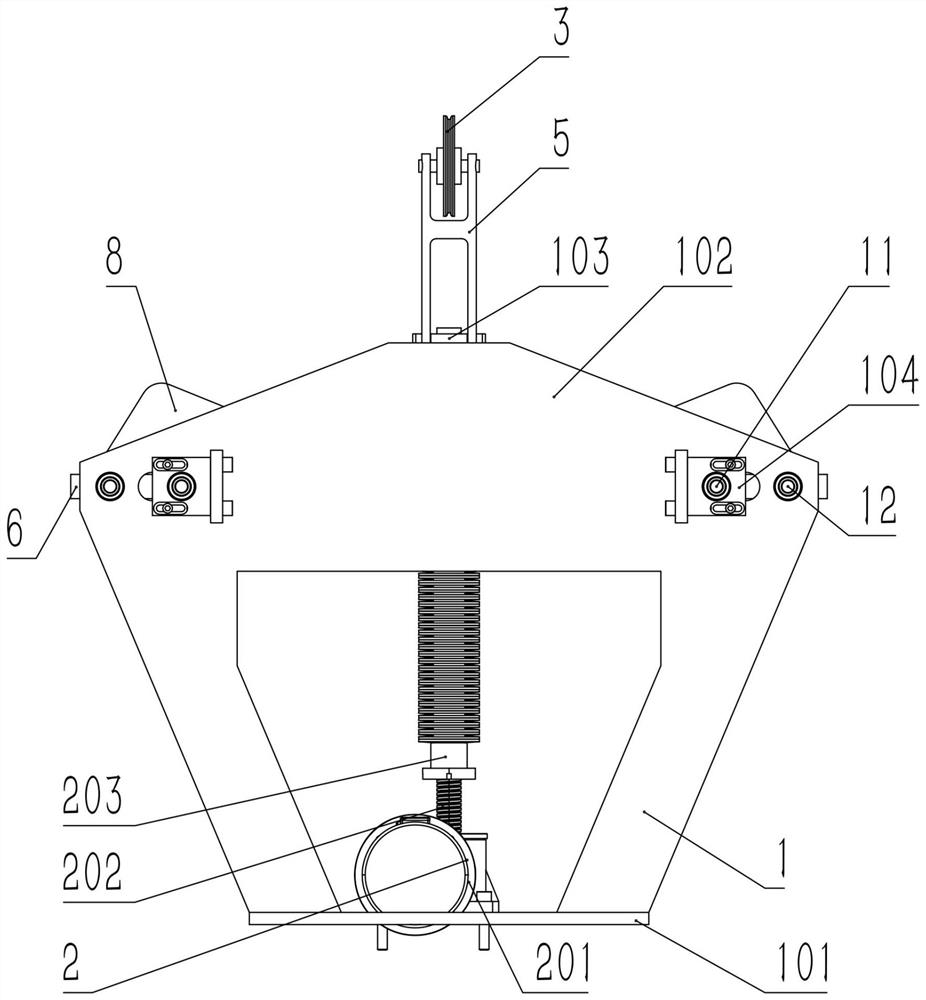
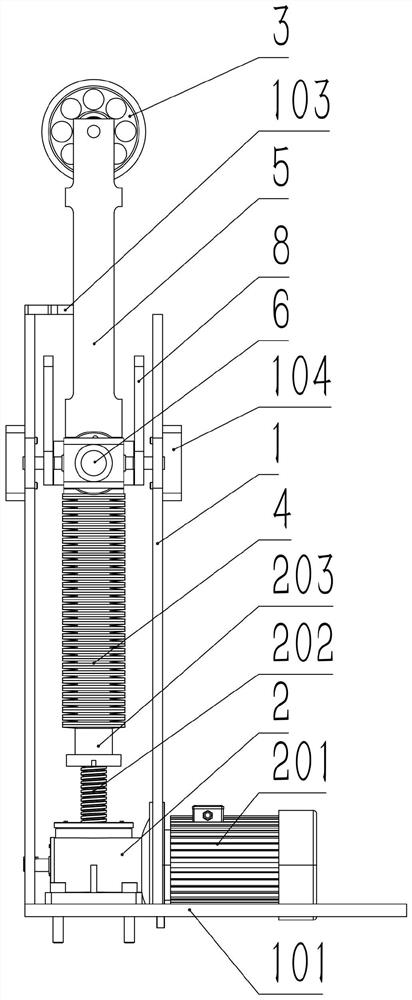
[0056] In further embodiments of the present invention, such as Figure 14 The formula for calculating the total stiffness of the hinge zero stiffness spring is:
[0057]
[0058] Among them, the lateral buffer mechanism is arranged symmetrically on the left and right, the following data is described with a single component of the lateral buffer mechanism on either side, K is the total stiffness of the hinge zero stiffness spring, and α is the connecting rod 8 relative to the horizontal equilibrium position. The angle of rotation of the second rotating shaft 12, θ is the angle at which the second shaft portion 6 rotates around the first rotating shaft 11 relative to the horizontal balance position, C is the center distance between the second rotating shaft 12 and the third rotating shaft 10, and L is the first rotating shaft 11 and the center distance between the third rotating shaft 10, A is the displacement of the vibration support 5 relative to the horizontal equilibrium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com