Myxococcus flavus large-fragment knockout plasmid and knockout method thereof
A large fragment and plasmid technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of high screening intensity, long mutant purification time, restricting the application of DK1622, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The Myxococcus flavum DK1622 strain involved in the present invention is a model strain.
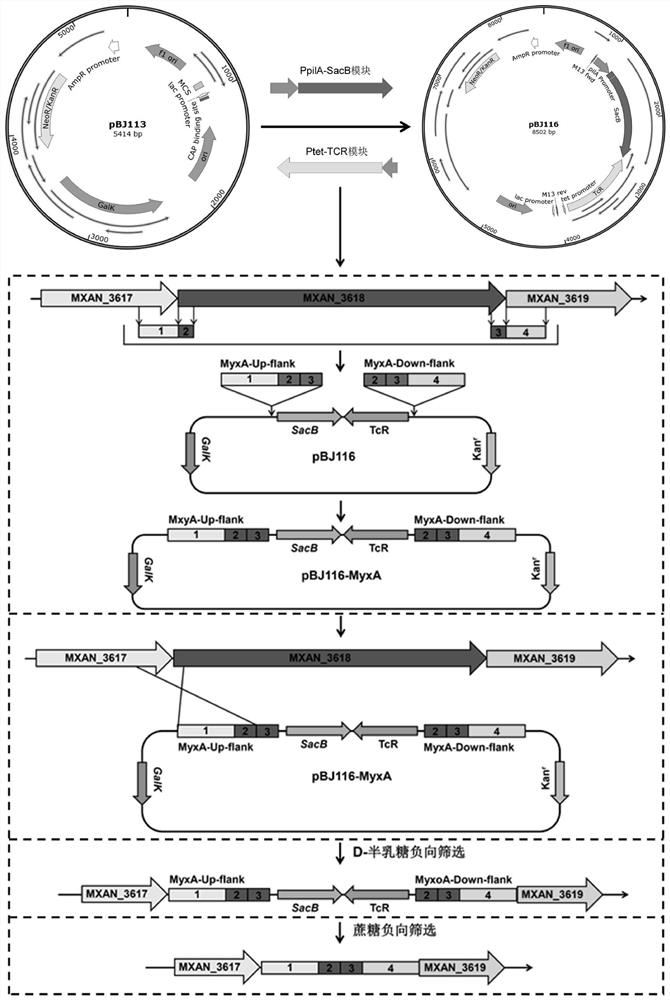
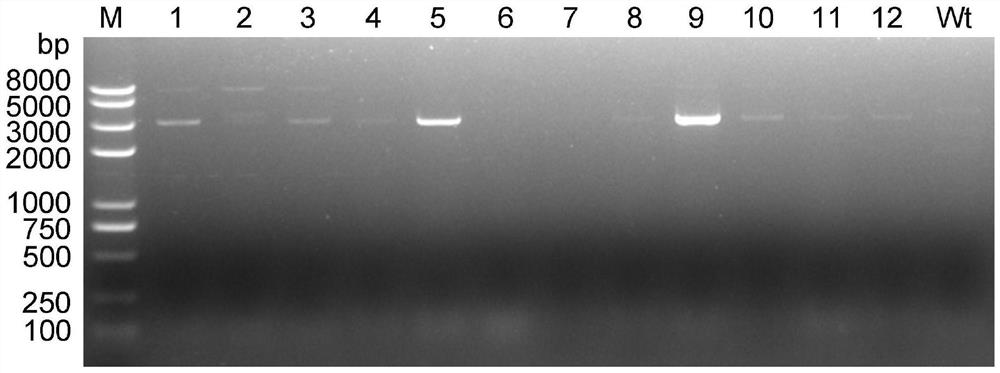
[0027] This example provides a method for constructing a large fragment knockout of Myxococcus xanthus, first of all, transforming the pBJ113 suicide vector. Using the genome of Myxococcus xanthus DK1622 as a template, primers pilA-1 and pilA-2 were used to amplify the promoter fragment P of pilA gene pilA (Its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1); With pJQ200SK plasmid as template, utilize primer SacB-1 and SacB-2 to amplify the ORF fragment of sacB gene (its nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 shown); the promoter fragment P of the pilA gene pilA There is a 20bp homologous sequence at the 3' end of the sacB gene and the 5' end of the ORF fragment of the pilA gene, and the promoter fragment P of the pilA gene pilA The ORF fragment of the sacB gene was used as a template, and PCR amplification was performed using pilA-1 and SacB-2 primers to obtain the ORF fus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com