Silage additive as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of silage and additives, which is applied to the preservation method of animal feed raw materials, the molding or processing of animal feed, bacteria used in food preparation, etc., can solve the problems of nutrient reduction, energy loss of silage, long storage time, etc. Achieve the effects of promoting animal growth and development, improving animal immunity, and short-term rapid fermentation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The preparation method of silage additive comprises the following steps:
[0028] Step 1. Weigh the following raw materials in parts by mass: 60 parts of fermentation raw materials; 30 parts of microbial mixed strains; 10 parts of calcium carbonate; 0.9 parts of pH regulator, set aside;
[0029] The mixed microbial strain is composed of the following bacteria powder by weight percentage: 12% of lactic acid bacteria; 20% of EM bacteria; 15% of Lactobacillus acidophilus; 5% of Enterococcus faecalis; 37% of Saccharomyces cerevisiae; ; Trichosporium dermatosa yeast 5%;
[0030] The pH regulator is selected from food grade disodium hydrogen phosphate and food grade sodium dihydrogen phosphate;
[0031] Step 2, steam sterilize the fermented raw materials. The steam sterilized conditions are: the pressure is 103.4kPa, sterilized at 121.3°C for 15 minutes to obtain the sterilized raw materials; the fermented raw materials include concentrated feed and roughage, and the two Th...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The preparation method of silage additive comprises the following steps:
[0035] Step 1. Weigh the following raw materials in parts by mass: 55 parts of fermentation raw materials; 20 parts of microbial mixed strains; 6 parts of calcium carbonate; 0.4 parts of pH regulator, set aside;
[0036] The microbial mixed strain is made up of the bacteria powder of following percentage by weight: 12% of lactic acid bacteria; 18% of EM bacteria; 22% of Lactobacillus acidophilus; 6% of Enterococcus faecalis; 28% of Saccharomyces cerevisiae; ; Trichosporium dermatitis 7%;
[0037] The pH regulator is selected from acetic acid and food grade sodium acetate;
[0038] Step 2, steam sterilize the fermented raw materials. The steam sterilized conditions are as follows: the pressure is 103.4kPa, sterilized at 121.3°C for 20 minutes to obtain the sterilized raw materials; the fermented raw materials include concentrated feed and roughage, and the two The mass ratio is 2.5:7.5;
[0039...
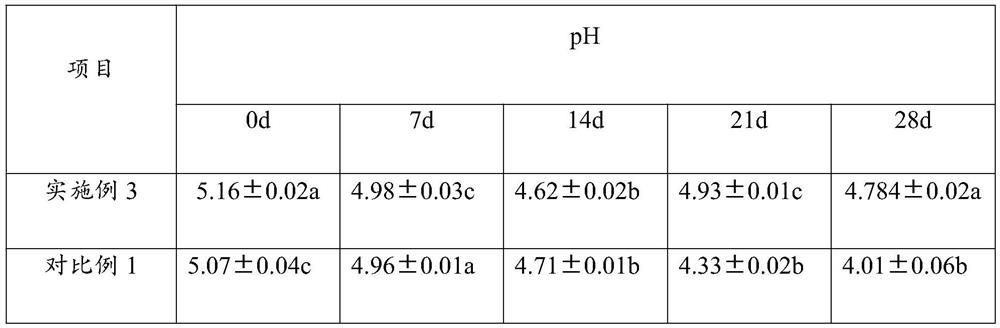
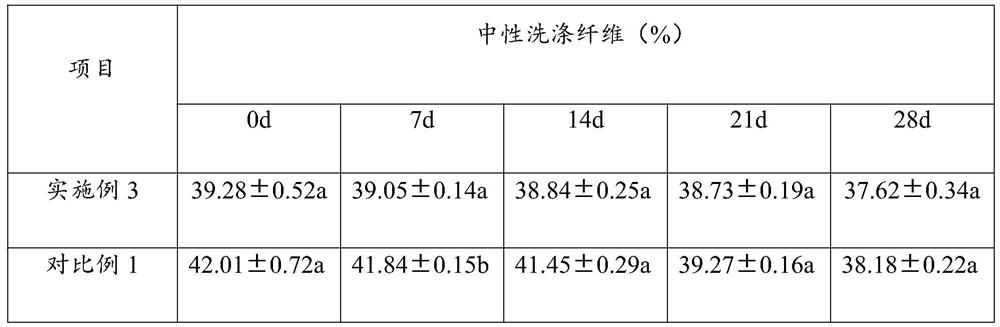
Embodiment 3
[0041] The preparation method of silage additive comprises the following steps:
[0042] Step 1. Weigh the following raw materials in parts by mass: 70 parts of fermentation raw materials; 25 parts of microbial mixed strains; 5 parts of calcium carbonate; 0.7 parts of pH regulator, set aside;
[0043]The microbial mixed strain is made up of the bacterial powder of following percentage by weight: 13% of lactic acid bacteria; 17% of EM bacteria; 20% of Lactobacillus acidophilus; 5% of Enterococcus faecalis; 29% of Saccharomyces cerevisiae; ; Trichosporium dermatitis 8%;
[0044] The pH regulator is selected from food grade disodium hydrogen phosphate and food grade sodium dihydrogen phosphate;
[0045] Step 2, steam sterilize the fermented raw materials. The steam sterilized conditions are as follows: the pressure is 103.4kPa, sterilized at 121.3°C for 18 minutes to obtain the sterilized raw materials; the fermented raw materials include concentrated feed and roughage, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com