[0003] Through long-term operation practice, due to the
erosion of
water flow, the damage of
dead wood leaves and
humus carried by
water flow, the concrete hard slope protection structure generally has problems such as
weathering,
honeycomb pitting, and structural damage. The color of the slope surface gradually changes from white gray to black, black gray, The durability of the hard slope protection structure is gradually reduced, and the slope surface of the hard slope protection also presents a
large range of irregularly shaped and irregularly distributed black patches, which is not only detrimental to the overall safety of the embankment, but also destroys the overall natural green landscape of the embankment, especially in urban areas. A section of embankment, with irregularly distributed black patches, seems to be pasted in patches on the green corridor of the Yangtze River
bank, destroying the scenic beauty of the
urban area along the river; As a result, plants cannot grow on the slope, aquatic animals lose their
habitat space, and the original ecological function of the embankment is destroyed; , to protect the green ecological corridor of the Yangtze River, it is necessary to carry out ecological restoration of the hard slope protection of the built dikes
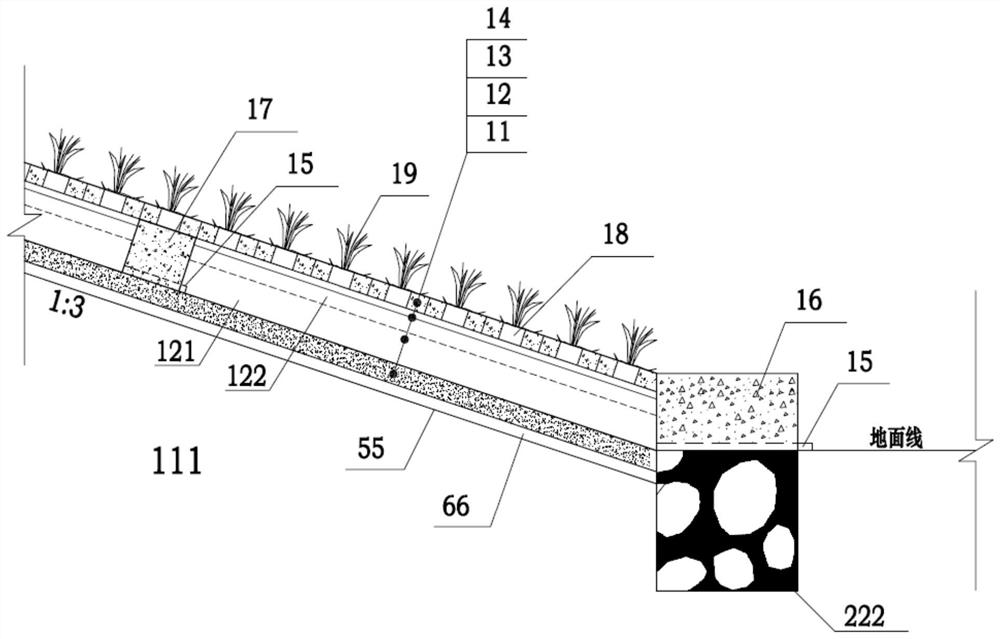
[0004] According to the existing conventional technical measures, the hard slope protection with blackened surface or structural damage is directly removed and then the new slope protection is re-laid. This kind of scheme has the following problems: (1) According to the completed drawings of the embankment reinforcement, the main dike of the Yangtze River has been filled for many years. The embankment 111 is mainly filled with silty
loam, the height of the embankment is about 6-8m, and the slope of the water facing surface is 19-25m long. Under the hard slope protection, there is often a "sandstone
cushion 66 + slope composite
geomembrane 55" or "Gravel
cushion 66+
geotextile 55 (150~200g / m 2 )”, the
geomembrane (cloth) 55 is pressed and fixed with masonry 222 at the crest and foot of the embankment. Regardless of manual or mechanical demolition of the hard slope protection, the sand and gravel
cushion under the slope protection concrete will inevitably be destroyed during construction.
Geomembrane (cloth) and earth embankment, etc., not only have low construction efficiency, time-consuming and laborious, but also cause major hidden dangers to embankment safety; (2) Even if a lot of time, manpower and
material resources are invested to remove the hard slope protection, due to the hard slope protection after
weathering The structural strength is low and cannot be reused. It can only be piled on the river beach and then transferred to the landfill, which increases the production and construction costs and the
workload of on-site coordination, which is not conducive to the protection of the local
ecological environment. The slope protection will form about 2860m 3 (Songfang)
construction waste; (3) Large-scale demolition of existing hard slope protection and replacement of new slope protection will cause potential safety hazards to the embankment anti-seepage
system during construction
The advantages of this kind of scheme are mechanized operation, high construction efficiency, rapid establishment of
vegetation, and better ecological affinity; its disadvantages and shortcomings are: (1) The
structural stability is poor after long-term immersion in water, and the ability to
resist water erosion is poor (2) The effects of
plant spraying and rock ecological regreening are greatly affected by human factors; (3) The thickness of the entire slope
protection layer is relatively thin (10cm thick), and there are steel
wire mesh and anchors, which is not convenient for embankment managers. Walking uphill is not conducive to embankment inspection work during the
flood season; (4) According to market surveys, the cost of the 10cm thick
vegetation concrete scheme is relatively high (the cost of 10cm thick
vegetation concrete is 160-190 yuan / m 2 ); (5) These two schemes are often used for ecological restoration of rock slopes that will not be soaked in water for a long time (such as road slopes), and there is no application case for rock slopes that need to retain water for a long time
The advantages of this solution are: the ecological bag has the functions of water and
soil conservation, small size, and convenient for construction; its disadvantages and shortcomings are: (1) It is difficult to accurately control the weight and placement shape of each ecological bag on site, and the
structural integrity is relatively low Poor; (2) Bags are mainly connected by connecting buckles, and the overall stability of the structure comes from its own gravity and connecting buckles. Under long-term
water immersion and washing, the
structural stability is poor; (3) Ecological bags are Made of non-
woven fabric, it is easy to be damaged during the construction process, and it is difficult to repair the bag after it is damaged during the later operation and management; (4) This scheme is suitable for rocky slopes that do not need to pass water, where the flow rate is slow or the
water level changes. Ecological restoration of slopes in small river sections
[0008] To sum up, on the premise of not destroying the integrity of the hard slope protection of the built embankment, "directly demolish the existing slope protection and lay a new slope protection", "slope protection with alien soil spraying and planting plants", "vegetation concrete slope protection", "ecological bag slope protection" None of these schemes can take into account the protection of the anti-seepage
system of the built embankment, the durability and stability of the slope protection structure, the resistance to
water erosion, the ecological characteristics, the convenience of construction, and the convenience of daily inspections by the dike management department, etc., and are not suitable for the ecological restoration of the hard slope protection of the Yangtze River dry embankment; Consolidate the safety of the built embankment structure, ecologically restore the hard slope protection of the embankment, and protect the green ecological corridor of the Yangtze River. For this reason, it is urgent to develop an ecological slope protection and its construction method that does not destroy the integrity of the hard slope protection of the built embankment
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More