Equivalent circuit-based steady-state modeling method for power spring-containing power distribution network
An equivalent circuit model, power spring technology, applied in circuit devices, AC network circuits, CAD circuit design, etc., can solve difficult problems to ensure the efficiency and convergence of the solution, and it is difficult to analyze and analyze the power spring's effect on power distribution. network influence and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving the solution speed and efficiency, improving the voltage, and reducing the complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
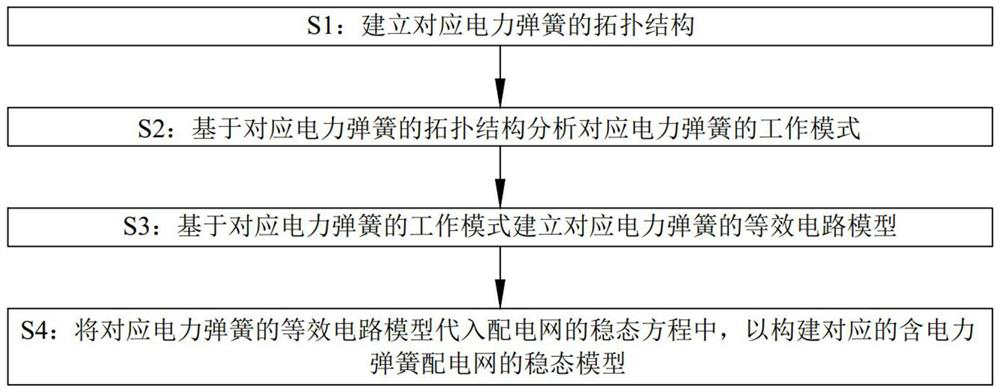
[0051] This embodiment discloses a steady-state modeling method for a distribution network with power springs based on an equivalent circuit.
[0052] like figure 1 As shown in the figure, a steady-state modeling method for a distribution network with power springs based on an equivalent circuit includes the following steps:
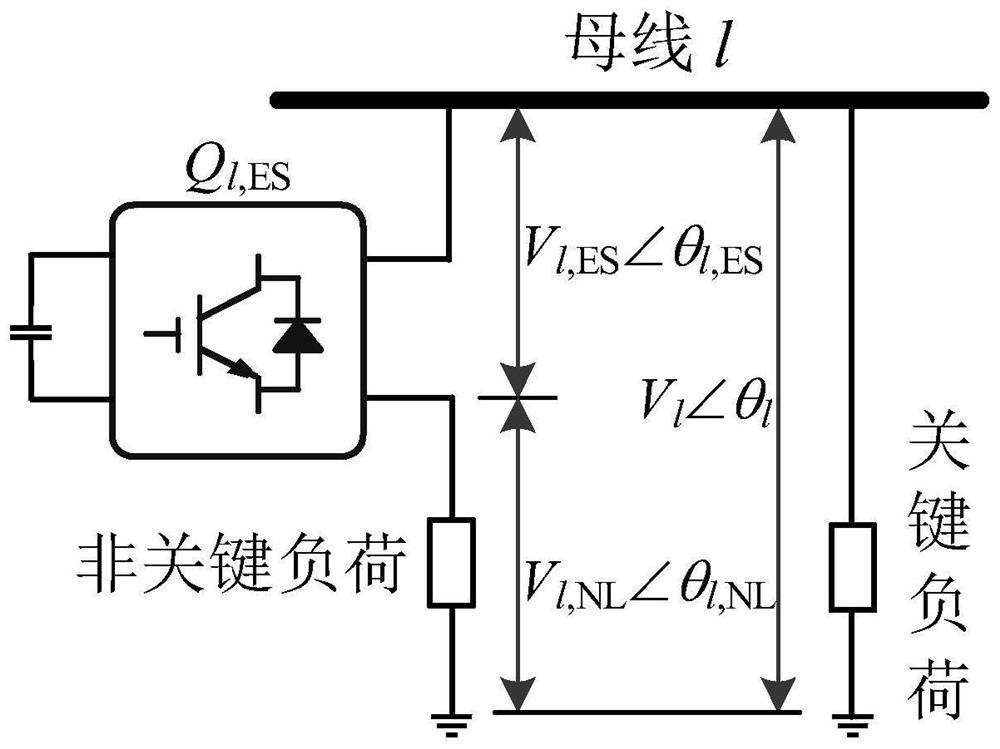
[0053] S1: Establish the topology structure corresponding to the power spring;
[0054] S2: Analyze the working mode of the corresponding power spring based on the topological structure of the corresponding power spring;
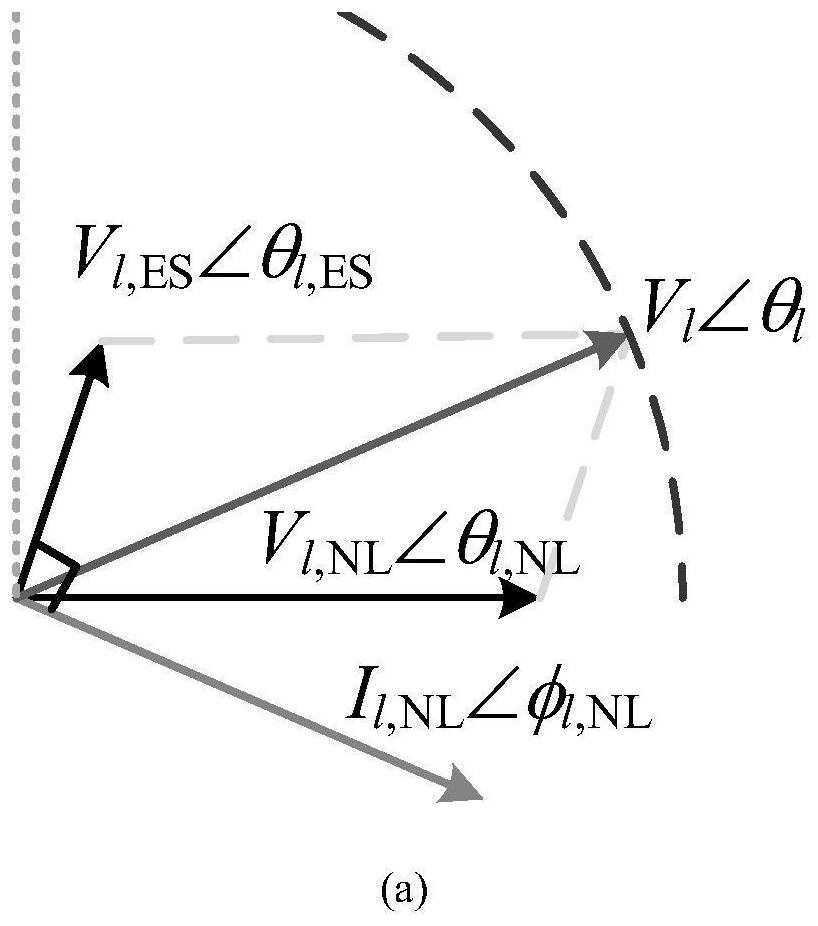
[0055] S3: Establish an equivalent circuit model of the corresponding power spring based on the working mode of the corresponding power spring;
[0056] S4: Substitute the equivalent circuit model of the corresponding power spring into the steady-state equation of the distribution network to construct the corresponding steady-state model of the distribution network with the power spring.
[0057] The present invention analyzes its w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com