Early warning method for paralytic saxitoxin in bivalve mollusks
A shellfish toxin, bivalve mollusk technology, applied in the direction of instruments, measuring devices, scientific instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to realize easy-to-operate, economical, sensitive, accurate and efficient early monitoring and early warning, and achieve economical and economical toxin extraction. , rapid detection, easy operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Example 1: Establish a method
[0018] Early warning methods for paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve shellfish include the following steps:
[0019] 1) Feeding 40 bivalve shellfish under laboratory detoxification conditions for one week;
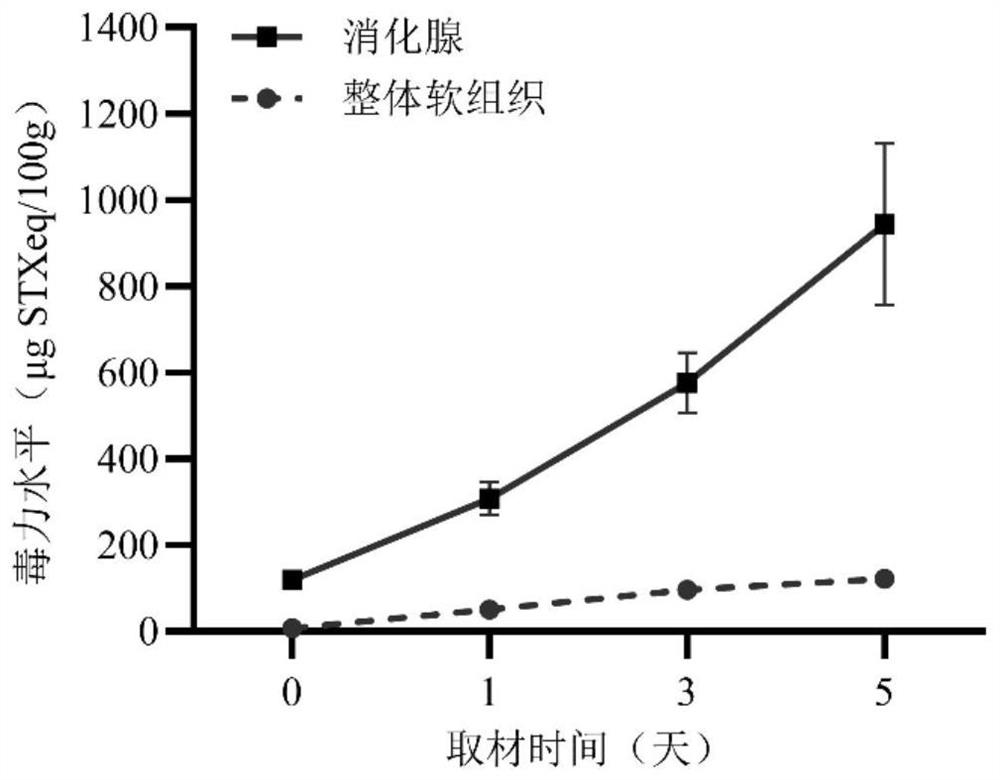
[0020] 2) The poisonous algae producing paralytic shellfish toxin were fed continuously for 5 days at the same concentration every day, and 10 were sampled at 4 different time periods on the 0th day, 1 day, 3 days and 5 days. Store the digestive glands separate from the remaining tissue at -20 °C when sampling;
[0021] 3) Add 0.1% of the formic acid solution homogenization to the tissues obtained in step 2) according to the ratio of 1:2 (tissue weight / g: reagent / mL), after 24 h of maceration at 4 °C, centrifuge at 12000 r / min for 10 min and aspirate the supernatant.
[0022] 4) Add the supernatant obtained in step 3) to the pre-activated well Purification is performed in the HLB solid phase extraction column.
[0023] 5) The purified li...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Ezo scallops are detected as samples
[0031] Taking Ezo scallops as an example, the detection is carried out according to the method of Example 1.
[0032] 1. Feed 40 Ezo scallops for one week under laboratory detoxification conditions;
[0033] 2. Ezo scallops were continuously fed at a daily concentration of 3000 cell / mL with paralyzing shellfish toxin-producing algae for 5 days, and 10 scallops were sampled on the 0th, 1st, 3rd and 5th days of feeding, respectively. Store the digestive glands separate from the remaining tissue at -20 °C when sampling;
[0034] 3. Add 0.1% of the formic acid solution to the sample tissue obtained in step 2 according to the ratio of 1:2 (tissue weight / g: reagent / mL), homogenize with a tissue homogenizer, and extract the supernatant after 24h at 4 °C, centrifuge at 12000 revolutions for 10 min.
[0035]4. Add the supernatant obtained in step 3 to activate it with 6mL methanol and 6mL of water in advance Purification is performe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com