Method for improving extraction of spider silk proteins
A spider silk protein and western blotting technology, applied in the field of improving the extraction of spider silk proteins, can solve the problems of low solid or fiber toughness, poor hand feeling, and poor yield, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0159] Embodiment 1: Calcium salt extraction
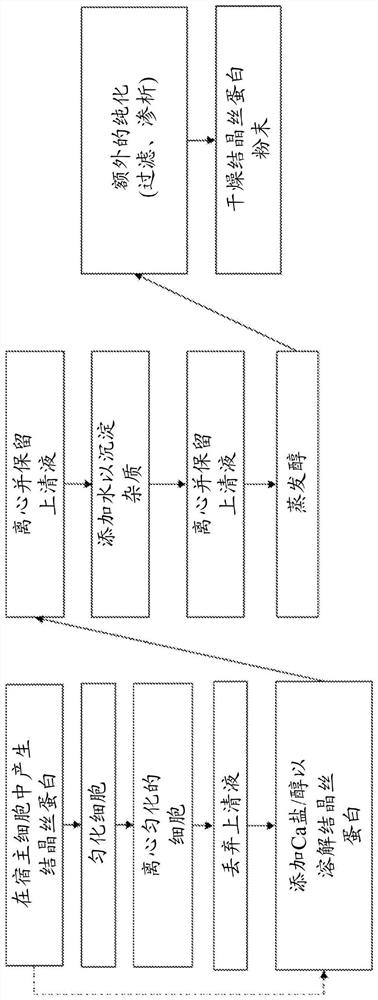
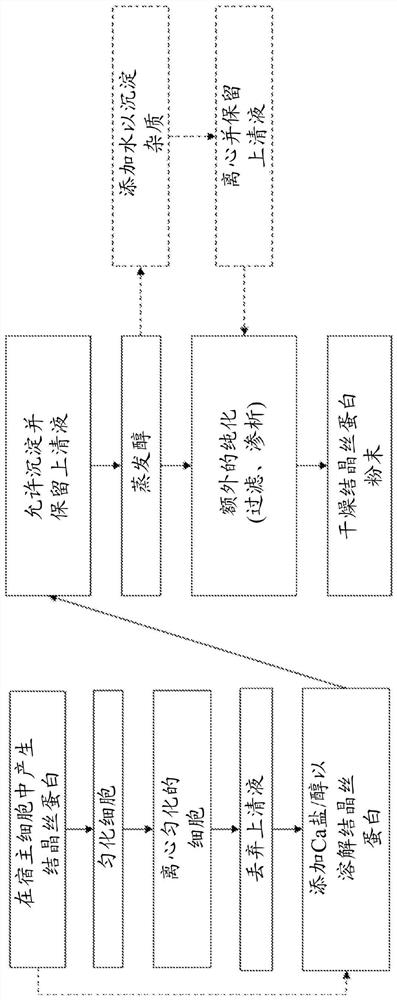
[0160] Highly crystalline silk forms aggregates in solution, leading to reduced solubility and thus reduced recovery from host cells during production. Therefore, there is a need for improved methods of dissolving such crystalline silk. The method described in these examples is the use of calcium salts and alcohols to increase the solubility of silk proteins.
[0161] Materials and methods
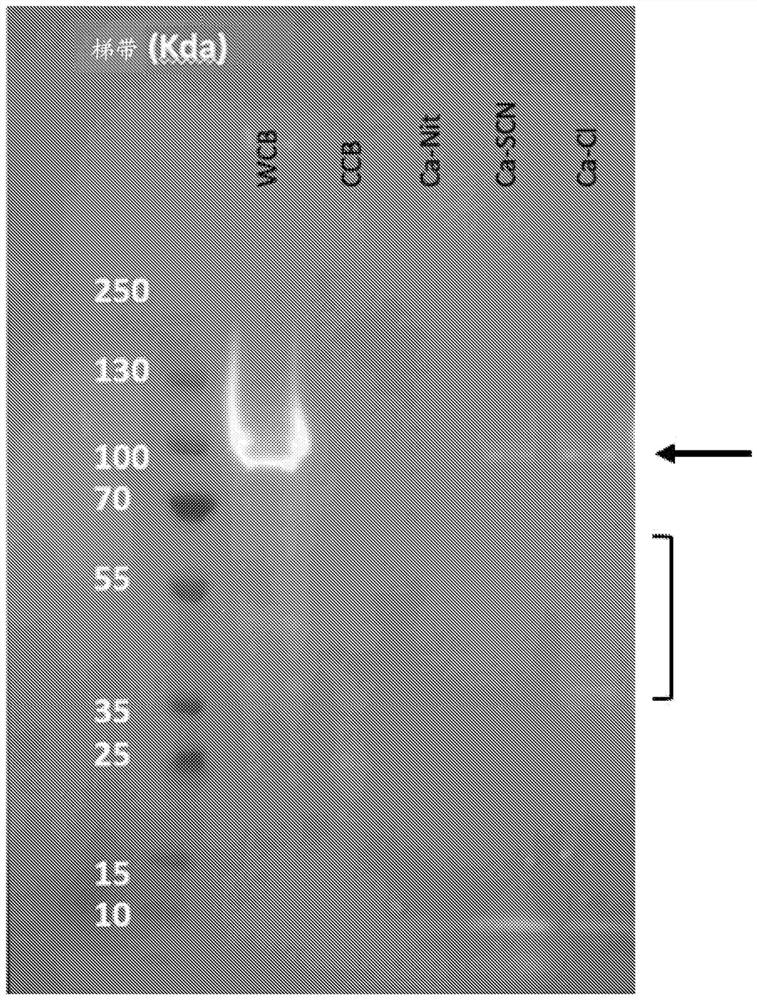
[0162] The UDMisp64k protein (also referred to as P0 (representative block amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 23)) was extracted using various calcium salts to identify optimal calcium salts. P0 is an exemplary highly crystalline silk protein. Escherichia coli was transformed with an expression vector containing a P0 silk gene fused to a 6x His tag (six histidines (GGGGG-HHHHHH) attached to the c-terminus of P0 with a glycine linker) in the presence of chloramphenicol. Broth (Terrific Broth, defined basal salt medium) growth. After 2...
Embodiment 2
[0166] Embodiment 2: alcohol extraction
[0167] Alcohol selection was investigated to determine optimal extraction conditions. First, mix insoluble P0 with CaCl 2 Incubate together in water or in methanol to determine if alcohol solvent needs to be included. Next, substitute ethanol and isopropanol as the main solvents. Finally, water was introduced as a solvent along with methanol to reduce the volatility of the process.
[0168] Materials and methods
[0169] P0 was expressed in E. coli cells as described in Example 1. Cells were lysed using a Microfluidic Nanohomogenizer, and insoluble material was pelleted via centrifugation. As shown in Table 4, CaCl in different solvents were prepared 2 solutions with different concentrations.
[0170]
[0171] 100 mg of insoluble cellular material was added to 1 ml of each solution and resuspended via pipetting. Samples in solution conditions 1-6 were incubated for 1 hour at room temperature (approximately 22°C). Parallel s...
Embodiment 3
[0181] Example 3: Incubation time and temperature
[0182] The extraction temperature was varied to determine the optimum temperature to achieve maximum extraction while minimizing extraction time. Agitation of the samples was also introduced. Lowering the temperature along with continuous mixing was investigated as a more scalable process option.
[0183] Materials and methods
[0184] P0 was expressed in E. coli cells as described in Example 1. Cells were lysed using a Microfluidic Nanohomogenizer, and insoluble material was pelleted via centrifugation. 1 ml of 2M CaCl in methanol 2 The solution was added to 100 mg of insoluble cell material, which was resuspended via pipetting. Twelve aliquots were prepared. Six aliquots were incubated with stirring at 35°C for 0, 15, 30, 60, 120 and 240 min. The remaining 6 aliquots were incubated with agitation at 55°C for 0, 5, 15, 30, 60 and 120 min. At each time point, samples were removed and centrifuged at 15,000 x g in a tab...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com